Abstract
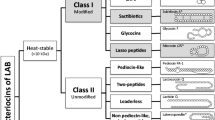
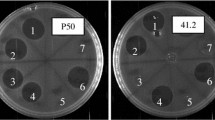
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) naturally inhibit the growth of other closely related bacteria by producing antimicrobial peptides called ‘bacteriocins’. Bacteriocins are heat stable, food-safe, and potently inhibit numerous food spoilage as well as pathogenic bacteria. Most importantly, bacteriocins are rapidly degraded by gastric enzymes, and there are no reports on the development of antimicrobial resistance to them by the pathogenic bacteria. These features have attracted the attention of researchers to study bacteriocins for their fundamental properties and possible applications as next-generation antimicrobial agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Suggested Reading
J Zheng, et al., A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae, International Journal of Systemic and Evolutionary Microbiology, Vol.70, PP.2782–2858, 2020.
R H Perez, T Zendo, K Sonomoto, Novel bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria (LAB): Various structures and applications, Microbial Cell Factories, Vol.13, PP.1–13, 2014.
M D López-Cuellar, A I Rodríguez-Hernández, N Chavarría-Hernández, LAB bacteriocin applications in the last decade, Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, Vol.30, PP.1039–1050, 2016.
L De Vuyst, F Leroy, Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Production, purification, and food applications, Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, Vol.13, PP.194–199, 2007.
S C Yang, C H Lin, C T Sung, J Y Fang, Antibacterial activities of bacteriocins: Application in foods and pharmaceuticals, Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol.5, PP.1–10, 2014.
D Beshkova, G Frengova, Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Microorganisms of potential biotechnological importance for the dairy industry, Engineering in Life Sciences, Vol.12, PP.419–432, 2012.
T Utsugi, et. al., Elevated expression of phosphatidylserine in the outer membrane leaflet of human tumor cells and recognition by activated human blood monocytes, Cancer Research, Vol.51, PP.3062–3066, 1991.
I Dobrzyńska, B Szachowicz-Petelska, S Sulkowski, Z Figaszewski, Changes in electric charge and phospholipids composition in human colorectal cancer cells, Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, Vol.276(1–2), PP.113–119, 2005.
M L Chikindas, et. al., Functions and emerging applications of bacteriocins, Current Opinion in Biotechnology, Vol.49, PP.23–28, 2018.
Acknowledgement
The academic activities related to antimicrobial resistance at the host institute are supported through ERASMUS+grant 598515-EPP-1-2018-1-IN-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Joyleen Fernandes is a project assistant at Symbiosis School of Biological Sciences, Pune. She is interested in molecular biology and microbiology.
Rohit Kumbhar was a student of M.Sc. Biotechnology Symbiosis School of Biological Sciences, Pune. He is interested in microbiology and bioprocess engineering.
Ram Kulkarni is an Associate Professor at Symbiosis International (Deemed University). He is interested in biochemical/molecular characterization of useful properties of lactic acid bacteria and their evolutionary and metabolic engineering.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, J., Kumbhar, R. & Kulkarni, R. Bacteriocins from Lactic Acid Bacteria. Reson 26, 387–398 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12045-021-1137-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12045-021-1137-9