Abstract
Background
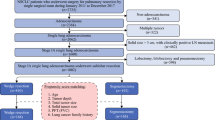
The aims of this study were to compare recurrence rate and recurrence-free survival following wedge resection and segmentectomy in stage IA non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and to validate the impact of the type of limited resection, according to tumor size, and surgical margin.
Methods
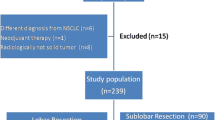
Anatomical segmentectomy was performed in 89 and wedge resection in 149 clinical stage IA NSCLC patients. Forty-four (29.5 %) patients in the wedge resection group and 12 (13.5 %) patients in the segmentectomy group were selected for sublobar resection because of high-risk status. The outcomes included type of recurrence and survival time. The surgical margin was measured retrospectively, and the margin/tumor size ratio (M/S ratio) was calculated.
Results
Forty-two of 149 (28.2 %) wedge resection patients and 13 of 89 (14.6 %) segmentectomy patients experienced recurrence during the follow-up period. The locoregional recurrence rate in the wedge resection group was significantly higher than in the segmentectomy group (p = 0.028). A multivariate analysis showed that wedge resection (p = 0.0437), a high percentage of solid tumor (p = 0.0399), and a low M/S ratio (p = 0.0003) were significant independent factors associated with decreased recurrence-free survival. For tumors 1.4 cm in size or greater, segmentectomy was associated with a longer recurrence-free survival. Recurrence-free survival after segmentectomy among patients with an M/S ratio greater than 1 was favorable.
Conclusions
The M/S ratio should be obtained when limited resection is considered for stage IA NSCLC. Segmentectomy with lymphadenectomy should be preferred for patients with tumor size greater than 1.4 cm.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ginsberg RJ, Rubinstein LV. Randomized trial of lobectomy versus limited resection for T1N0 non-small cell lung cancer Lung Cancer Study Group. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995;60:615–22.
Scott WJ, Howington J, Feigenberg S, Movsas B, Pisters K. American College of Chest Physicians. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer stage I and stage II: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest. 2007; 132: 234S–42S.
Sienel W, Dango S, Kirschbaum A, et al. Sublobar resections in stage IA non-small cell lung cancer: segmentectomies result in significantly better cancer-related survival than wedge resections. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;33:728–34.
El-sherif A, Fernando HC, Santos R, et al. Margin and local recurrence after sublobar resection of non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:2400–5.
Jensik RJ, Faber LP, Milloy FJ, Monson DO. Segmental resection for lung cancer. A fifteen-year experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973;66:563–72.
Schuchert MJ, Pettiford BL, Keeley S, et al. Anatomic segmentectomy in the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84:926–33.
Martini N, Bains MS, Burt ME, et al. Incidence of local recurrence and second primary tumors in resected stage I lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995;109:120–9.
Suzuki K, Koike T, Asakawa T, et al. A prospective radiological study of thin-section computed tomography to predict pathological noninvasiveness in peripheral clinical IA lung cancer (Japan Clinical Oncology Group 0201). J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:751–6.
Koike T, Yamato Y, Yoshiya K, Shimoyama T, Suzuki R. Intentional limited pulmonary resection for peripheral T1N0M0 small-sized lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;125:924–8.
Whitson BA, Groth SS, Andrade RS, Maddaus MA, Habermann EB, D’Cunha J. Survival after lobectomy versus segmentectomy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a population based analysis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92:1943–50.
Landreneau RJ, Sugarbaker DJ, Mack MJ, et al. Wedge resection versus lobectomy for stage I (T1 N0 M0) non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997;113:691–8.
Okada M, Koike T, Higashiyama M, Yamato Y, Kodama K, Tsubota N. Radical sublobar resection for small-sized non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;132:769–75.
Fernando HC, Santos R, Benfield JR, et al. Lobar and sublobar resection with and without brachytherapy for small stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129:261–7.
Martin-Ucar AE, Nakas A, Pilling JE, West KJ, Waller DA. A case-matched study of anatomical segmentectomy versus lobectomy for stage I lung cancer in high-risk patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005;27:675–9.
Ketchedjian A, Daly B, Landreneau R, Fernando H. Sublobar resection for the subcentimeter pulmonary nodule. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;17:128–33.
Okada M, Nishio W, Sakamoto T, et al. Effect of tumor size on prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: the role of segmentectomy as a type of lesser resection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129:87–93.
Okami J, Ito Y, Higashiyama M, et al. Sublobar resection provides an equivalent survival after lobectomy in elderly patients with early lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90:1651–7.
El-Sherif A, Gooding WE, Santos R, et al. Outcomes of sublobar resection versus lobectomy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a 13-year analysis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82:408–16.
Sienel W, Stremmel C, Kirschbaum A, Hinterberger L, Stoelben E, Hasse J, et al. Frequency of local recurrence following segmentectomy of stage IA non-small cell lung cancer is influenced by segment localization and width of resection margins—implications for patient selection for segmentectomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007;31:522–7.
Houssami N, Macaskill P, Marinovich ML, Morrow M. The association of surgical margins and local recurrence in women with early-stage invasive breast cancer treated with breast-conserving therapy: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:717–30.
Mohiuddin K, Haneuse S, Sofer T, et al. Relationship between margin distance and local recurrence among patients undergoing wedge resection for small non- small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:1169–75.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
MaT, MuT, SY and DS analyzed and interpreted the patient data. MaT performed the literature review and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. IM performed the final editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamura, M., Matsumoto, I., Takata, M. et al. Sublobar resections in stage IA non-small cell lung cancer: segmentectomy versus wedge resection. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 30, 264–271 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-014-0317-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-014-0317-6