Abstract
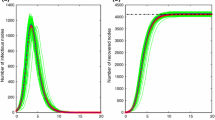
Although the interactions between traffic flow and epidemic spread dynamics have been extensively studied, the impact of routing strategies on the susceptible–infected–recovered (SIR) epidemic spread driven by traffic flow have not received enough attention. In this paper, the traffic-driven SIR epidemic spread model under the probability path routing strategy and the efficient path routing strategy are studied. The instantaneous scale \(I_{p}\) of the infected nodes’ density and the final scale \(R_{e}\) of the ever infected nodes’ density are obtained through simulation, and it is found that there exist optimal values of routing parameters to minimise \(I_{p}\) and \(R_{e}\), what is more, \(I_{p}\) and \(R_{e}\) under the probability path routing strategy are smaller than the values under the efficient path routing strategy. This means that the epidemic spreading can be effectively controlled by adjusting the routing strategy. In addition, when the routing parameter is the optimal value, the influence of packet generation rates, infection rates and cure rates on the epidemic spreading under different routing strategies is further discussed, and it is found that the higher the cure rate, the fewer nodes will be infected. Infected nodes’ density increases as the infection rate and packet generation rate increase, thereby accelerating epidemic spreading. These studies have certain guiding significance for controlling the spread of the epidemic.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
R Pastor-Satorras and A Vespignani, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3200 (2001)
M Barthélemy, A Barrat, R Pastor-Satorras and A Vespignani, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 178701 (2004)
R Pastor-Satorras and A Vespignani, Phys. Rev. E 65, 035108 (2002)
E Estrada, S Meloni, M Sheerin and Y Moreno, Phys. Rev. E 94, 052316 (2016)
G Yan, Z Q Fu, J Ren and W X Wang, Phys. Rev. E 75, 016108 (2007)
Z Ruan, M Tang and Z Liu, Phys. Rev. E 86, 036117 (2012)
M Boguná, C Castellano and R Pastor-Satorras, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 068701 (2013)
J L Ma, M Li and H J Li, IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II 69, 1697 (2021)
S Lamzabi, S Lazfi, A Rachadi, H Ez-Zahraouy and A Benyoussef, Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 27, 1650068 (2016)
R Pastor-Satorras, C Castellano, P Van Mieghem and A Vespignani, Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 925 (2015)
W O Kermack and A G McKendrick, Proc. R. Soc. London: Ser. A 115, 700 (1927)
D J Watts and S H Strogatz, Nature 393, 440 (1998)
A L Barabási and R Albert, Science 286, 509 (1999)
S Meloni and J Gómez-Gardeñes, Phys. Rev. E 82, 056105 (2010)
Y Wu, C Pu, L Li and G Zhang, Digit. Commun. Netw. 5, 56 (2019)
S Meloni, A Arenas and Y Moreno, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 16897 (2009)
S Meloni, N Perra, A Arenas, S Gomez, Y Moreno and A Vespignani, Sci. Rep. 1, 1 (2011)
H X Yang, W X Wang, Y C Lai and B H Wang, Europhys. Lett. 98, 68003 (2012)
H X Yang, W X Wang, Y C Lai, Y B Xie and B H Wang, Phys. Rev. E 84, 045101 (2011)
H X Yang and Z X Wu, J. Stat. Mech.-Theory Exp. 2014, P03018 (2014)
A Dwivedi, R Keval and S Khajanchi, Phys. Scr. 97(8), 085214 (2022)
S Ghosh, A Senapati, J Chattopadhyay, C Hens and D Ghosh, Chaos 31, 071101 (2021)
S Ghosh, A Senapati, A Mishra, J Chattopadhyay, S K Dana, C Hens and D Ghosh, Phys. Rev. E 104, 014308 (2021)
S P Ansari, S K Agrawal and S Das, Pramana – J. Phys. 84, 23 (2015)
F Nian and S Yao, Mod. Phys. Lett. B 31, 1750131 (2017)
S M Salman, Pramana – J. Phys. 92, 1 (2019)
L Zhu, X Wang, H Zhang, S Shen, Y Li and Y Zhou, Phys. Scr. 95, 035213 (2020)
H X Yang, Z X Wu and B H Wang, Phys. Rev. E 87, 064801 (2013)
M Barthelemy, A Barrat, R Pastor-Satorras and A Vespignani, J. Theor. Biol. 235, 275 (2005)
P Echenique, J Gómez-Gardeñes and Y Moreno, Phys. Rev. E 70, 056105 (2004)
W X Wang, B H Wang, C Y Yin, Y B Xie and T Zhou, Phys. Rev. E 73, 026111 (2006)
G Yan, T Zhou, B Hu, Z Q Fu and B H Wang, Phys. Rev. E 73, 046108 (2006)
M Tang, Z Liu, X Liang and P M Hui, Phys. Rev. E 80, 026114 (2009)
X Ling, M B Hu, R Jiang and Q S Wu, Phys. Rev. E 81, 016113 (2010)
R Yang, B H Wang, J Ren, W J Bai, Z W Shi, W X Wang and T Zhou, Phys. Lett. A 364, 189 (2007)
C Pu, S Li, X X Yang, Z Xu, Z Ji and J Yang, Physica A 446, 129 (2016)
P Bajardi, C Poletto, J J Ramasco, M Tizzoni, V Colizza and A Vespignani, PLoS ONE 6, e16591 (2011)
R Guimerà, A Díaz-Guilera and F Vega-Redondo, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 248701 (2002)
M E J Newman, Phys. Rev. E 64, 016132 (2001)
G Li, S D S Reis, A A Moreira, S Havlin, H E Stanley and J S Andrade Jr, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 018701 (2010)
X Zhang, Z He, Z He and L Rayman-Bacchus, Physica A 392, 953 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant No. F2022208002) and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department (Key Program) (Grant Nos ZD2021048 and ZD2022031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Ma, JL., Xiang, TT. et al. Traffic-driven epidemic spreading network dynamics with different routing strategies. Pramana - J Phys 97, 134 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-023-02616-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-023-02616-y