Abstract
Introduction and objective
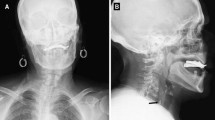
Foreign body getting lodged in esophagus is quite common, commonly due to ingestion of coin, pin, fish bone and meat. But accidental ingestion of artificial denture is a less often found condition. This paper studies the etiology, management, complications and final outcome of denture obstructing the esophagus.
Material and methods
Fourteen patients with denture esophagus were reviewed retrospectively, admitted between Jan 2012 to Oct 2016. The clinical presentations, cause of the denture ingestion, radiological findings, surgical intervention, complication and final outcome were studied. Most common site of impaction is crico pharynx junction. Denture was removed by cervical incision in all cases. Post-operatively ryles tube was kept routinely in all patients and gastrograffin swallow was performed. After mandatory follow up of one year, patients were followed as and when needed.
Results
All the patients presented with complaint of difficulty in swallowing. Five of them also had pain in neck and fever. Cause of denture ingestion was found to be very old denture, fitted by quacks, which they did not change for years. Hence they get loose and accidentally got ingested during sleeping or with the meal. Intra-operatively posterior esophageal wall ruptured in 3 cases for which repair was performed. All patients had severe periesophagitis. Post-operatively 3 patients developed esophagocutaneous fistula. Post-operative stricture was not seen in any case.
Conclusion
Early surgical intervention is must to prevent complications. Sharp metallic wires in esophagus prevent their endoscopic removal. They should be regularly changed, before they get loose. Denture implants should be done by qualified dentists only.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsieh CH, Wang YC, Chen RJ, et al. Comparison of the clinical presentations of ingested foreign bodies requiring operative and nonoperative management. Int Surg. 2005;90:99–102.
Haghighi M, Shoaei SD. Pharyngeal aspiration of complete upper denture in 90-year-old man; a case report. Emergency. 2015;3:117–9.
Huoh KC, Yung KC. Retained denture in oropharynx. Otolaryngology. 2012;2:121–2.
Nwaorgu OG, Onakoya PA, Sogebi OA, Daniel D, Kokong DD, Dosumu OO. Esophageal impacted dentures. J Natl Med Assoc. 2004;96:1350–3.
Agrawal D, Lahiri TK, Parmar A, Sharma S. Swallowed partial dentures. Indian J Dent Sci. 2012;4:7–12.
Mishra A, Shukla GK, Mishra SC, Bhatia N, Agarwal SP. The problems of denture impaction. Ind J Otolaryngology Head Neck Surg. 1996;48:241–4.
Zarb GA, Bolender CL, Carlsson GE. Boucher's prosthodontic treatment for edentulous patients. 11th ed. St Louis: Mosby; 1997. p. 337–42.
Akinpelu OV, Amusa YB, Eziyi JA, Haastrup AA, Ameye SA. Oesophageal denture impaction producing Horner's syndrome: a case report. J Laryngol Otol. 2007;121:e17.
Singh RK, Varshney S, Bist SS, Gupta N. An iatrogenic esophageal perforation with dentures: how does it happen? Int J Head Neck Surg. 2008;2:78.
DeRuiter MH, van Damme PA, Drenth JP. Serious complications following removal of an ingested partial denture. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2007;151:194–7.
Goh YH, Tan NG. Radiological features of unusual ingested foreign bodies. Singap Med J. 2001;42:129–30.
Newton JP, Abel RW, Lloyd CH, Yemm R. The use of computed tomography in the detection of radiolucent denture base material in the chest. J Oral Rehabil. 1987;14:193–202.
Tihan D, Trabulus D, Altunkay A, Karaca S, Cihan A, Alis H. Esophageal perforation due to inadvertent swallowing of a dental prosthesis. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2011;22:529–33.
Yeoh NT. Impacted dentures in the oesophagus. Med J Malaysia. 1982;37:344–8.
Abdullah BJ, Teong LK, Mahadevan J, Jalaludin A. Dental prosthesis ingested and impacted in the esophagus and orolaryngopharynx. J Otolaryngol. 1998;27:190–4.
Adedeji TO, Olaosun AO, Sogebi OA, Tobih JE. Denture impaction in the oesophagus experience of a young ENT practice in Nigeria. Pan Afr Med J. 2014;18:330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakhotia, S., Das, N.N. Surgical outcome of impacted artificial denture in esophagus. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 33, 225–228 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-017-0532-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-017-0532-z