Abstract
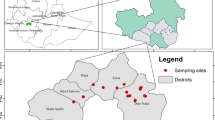
To ensure the safe and sustainable use of water, it is crucial to assess the quality of the groundwater. Utilizing the water quality index (WQI), an attempt has been made to understand the groundwater quality in three Talukas of the Sindhudurg District of Maharashtra State. The groundwater samples were collected from 37 observation wells located in study area in post-monsoon season. The overall groundwater quality of study area was assessed using the water quality index (WQI). Spatial distribution maps of pH, turbidity, TDS, hardness, alkalinity, Na, K, Fe, Zn, Cl, Ca, Cl− and NO3 have been prepared using the Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) approach using QGIS 3.22.1 software. The water samples in the study region have been categorized from excellent to good, according to the water quality index map. Vengurla and Vadakhol have water quality index ratings of 25 and 26.23, respectively indicating the maximum value of the water quality index in the study area. The elevated levels of total dissolved solids (TDS), sodium, iron, zinc and turbidity in groundwater can indeed contribute to a high-water quality index value at monitoring stations and it indicates over-exploitation and anthropogenic activities such as more agricultural and domestic uses. The higher values of chlorine, total dissolved solids, turbidity and hardness indicate the contamination of groundwater due to seawater intrusion near these stations.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dohare D, Deshpande S and Kotiya A 2014 Analysis of ground water quality parameters: A review. Res. J. Eng. Sci. 3(5): 2278–2472
Jinwal A and Dixit S 2008 Pre and post-monsoon variation in physico-chemical characteristics in groundwater quality of Bhopal The City of Lakes India. Asian J. Exp. Sci. 22(3): 311–316
Mitra B K, Sasaki C and Keijirou E 2013 Spatial and temporal variation of ground water quality in Sand Dune Area of Aomori Prefecture in Japan. Eng. Geol. Environ. 3(1): 2–12
Vasanthavigar M, Srinivasamoorthy K, Vijayaragavan K, Rajiv Ganthi R, Chidambaram S and Anandhan P 2010 Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 171(4): 595–609
Chatterjee R, Tarafder G and Paul S 2010 Groundwater quality assessment of Dhanbad district, Jharkhand, India. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 69(1): 137–141
Chachadi A G, Carcomo J P, Ferreira L and Choudri B S 2016 Assessing the impact of sea-level rise on salt water intrusion in coastal aquifers using GALDIT model. Forest fires impact on groundwater View project MARSOL. Demonstrating Managed Aquifer Recharge as a Solution to Water Scarcity. 32-43
Idowu T E and Lasisi K H 2020 Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of East and Horn of Africa: A review from a regional perspective. Sci. African 8: 395–402
Milovanovic M 2007 Water quality assessment and determination of pollution sources along the Axios/Vardar River, Southeastern Europe. Desalination 213(3): 159–173
Simeonov V, Stratis J A, Samara C, Zachariadis G, Voutsa D, Anthemidis A, Sofoniou M and Kouimtzis T 2003 Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res. 37(17): 4119–4124
Prusty P and Farooq S H 2020 Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of India—A review. HydroResearch 3: 61–74
Kumar D and Ahmed S 2003 Seasonal behaviour of spatial variability of groundwater level in a granitic aquifer in monsoon climate. Curr. Sci. 84(2): 188–196
Sundar M L and Saseetharan M K 2008 Ground water quality in coimbatore, Tamil Nadu along Noyyal river. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 50(3): 187–190
Isawi H, El-Sayed M H, Eissa M, Shouakar-Stash O, Shawky H and Abdel Mottaleb M S 2016 Integrated geochemistry, isotopes, and geostatistical techniques to investigate groundwater sources and salinization origin in the Sharm EL-Shiekh Area, South Sinia, Egypt. Water Air Soil Pollut. 227(5): 136–142
Stambuk Giljanovic N 1999 Water quality evaluation by index in Dalmatia. Water Res. 33(16): 3423–3440
Sundaray S K, Panda U C, Nayak B B and Bhatta D 2006 Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of the Mahanadi river-estuarine system (India)—A case study. Environ. Geochem. Health 28(4): 317–330
Rao G S and Nageswararao G 2013 Assessment of groundwater quality using water quality index. Arch. Environ. Sci. 7: 1–5
Edmunds W M, Carrillo-Rivera J J and Cardona A 2002 Geochemical evolution of groundwater beneath Mexico City. J. Hydrol. 258(4): 1–24
Verma P, Singh P K, Sinha R R and Tiwari A K 2020 Assessment of groundwater quality status by using water quality index (WQI) and geographic information system (GIS) approaches: A case study of the Bokaro district, India. Appl. Water Sci. 10(1): 1–16
Wunderlin D A, Maria Del Pilar D, Maria Valeria A, Cecilia H A, De Los Maria and Angeles B 2001 Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A Case Study: Suquia River basin (Cordoba-Argentina). Water Res. 35(12): 2881–2894
Rahman M M, Islam M A, Bodrud-Doza M, Muhib M I, Tareq S M and Kurasaki M 2018 Spatio-temporal assessment of groundwater quality and human health risk: A case study in Gopalganj, Bangladesh. Expo. Heal. 10(3): 167–188
Herschy R W 2012 Water quality for drinking: WHO guidelines. Encycl. Earth Sci. Ser. 876–883
BIS 2012 Indian Standard Drinking Water Specification (Second Revision) Bur. Indian Stand. IS 10500: 1–11
Majumdar D and Gupta N 2000 Nitrate pollution of groundwater and associated human health disorders. Indian J. Environ. Health 42(1): 28–39
Voutsa D, Samara C and Kouimtzis T 1994 Groundwater quality in the major industrial area of Thessaloniki, Greece part 2: Heavy metal distribution-source identification. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 45(2): 105–119
Vengadesan M and Lakshmanan E 2018 Management of coastal groundwater resources. Coast. Manag. 17: 383–397
Heejun Suk K L 1999 Characterization of a ground water hydrochemical system through multivariate analysis: Clustering into ground water zones. Groundwater NGWA 37(3): 358–366
Gulgundi M S and Shetty A 2018 Groundwater quality assessment of urban Bengaluru using multivariate statistical techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 8(1): 1–15
Praveen K and Roy L B 2022 Assessment of groundwater quality using water quality indices: A case study of Paliganj Distributary, Bihar, India. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 12(1): 8199–8203
Reza R and Singh G 2010 Assessment of ground water quality status by using water quality index method in Orissa, India. World Appl. Sci. J. 9(12): 1392–1397
Al Bassam B F 2009 Assessment of shallow groundwater quality in Zhengzhou area using remote sensing and GIS. J. Eng. Dev. 13(3): 72–86
Singh P and Khan I A 2011 Ground water quality assessment of Dhankawadi Ward of Pune by using GIS. Int. J. Geomatics Geosci. 2(2): 688–703
Asadi S S, Vuppala P and Reddy M A 2007 Remote sensing and GIS techniques for evaluation of groundwater quality in municipal corporation of Hyderabad (zone-V), India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 4(1): 45–52
Moharir K, Pande C, Singh S K, Choudhari P, Kishan R and Jeyakumar L 2019 Spatial interpolation approach-based appraisal of groundwater quality of arid regions. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 68(6): 431–447
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
KUSHE, V.P., MISHRA, S.S. & CHARHATE, S. Assessment of ground water quality parameters during post monsoon season in three Taluka of Sindhudurg district of Maharashtra using water quality index. Sādhanā 49, 171 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-024-02504-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-024-02504-0