Abstract
Background
This prospective observational study aimed to identify the predictors of intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) insertion in patients undergoing elective coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and to formulate a scoring system to categorize the patients to low-, moderate-, and high-risk groups.
Patients and methods
Of the consecutive patients, 105 were enrolled for elective CABG. Pre-operative evaluation consisted of history, examination, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and coronary angiogram. IABP was inserted either intra- or post-operatively depending on indications laid down in the study. Various pre-, intra-, and post-operative data were analyzed and the patients were followed up till their discharge from the hospital.
Results
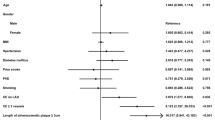
The mean age of the study population was 59.1 ± 8.9 years. The risk factors for IABP requirement were NYHA class III/IV angina (p = 0.019, CI 1.18–11.89), family history of hypertension (p = 0.025, CI 1.09–18.12), pre-operative serum creatine kinase myocardial isozyme ≥30 U/L (p = 0.008, CI 1.37–10.43), cardiomegaly (p = 0.002) and pleural effusion (0.014), abnormal rhythm and ST-T changes (p = 0.011), left ventricular ejection fraction <50% (p = 0.001, CI 2.50–17.60), non-usage of arterial grafts (p = 0.002, CI 1.70–13.91), transfusion requirement ≥1500 mL (p = 0.003, CI 1.51–9.80), and intra-operative defibrillation (p = 0.014). Six deaths were reported in the study (5.7%), and the mortality was significantly higher in the IABP group (n = 5, 19.2%) as compared to the non-IABP group (n = 1, 1.26%). A scoring system was formulated based on four risk factors identified by the multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Conclusions
We conclude that patients with higher risk scores (derived from risk factors identified in the study) are more likely to require IABP which may be instituted at an early phase to avoid late cardiac decompensation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao V, Ivanov J, Weisel RD, Ikonomidis JS, Christakis GT, David TE. Predictors of low cardiac output syndrome after coronary artery bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996;112:38–51.
Diez C, Silber R-E, Wächner M, Stiller M, Hofmann H-S. EuroSCORE directed intraaortic balloon pump placement in high-risk patients undergoing cardiac surgery—retrospective analysis of 267 patients. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2008;7:389–95.
Parsonnet V, Dean D, Bernstein AD. A method of uniform stratification of risk for evaluating the results of surgery in acquired adult heart disease. Circulation. 1989;79:I3–12.
Dunning J, Au JKK, Millner RWJ, Levine AJ. Derivation and validation of a clinical scoring system to predict the need for an intra-aortic balloon pump in patients undergoing adult cardiac surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2003;2:639–43.
Miceli A, Duggan SMJ, Capoun R, Romeo F, Caputo M, Angelini GD. A clinical score to predict the need for intraaortic balloon pump in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90:522–6.
Christenson JT, Simonet F, Badel P, Schmuziger M. Evaluation of preoperative intra-aortic balloon pump support in high risk coronary patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1997;11:1097–103.
Okonta K, Kanagarajan N, Anbarasu M. Intra aortic balloon pump in coronary artery bypass graft—factors affecting outcome. J West Afr Coll Surg. 2011;1:28–40.
Miceli A, Fiorani B, Danesi TH, Melina G, Sinatra R. Prophylactic intra-aortic balloon pump in high-risk patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: a propensity score analysis. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009;9:291–4.
Ding W, Ji Q, Wei Q, Shi Y, Ma R, Wang C. Prophylactic application of an intra-aortic balloon pump in high-risk patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. Cardiology. 2015;131:109–15.
Parissis H, Leotsinidis M, Akbar MT, Apostolakis E, Dougenis D. The need for intra aortic balloon pump support following open heart surgery: risk analysis and outcome. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010;5:20.
Theologou T, Field ML. Preoperative IABP in high risk patients undergoing CABG. HSR Proc Intensive Care Cardiovasc Anesth. 2011;3:21–2.
Baskett RJF, Ghali WA, Maitland A, Hirsch GM. The intraaortic balloon pump in cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;74:1276–87.
Saeed D, El-Banayosy A, Kizner L, et al. Predictors of survival in patients requiring IABP support following cardiac surgery. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;54:V_70.
Bedi HS, Sohal CS, Sengar BS. Elective preoperative use of intra aortic balloon counterpulsation in high risk group of coronary artery disease patients to facilitate off pump surgery. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;23:128–34.
Miceli A, Capoun R, Fino C, et al. Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy on clinical outcome in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:1778–84.
Ouzounian M, Buth KJ, Valeeva L, Morton CC, Hassan A, Ali IS. Impact of preoperative angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor use on clinical outcomes after cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:559–64.
Tuman KJ, McCarthy RJ, O’Connor CJ, Holm WE, Ivankovich AD. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors increase vasoconstrictor requirements after cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth Analg. 1995;80:473–9.
Carrel T, Englberger L, Mohacsi P, Neidhart P, Schmidli J. Low systemic vascular resistance after cardiopulmonary bypass: incidence, etiology, and clinical importance. J Card Surg. 2000;15:347–53.
Arora P, Rajagopalam S, Ranjan R, et al. Preoperative use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers is associated with increased risk for acute kidney injury after cardiovascular surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:1266–73.
Riaz W, Shahbaz A, Sami W, Khan JS. Early vascular complications of intraaortic balloon counterpulsation in patients undergoing open heart surgery. J Ayub Med Coll. 2008;20:80–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was duly approved by the Institute Ethics Committee.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was taken from all the study participants before enrolling them for the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
We all the authors declare that we did not receive any funding from any source for conducting this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, M.K., Das, A., Hote, M.P. et al. Predictors of intra-aortic balloon pump insertion in different spectrum of patients undergoing elective coronary artery bypass grafting. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 33, 296–302 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-017-0577-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-017-0577-z