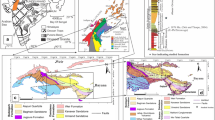
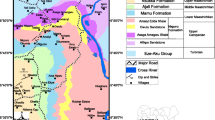
Abstract
The creation and obliteration of accommodation space are controlled primarily by the local changes in sea level. The sedimentation rate, on the other hand, played a pivotal role in determining the sequence stratigraphic trend during filling up of that accommodation space. The current study involving the two basal members of the Kundargi Formation, Bagalkot Group, Kaladgi Basin, provides an opportunity to highlight the importance of sedimentation rate in sequence building. Quantification of the actual sedimentation rate is beyond question in such a Proterozoic succession due to lack of accurate age data; however, their qualitative variations can be traced laterally across the basin. The study initiates with facies analysis that revealed four distinct facies associations, incorporating 25 facies. Three-dimensional facies variability suggests palaeogeographic realm shifted from fluvial to open marine shoreface, along depositional dip, through an intervening locally developed estuary. The shoreface assemblage gradually passes upwards into deeper water fines demarcating gradual deepening of the basin. Bounded between an unconformity and a transgressive lag, the fluvial interval represents a lowstand (LST) product. Study area, located near the paleoconfluence, received higher sedimentation, which resulted in progradation of the bay-head delta over estuarine fines during the ‘quasi-standstill’ period in-between two faster periods of relative sea-level rises. While the first episode of faster sea-level rise produced the estuary, the second one led to the submergence of the estuary and complete marine inundation of the entire area. However, away from the paleoconfluence, sediments, deposited during the quasi-standstill period, were eroded during the younger period of faster sea level rise leaving amalgamated bodies of beach conglomerates. Present study reveals spatial variability in the rate of net sedimentation played the pivotal role in shaping sequence architecture.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahokas J M, Nystuen J P and Martinius A W 2014 Stratigraphic signatures of punctuated rise in relative sea-level in an estuary-dominated heterolithic succession: Incised valley fills of the Toarcian Ostreaelv Formation, Neill Klinter Group (Jameson Land, East Greenland); Mar. Petrol. Geol. 50 103–129, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.11.001.
Aitken J F and Flint S S 1995 The application of high-resolution sequence stratigraphy to fluvial systems: A case study from the Upper Carboniferous Breathitt Group, eastern Kentucky, USA; Sedimentology 42 3–30, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1995.tb01268.x.
Allen J R L 1984 Sedimentary structures: Their character and physical basis; Elsevier, Amsterdam, 663p.
Allen J P and Fielding C R 2007 Sequence architecture within a low-accommodation setting: An example from the Permian of the Galilee and Bowen basins, Queensland, Australia; AAPG Bull. 90(11) 1503–1539, https://doi.org/10.1306/07020706131.
Allen G P and Posamentier H W 1993 Sequence stratigraphy and facies model of an incised valley fill: The Gironde Estuary, France; J. Sedim. Res. 63 378–391, https://doi.org/10.1306/D4267B09-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Archer A W and Feldman H R 1995 Incised valleys and estuarine facies of the Douglas Group (Virgilian) – implications for similar Pennsylvanian sequences in the U.S. Mid-Continent; In: Sequence stratigraphy of the mid-continent (ed.) Hyne N J, Tulsa Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 4 119–140.
Archer A W, Lanier W P and Feldman H R 1994 Stratigraphy and depositional history within incised-paleovalley fills and related facies, Douglas Group (Missourian/Virgilian; Upper Carboniferous) of Kansas, USA; In: Incised-valley systems: Origin and sedimentary sequences (eds) Dalrymple R W, Boyd R and Zaitlin B A, SEPM Spec. Publ. 51 353–368.
Best J L, Ashworth P J, Bristow C S and Roden J 2003 Three-dimensional sedimentary architecture of a large, mid-channel sand braid bar, Jamuna River, Bangladesh; J. Sedim. Res. 73(4) 516–530, https://doi.org/10.1306/010603730516.
Bhattacharya J P and Willis B J 2001 Lowstand deltas in the Frontier Formation, Powder River Basin, Wyoming: Implications for sequence stratigraphic models; AAPG Bull. 85(2) 261–294, https://doi.org/10.1306/8626C7B7-173B-11D7-8645000102C1865D.
Blatt H, Middleton G V and Murray R 1980 Origin of sedimentary rocks (2nd edn); Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersy, 782p.
Bose P K and Chanda S 1986 Storm deposits and Hummocky cross-stratification: A geological viewpoint; Quat. J. Geol. 58 53–68.
Bose P K and Das N G 1986 A transgressive storm- and fair-weather wave-dominated shelf sequence: Cretaceous Nimar Formation, Chakrud, Madhya Pradesh, India; Sedim. Geol. 46 147–167, https://doi.org/10.1016/0037-0738(86)90011-4.
Bose P K, Mazumder R and Sarkar S 1997 Tidal sandwaves and related storm deposits in the transgressive Protoproterozoic Chaibasa Formation, India; Precamb. Res. 84 63–81, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-9268(97)00016-8.
Bose P K, Sarkar S, Mukhopadhyay S, Saha B and Eriksson P G 2008 Precambrian basin-margin fan deposits: Mesoproterozoic Bagalkot Group, India; Precamb. Res. 162 264–283, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2007.07.022v.
Boyd R, Diessel C F K, Wadsworth J, Leckie D and Zaitlin B A 2000 Organization of non-marine stratigraphy; In: Advances in the study of the Sydney Basin (eds) Boyd R, Diessel C F K and Francis S, Proceedings of the 34th Newcastle Symposium, University of Newcastle, Callaghan, New South Wales, Australia, pp. 1–14.
Bridge J S 2003 Rivers and Floodplains; Wiley Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, 504p.
Cant D J and Walker R G 1978 Fluvial processes and facies sequences in the sandy braided South Saskatchewan River, Canada; Sedimentology 25 625–648, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1978.tb00323.x.
Catuneanu O 2003 Sequence stratigraphy of clastic systems; Geol. Assoc. Canada; Short Course Notes 16 248p.
Catuneanu O 2006 Principles of sequence stratigraphy; Elsevier, Amsterdam, 336p.
Catuneanu O 2019a Scale in sequence stratigraphy; Mar. Pet. Geol. 106 128–159, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.04.026.
Catuneanu O 2019b Model-independent sequence stratigraphy; Earth-Sci. Rev. 188 312–388, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.09.017.
Catuneanu O, Willis A J and Miall A D 1998 Temporal significance of sequence boundaries; Sediment. Geol. 121 157–178, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00084-0.
Catuneanu O, Sweet A R and Miall A D 1999 Concept and styles of reciprocal stratigraphies: Western Canada foreland system; Terra Nova 11(1) 1–8.
Catuneanu O, Hancox P J, Cairncross B and Rubidge B S 2002 Foredeep submarine fans and forebulge deltas: Orogenic off-loading in the underfilled Karoo Basin; J. Afr. Earth Sci. 35(4) 489–502, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-5362(02)00154-9.
Catuneanu O, Abreu V, Bhattacharya J P, Blum M D, Dalrymple R W, Eriksson P G, Fielding C R, Fisher W L, Galloway W E, Gibling M R, Giles K A, Holbrook J M, Jordan R, Kendall C G St C, Macurda B, Martinsen O J, Miall A D, Neal J E, Nummendal D, Pomar L, Posamentier H W, Pratt B R, Sarg J F, Shanley K W, Steel R J, Strasser A, Tucker M E and Winker C 2009 Towards the standardisation of sequence stratigraphy; Earth-Sci. Rev. 92(1–2) 1–33, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2008.10.003.
Catuneanu O, Bhattacharya J P, Blum M D, Dalrymple R W, Eriksson P G, Fielding C R, Fisher W L, Galloway W E, Gianolla P, Gibling M R, Giles K A, Holbrook J M, Jordan R, Kendall C G St C, Macurda B, Martinsen O J, Miall A D, Nummedal D, Posamentier H W, Pratt B R, Shanley K W, Steel R J, Strasser A and Tucker M E 2010 Sequence stratigraphy: Common ground after three decades of development; First Break 28 21–34, https://doi.org/10.3997/1365-2397.2010002.
Catuneanu O, Martins-Neto M A and Eriksson P G 2012 Sequence stratigraphic framework and application to the Precambrian; Mar. Pet. Geol. 33 26–33, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.10.002.
Chakrabarti A 2005 Sedimentary structures of tidal flats: A journey from coast to inner estuarine region of eastern India; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 114(3) 353–368, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702954.
Collinson J D 1996 Alluvial sediments; In: Sedimentary environments: Processes, facies and stratigraphy (3rd edn) (ed.) Reading H G, Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp. 37–82.
Collinson J D and Thompson D B 1989 Sedimentary structures (2nd edn); Unwin Hyman, London, 207p.
Colombera L and Mountney N P 2020 Accommodation and sediment-supply controls on clastic parasequences: A meta-analysis; Sedimentology 67 1667–1709, https://doi.org/10.1111/sed.12728.
Corbett D R, Dail M and McKee B 2007 High-frequency time-series of the dynamic sedimentation processes on the western shelf of the Mississippi River Delta; Cont. Shelf Res. 27 1600–1615.
Dalrymple R W and Rhodes R N 1995 Estuarine dunes and barforms; In: Geomorphology and sedimentology of estuaries (ed.) Perillo G M, Dev. Sedimentol. 53 359–422, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0070-4571(05)80033-0.
Dalrymple R W and Choi K S 2007 Morphologic and facies trends trough the fluvial marine transition in tide-dominated depositional systems: A schematic framework for environmental and sequence stratigraphic interpretation; Earth-Sci. Rev. 81 135–174, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.10.002.
Dalrymple R W, Knight J R, Zaitlin B A and Middleton G V 1990 Dynamics and facies model of a macrotidal sand-bar complex, Cobequid Bay-Salmon River Estuary (Bay of Fundy); Sedimentology 37 577–612, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1990.tb00624.x.
Dalrymple R W, Zaitlin B A and Boyd R 1992 Estuarine facies models: Conceptual basis and stratigraphic implications; J. Sedim. Petrol. 62 1130–1146, https://doi.org/10.1306/D4267A69-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
De Boer P L, Oost A P and Visser M J 1989 The diurnal inequality of the tide as a parameter for recognising tidal influence; J. Sedim. Petrol. 59 912–921, https://doi.org/10.1306/212F90B1-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Dey S 2015 Geological history of the Kaladgi–Badami and Bhima basins, south India: Sedimentation in a Proterozoic intracratonic setup; In: Precambrian basins of India – Stratigraphic and tectonic context (eds) Eriksson P G and Mazumder R, Geol. Soc. London Memoir 43(1) 283–296, https://doi.org/10.1144/M43.19.
Dey S, Rai A and Chaki A 2009 Palaeoweathering, composition and tectonics of provenance of the Proterozoic intracratonic Kaladgi–Badami basin, Karnataka, southern India: Evidence from sandstone petrography and geochemistry; J. Asian Earth Sci. 34(6) 703–715, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.003.
Eriksson P G, Bumby A J, Brümer J J and van der Neut M 2006 Precambrian fluvial deposits: Enigmatic palaeohydrological data from the c. 2–1.9 Ga Waterberg Group, South Africa; Sedim. Geol. 190(1–4) 25–46, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.05.003.
Eriksson P G, Condie K C, Tirsgaard H, Mueller W U, Altermann W, Miall A D, Aspler L B, Catuneanu O and Chiarenzelli J R 1998 Precambrian clastic sedimentation systems; Sedim. Geol. 120(1–4) 5–53, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00026-8.
Ethridge F G, Wood L J and Schumm S A 1998 Cyclic variables controlling fluvial sequence development: Problems and perspectives; In: Relative role of eustasy, climate and tectonism in continental rocks (eds) Shanley K W and McCabe P J, SEPM Spec. Publ. 59 17–29.
Fischbein S A, Joeckel R M and Fielding C R 2009 Fluvial–estuarine reinterpretation of large, isolated sandstone bodies in epicontinental cyclothems, Upper Pennsylvanian, northern Midcontinent, USA, and their significance for understanding late Paleozoic sea-level fluctuations; Sedim. Geol. 216(1–2) 15–28, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2009.01.009.
Gibling M R and Bird D J 1994 Late Carboniferous cyclothems and alluvial palaeovalleys in the Sydney Basin, Nova Scotia; GSA Bull. 106(1) 105–117, https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1994)106%3C0105:LCCAAP%3E2.3.CO;2.
Hadlari T, Rainbird R H and Donaldson J A 2006 Alluvial, eolian and lacustrine sedimentology of a Paleoproterozoic half-graben, Baker Lake Basin, Nunavut, Canada; Sedim. Geol. 190(1–4) 47–70, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.05.005.
Hallam A 1981 Facies interpretation and the stratigraphic record; W.H. Freeman, Oxford, 291p.
Harms J C and Fahnstock R K 1965 Stratification, bedforms and flow phenomena (with an example from the Rio Grande); In: Primary sedimentary structures and their hydrodynamic interpretation (ed.) Middleton G V, SEPM Spec. Publ. 12 84–115, https://doi.org/10.2110/pec.65.08.0084.
Harms J C, Southard J B, Spearing D R and Walker R G 1975 Depositional environments as interpreted from primary sedimentary structures and stratification sequences; SEPM Short Course 2 161, https://doi.org/10.2110/scn.75.02.
Heller P L and Paola C 1996 Downstream changes in alluvial architecture: An exploration of controls on channel-stacking patterns; J. Sedim. Res. 66(2) 297–305, https://doi.org/10.1306/D4268333-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Hill P R, Meule S and Longuepee H 2003 Combined-flow processes and sedimentary structures on the shore face of the wave-dominated Grande-riviere-de-la-Baleine delta; J. Sedim. Res. 73(2) 217–226, https://doi.org/10.1306/080802730217.
Holbrook J M 2001 Origin, genetic interrelationships, and stratigraphy over them continuum of fluvial channel-form bounding surfaces: An illustration from middle Cretaceous strata, southeastern Colorado; Sedim. Geol. 144(3–4) 202–246, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00118-X.
Holbrook J M, Scot R W and Oboh-Ikuenobe F E 2006 Base-level buffers and buttresses: A model for upstream versus downstream control on fluvial geometry and architecture within sequences; J. Sedim. Res. 76(1) 162–174, https://doi.org/10.2110/jsr.2005.10.
Holland T H 1907 Geology, Imperial Gazetteer of India; Government of India, Delhi 1 50–103.
Hunter R E 1973 Pseudo-cross lamination formed by climbing adhesion ripples; J. Sedim. Petrol. 43(4) 1125–1127.
Hunter R E 1977 Basic types of stratification in small eolian dunes; Sedimentology 24(3) 361–387, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1977.tb00128.x.
Hunter R E 1981 Stratification styles in eolian sandstones: Some Pennsylvanian to Jurassic examples from the Western Interior U.S.A.; In: Recent and ancient nonmarine depositional environments: Models for exploration (eds) Ethridge F G and Flores R M, SEPM Spec. Publ. 31 315–329.
Jayaprakash A V, Sundaram V, Hans S K and Mishra R N 1987 Geology of the Kaladgi–Badami Basin, Karnataka; In: Purana Basins of Peninsular India, Geol. Soc. India Memoir 6 201–225.
Jervey M T 1988 Quantitative geological modeling of siliciclastic rock sequences and their seismic expression; In: Sea level changes: An integrated approach (eds) Wilgus C K, Hastings B S, Kendall C G St C, Posamentier H W, Ross C A and Van Wagoner J, SEPM Spec. Publ. 42 47–69, https://doi.org/10.2110/pec.88.01.
Joeckel R M and Korus J T 2012 Bayhead delta interpretation of an Upper Pennsylvanian sheetlike sandbody and the broader understanding of transgressive deposits in cyclothems; Sedim. Geol. 275 22–37, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.07.002.
Johnson H D and Baldwin C T 1996 Shallow clastic seas; In: Sedimentary environments: Process, facies and stratigraphy (3rd edn) (ed.) Reading H G, Blackwell Science, Oxford (UK), pp. 232–280.
Kocurek G 1996 Desert aeolian systems; In: Sedimentary environments: Process, facies and stratigraphy (3rd edn) (ed.) Reading H G, Blackwell Science, Oxford (UK), pp. 125–153.
Kocurek G and Dott R H Jr 1981 Distinctions and uses of stratification types in the interpretation of eolian sands; J. Sedim. Petrol. 51(2) 579–595, https://doi.org/10.1306/212F7CE3-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Kocurek G and Feilder G 1982 Adhesion structures; J. Sedim. Petrol. 52(4) 1229–1241, https://doi.org/10.1306/212F8102-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Labourdette R and Jones R R 2007 Characterisation of fluvial architectural elements using a three-dimensional outcrop dataset: Escanilla braided system, South-Central Pyrenees, Spain; Geosphere 3(6) 422–434, https://doi.org/10.1130/GES00087.1.
Laming D J C 1966 Imbrications, palaeocurrents and other sedimentary features in the Lower New Red Sandstone, Devonshire, England; J. Sedim. Petrol. 36(4) 940–959, https://doi.org/10.1306/74D715C8-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Lanier W P, Feldman H R and Archer A W 1993 Tidal sedimentation from a fluvial to estuarine transition, Douglas Group, Missourian–Virgilian, Kansas; J. Sedim. Petrol. 63(5) 860–873, https://doi.org/10.1306/D4267C2B-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Leeder M R, Harris T and Kirkby J 1998 Sediment supply and climatic change: Implications for basin stratigraphy; Basin Res. 10 7–18.
Legarreta L and Uliana M A 1998 Anatomy of hinterland depositional sequences: Upper Cretaceous fluvial strata, Neuqurn Basin, West-Central Argentina; In: Relative role of eustasy, climate, and tectonism in continental rocks (eds) Shanley K W and McCabe P J, SEPM Spec. Publ. 9 83–92.
Legler B, Johnson H D, Hampson G J, Massart B Y G, Jackson C A L, Jackson M D, ElBarkooky A and Ravnas R 2013 Facies model of a fine-grained, tide-dominated delta: Lower Dir Abu Lifa Member (Eocene), Western Desert, Egypt; Sedimentology 60(5) 1313–1356, https://doi.org/10.1111/sed.12037.
Long D G F 2006 Architecture of pre-vegetation sandy-braided perennial and ephemeral river deposits in the Paleoproterozoic Athabasca Group, northern Saskatchewan, Canada as indicators of Precambrian fluvial style; Sedim. Geol. 190(1–4) 71–95, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.05.006.
Mackey S D and Bridge J S 1995 Three-dimensional model of alluvial stratigraphy: Theory and application; J. Sedim. Res. 65(1b) 7–31, https://doi.org/10.1306/D42681D5-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Martinsen O J, Ryseth A, Helland-Hansen W, Flesche H, Torkildsen G and Idil S 1999 Stratigraphic base level and fluvial architecture: Ericson Sandstone (Campanian), Rock Springs Uplift, SW Wyoming, USA; Sedimentology 46(2) 235–263, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3091.1999.00208.x.
Mazumder R and Sarkar S 2004 Sedimentation history of the Palaeoproterozoic Dhanjori Formation, Singhbhum, eastern India; Precamb. Res. 130(1–4) 267–287, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2003.12.005.
Mellere D and Steel R J 1996 Tidal sedimentation in Inner Hebrides half grabens, Scotland: The Mid-Jurassic Bearreraig Sandstone Formation; In: Geology of siliciclastic shelf seas (eds) De Batist M and Jacobs P, Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ. 117(1) 49–79, https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.117.01.04.
Miall A D 1980 Cyclicity and the facies model concept in geology; Bull. Can. Petrol. Geol. 28(1) 59–79, https://doi.org/10.35767/gscpgbull.28.1.059.
Miall A D 1985 Architectural element analysis: A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits; Earth Sci. Rev. 22(4) 261–308, https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(85)90001-7.
Miall A D 1988 Facies architecture in clastic sedimentary basins; In: New perspective in basin analysis (eds) Kleinspehn K and Paola C, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp. 67–81, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-3788-4_4.
Miall A D 1992 Alluvial deposits; In: Facies models: Response to sea level change (eds) Walker R G and James N P, Geol. Assoc. Can., St. John’s, Newfoundland, pp. 119–142.
Miall A D 1996 The geology of fluvial deposits: Sedimentary facies, basin analysis and petroleum geology; Springer-Verlag Inc., Heidelberg, 582p.
Miall A D and Jones B G 2003 Fluvial architecture of the Hawkesbury Sandstone (Triassic), near Sydney, Australia; J. Sedim. Res. 73(4) 531–545, https://doi.org/10.1306/111502730531.
Milli S, D’Ambrogi C, Bellotti P, Calderoni G, Carboni M G, Celant A, Di Bella L, Di Rita F, Frezza V, Magri D, Pichezzi R M and Ricci V 2013 The transition from wave-dominated estuary to wave-dominated delta: The Late Quaternary stratigraphic architecture of Tiber River deltaic succession (Italy); Sedim. Geol. 284 159–180, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.12.003.
Milli S, Mancini M, Moscatelli M, Stigliano F, Marini M and Cavinato G P 2016 From river to shelf, anatomy of a high-frequency depositional sequence: The Late Pleistocene to Holocene Tiber depositional sequence; Sedimentology 63(7) 1886–1928, https://doi.org/10.1111/sed.12277.
Mukhopadhyay S, Samanta P, Bhattacharya S and Sarkar S 2019 Stratigraphic evolution and architecture of the terrestrial succession at the base of the Neoproterozoic Badami Group, Karnataka, India; In: Geological evolution of Precambrian Indian shield (ed.) Mondal M E A, Society for Earth Scientists Series, Springer, pp. 121–157, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-89698-4_6.
Muto T, Steel R J and Swenson J B 2007 Autostratigraphy: A framework norm for genetic stratigraphy; J. Sedim. Res. 77 2–12.
Olsen H 1988 The architecture of a sandy braided-meandering river system: An example from the lower Triassic Soiling Formation (M. Buntsandstein) in W. Germany; Int. J. Earth Sci. 77(3) 797–814, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01830186.
Olsen H 1989 Sandstone-body structures and ephemeral stream processes in the Dinosaur Canyon Member, Moenave Formation (Lower Jurassic), Utah, U.S.A.; Sedim. Geol. 61(3–4) 207–221.
Olsen T R, Steel R, Hogseth K, Skar T and Roe S L 1995 Sequential architecture in a fluvial succession: Sequence stratigraphy in the Upper Cretaceous Mesaverde Group, Price Canyon, Utah; J. Sedim. Res. 65(2b) 265–280, https://doi.org/10.1306/D426822A-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Patruno S and Helland-Hansen W 2018 Clinoforms and clinoform systems: Review and dynamic classification scheme for shorelines, subaqueous deltas, shelf edges and continental margins; Earth-Sci. Rev. 185 202–233.
Pfluger F and Seilacher A 1991 Flash flood conglomerates; In: Cycles and events in stratigraphy (eds) Einsele G, Ricken W and Seilacher A, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, New York 383 391p.
Pillai S P and Kale V S 2011 Seismites in the Lokapur Subgroup of the Proterozoic Kaladgi Basin, South India: A testimony to syn-sedimentary tectonism; Sedim. Geol. 240(1–2) 1–13, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2011.06.013.
Plint A G, McCarthy P J and Faccini U F 2001 Nonmarine sequence stratigraphy: Updip expression of sequence boundaries and systems tracts in a high-resolution framework, Cenomanian Dunvegan Formation, Canada; AAPG Bull. 85(11) 1967–2001, https://doi.org/10.1306/8626D0C7-173B-11D7-8645000102C1865D.
Posamentier H W and Allen G P 1999 Siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy: Concepts and applications; SEPM Spec. Publ. 7 210.
Posamentier H W and Vail P R 1988 Eustatic controls on clastic deposition II – sequence and systems tract models; In: Sea level change – an integrated approach (eds) Wilgus C K, Hastings B S, Kendall C G St C, Posamentier H W, Ross C A and Van Wagoner J C, SEPM Spec. Publ. 42 125–154.
Posamentier H W and Walker R G 2006 Deep-water turbidites and submarine fans; In: Facies models revisited (eds) Posamentier H W and Walker R G, SEPM Spec. Publ. 84 399–520, https://doi.org/10.2110/pec.06.84.0399.
Posamentier H W, Jervey M T and Vail P R 1988 Eustatic controls on clastic deposition I – conceptual framework; In: Sea level change-an integrated approach (eds) Wilgus C K, Hastings B S, Kendall C G St C, Posamentier H W, Ross C A and Van Wagoner J C, SEPM Spec. Publ. 42 125–154.
Radhakrishna B P and Vaidyanadhan R 1994 Geology of Karnataka; Geol. Soc. India, Bangalore, pp. 239–251.
Rao V V S, Sreenivas B, Balaram V, Govil P K and Srinivasan R 1999 The nature of the Archean upper crust as revealed by the geochemistry of the Proterozoic shales of the Kaladgi basin, Karnataka, Southern India; Precamb. Res. 98(1–2) 53–65, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-9268(99)00038-8.
Reading H G 1986 Sedimentary environments and facies (2nd edn); Blackwell Science Publication, Oxford, 615p.
Reading H G 1996 Sedimentary environments: Processes, facies and stratigraphy; Blackwell Science, Oxford, 688p.
Reineck H E and Singh I B 1980 Depositional sedimentary environments (2nd Edn); Springer-Verlag, New York, 549p.
Reinson G E 1992 Transgressive barrier island and estuarine systems; In: Facies models: Response to sea level change (eds) Walker R G and James N P, Geol. Assoc. Can., St. John’s, Newfoundland, pp. 179–194.
Reynolds A D 2009 Paralic successions; In: Sequence stratigraphy (eds) Emery D and Myers K J, Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp. 134–177.
Robinson A H W 1960 Ebb-flood channel systems in sandy bays and estuaries; Geography 45(3) 183–199.
Rodriguez A B and Meyer C T 2006 Sea-level variation during the Holocene deduced from the morphologic and stratigraphic evolution of Morgan Peninsula, Alabama, USA; J. Sedim. Res. 76 257–269.
Rubin D M and Hunter R E 1982 Bedform climbing in theory and nature; Sedimentology 29(1) 121–138, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1982.tb01714.x.
Sambrook Smith G H, Best J L, Bristow C S and Petts G E 2006 Braided rivers: Process, deposits, ecology and management; IAS Spec. Publ. 36, Blackwell, Oxford, 396p, https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444304374.
Sarkar S, Samanta P, Mukhopadhyay S and Bose P K 2012 Stratigraphic architecture of the Sonia Fluvial interval, India in its Precambrian context; Precamb. Res. 214 210–226, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2012.01.001.
Scherer C M, Goldberg K and Bardola T 2015 Facies architecture and sequence stratigraphy of an early post-rift fluvial succession, Aptian Barbalha Formation, Araripe Basin, north-eastern Brazil; Sedim. Geol. 322 43–62.
Schlager W 1993 Accommodation and supply – a dual control on stratigraphic sequences; Sedim. Geol. 86(1–2) 111–136, https://doi.org/10.1016/0037-0738(93)90136-S.
Schumm S A 1993 River response to baselevel change: Implications for sequence stratigraphy; J. Geol. 101(2) 279–294.
Selley R C 2000 Applied sedimentology; Academic Press, London, 523p.
Shanley K W and McCabe P J 1993 Alluvial architecture in a sequence stratigraphic framework: A case history from the Upper Cretaceous of southern Utah, USA; In: The geological modelling of hydrocarbon reservoirs and outcrop analogues (eds) Flint S S and Bryant I D, IAS Spec. Publ. 15 21–56.
Shanley K W and McCabe P J 1994 Perspectives on the sequence stratigraphy of continental strata; AAPG Bull. 78(4) 544–568, https://doi.org/10.1306/BDFF9258-1718-11D7-8645000102C1865D.
Shanley K W, McCabe P J and Hettinger R D 1992 Tidal influence in Cretaceous fluvial strata from Utah, USA: A key to sequence stratigraphic interpretation; Sedimentology 39(5) 905–930, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1992.tb02159.x.
Simons D B, Richardson E V and Nordin C L Jr 1965 Sedimentary structures generated by flow in alluvial channels; In: Primary sedimentary structures and their hydrodynamic interpretation (ed.) Middelton G V, SEPM Spec. Publ. 12 84–115, https://doi.org/10.2110/pec.65.08.0034.
Smith D G 1987 Meandering River Point Bar lithofacies: Modern and ancient examples compared; In: Recent developments in fluvial sedimentology (eds) Ethridge F, Flores R and Harvey M, SEPM Spec. Publ. 39 83–91.
Smith N D 1970 The braided stream depositional environment: Comparison of the Platte River with some Silurian clastic rocks, North Central Appalachians; GSA Bull. 81(10) 2993–3014, https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1970)81[2993:TBSDEC]2.0.CO;2.
Smith N D and Rogers J 1999 Fluvial sedimentology VI; Blackwell Sciences, Oxford, 478p.
Suter J R and Clifton H E 1999 The Shannon Sandstone and isolated linear sand bodies: Interpretations and realisations; In: Isolated shallow marine sand bodies: Sequence stratigraphic analysis and sedimentologic interpretation (eds) Bergman K M and Snedden J W, SEPM Spec. Publ. 64 321–356, https://doi.org/10.2110/pec.99.64.0321.
Swift D J P 1975 Barrier-island genesis: Evidence from the central Atlantic shelf, eastern USA; Sedim. Geol. 14(1) 1–43, https://doi.org/10.1016/0037-0738(75)90015-9.
Swift D J P, Kofoed J W, Saulsbury F B and Sears P C 1972 Holocene evolution of the shelf surface, central and southern Atlantic shelf of North America; In: Shelf sediment transport: Process and pattern (eds) Swift D J P, Duane D B and Pilkey O H, Dowden Hutchinson & Ross; Stroundsburg PA, pp. 499–574.
Swift D J P, Phillips S and Thorne J A 1991 Sedimentation on continental margins, V: Parasequences; In: Shelf sand and sandstone bodies: Geometry, facies and sequence stratigraphy (eds) Swift D J P, Oertel G F, Tillman R W and Thorne J A, IAS Spec. Publ. 14 153–187.
Terwindt J H J 1988 Palaeo-tidal reconstructions of inshore tidal depostional environments; In: Tide-influenced sedimentary environments and facies, sedimentology and petroleum geology (eds) de Boer P L, van Gelder A and Nio S D, D. Reidel Publishing, Dordrecht, pp. 233–263.
Thomas R G, Smith D G, Wood J M, Visser J, Calverly-Range E A and Koster E H 1987 Inclined heterolithic stratification; terminology, description, interpretation and significance; Sedim. Geol. 53(1–2) 123–179, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(87)80006-4.
Tirsgaard H and Øxnevad I E I 1998 Preservation of pre-vegetational mixed fluvio-aeolian deposits in a humid climatic setting: An example from the Middle Proterozoic Eriksfjord Formation, Southwest Greenland; Sedim. Geol. 120(1–4) 295–317, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00037-2.
Van Wagoner J C, Posamentier H W, Mitchum R M, Vail P R, Sarg J F, Loutit T S and Hardenbol J 1988 An overview of the fundamentals of sequence stratigraphy and key definitions; In: Sea level changes: An integrated approach (eds) Wilgus C K, Hastings B S, Kendall C G St C, Posamentier H W, Ross C A and Van Wagoner J C, SEPM Spec. Publ. 42 39–45.
Visser M J 1980 Neap-spring cycles reflected in Holocene subtidal large-scale deposits: A preliminary note; Geology 8(11) 543–546, https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1980)8%3C543:NCRIHS%3E2.0.CO;2.
Walker R G 1984 Turbidites and associated coarse clastic deposits; In: Facies models (2nd edn) (ed.) Walker R G, Geological Association of Canada, Geoscience Canada Reprint Series 1, Toronto, pp. 171–188.
Walker R G and Plint A G 1992 Wave- and storm-dominated shallow marine systems; In: Facies models: Response to sea level change (eds) Walker R G and James N P, Geol. Assoc. Can., St. John’s, Newfoundland, pp. 219–238.
Weltje G J, Meijer X D and de Boer P L 1998 Stratigraphic inversion of siliciclastic basin fills: A note on the distinction between supply signals resulting from tectonic and climatic forcing; Basin Res. 10(1) 129–153, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2117.1998.00057.x.
Wentworth C K 1919 A laboratory and field study of cobble abrasion; J. Geol. 27(7) 507–521, https://doi.org/10.1086/622676.
Wright L D and Nittrouer C A 1995 Dispersal of river sediments in coastal seas: Six contrasting cases; Estuaries 18 494–508.
Zaitlin B A, Dalrymple R W and Boyd R 1994 The stratigraphic organisation of incised-valley systems associated with relative sea-level change; In: Incised-Valley Systems: Origin and sedimentary sequences (eds) Dalrymple R, Boyd R and Zaitlin B A, SEPM Spec. Publ. 51 45–60, https://doi.org/10.2110/pec.94.12.0045.
Zaitlin B A, Potocki D, Warren M J, Rosenthal L and Boyd R 2000 Sequence stratigraphy in low accommodation foreland basins: An example from the lower Cretaceous Basal Quartz Formation of southern Albert; Canadian Soc. Petrol. Geol. Reservoir 26(8) 12–13.
Zecchin M and Catuneanu O 2013 High-resolution sequence stratigraphy of clastic shelves I: Units and bounding surfaces; Mar. Petrol. Geol. 39(1) 1–25.
Acknowledgements
SM acknowledges DST (Project no. SR/S4/ES-501/2010), Govt. of India, for providing financial help. PS acknowledges Department of Geology, University of North Bengal, for infrastructural support. PS also acknowledges NBU research assistance for financial support. SM highly indebted to the Department of Geological Sciences, Jadavpur University, for providing the infrastructural facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S Mukhopadhyay: Conception and design of the study, acquisition of data, analysis and/or interpretation of data, drafting the manuscript. P Samanta: Acquisition of data, analysis and/or interpretation of data, revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Santanu Banerjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, S., Samanta, P. The controlling factors of lateral variability in coastal marine sequence building pattern. J Earth Syst Sci 131, 245 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-01987-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-01987-x