Abstract
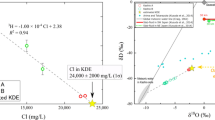
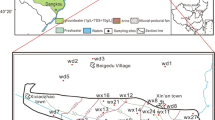
Chlorine isotopes can be used to study the evolution of different fluids, sources and the causes of various related deposits. In this study, Cl concentrations and chlorine isotope (δ37Cl, IAEA ISL-354 NaCl standard) values were determined for brine samples from Nangqen basin, located on the southern boundary of the Qinghai–Tibet plateau to study the source and the processes of these saline springs. The results demonstrated that the saline springs are distributed around a fault or fault zone, with a high average salinity of 228.30 g/l and flow rates ranging from 1.7 to 0.01 l/s. Na+ and Cl− are the predominant cations and anions, respectively, accounting for more than 90% of the total. The δ37Cl values range from −1.55‰ to +0.97‰, and the Cl/Br ratios are from 1739 to 175,260. Coupled with the previous H, O and B isotope compositions (δD, VSMOW2 standard, ranges from −100.91‰ to −132.98‰, δ18O, VSMOW2 standard, from −12.88‰ to −16.05‰ and δ11B, NIST 951 standard, from +3.55‰ to +29.59‰), it can be interpreted that the saline springs are mainly the result of the dissolution of halite hosted in mudstone and volcanic country rocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks D A, Green R, Cliff R A and Yardley B W D 2000 Chlorine isotopes in fluid inclusions: Determination of the origins of salinity in magmatic fluids; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 64(10) 1785–1789.
Barnes J D and Sharp Z D 2017 Chlorine isotope geochemistry; Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 82(1) 345–378.
Bodnar R J 1994 Synthetic fluid inclusions: XII. The system H2O–NaCl. Experimental determination of the halite liquidus and isochores for a 40 wt% NaCl solution; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 58(3) 1053–1063.
Bonifacie M, Jendrzejewski N, Agrinier P, Humler E, Coleman M and Javoy M 2008 The chlorine isotope composition of Earth’s mantle; Science 319(5869) 1518–1520.
Brian K, Zhou J, Matt S, An Y and Wang J H 2000 Paleogene (?) deposystems and basin evolution in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau: Nangqian and Xialaxiu basins; Geosci. Front. 7(suppl.) 282–283.
Bureau H, Keppler H and Métrich N 2000 Volcanic degassing of bromine and iodine: Experimental fluid/melt partitioning data and applications to stratospheric chemistry; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 183(1–2) 51–60.
Chi G and Savard M M 1997 Sources of basinal and Mississippi Valley-type mineralizing brines: Mixing of evaporated seawater and halite-dissolution brine; Chem. Geol. 143(3) 121–125.
Deng W M, Sun H J and Zhang Y Q 2000 K–Ar age of the Cenozoic volcanic rocks in the Nangqen Basin, Qinghai Province and its geological significance; Chin. Sci. Bull. 45(11) 1015–1019.
Du H F, Jiang Y B, Yan Z B, Hou Z Q, Yang T N, Guo F S and Yang Q K 2011 Sedimentary characteristics and environment of the Paleogene Nangqian Basin in Qinghai Province; Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. 85(3) 383–395 (in Chinese).
Eastoe C J and Dettman D L 2016 Isotope amount effects in hydrologic and climate reconstructions of monsoon climates: Implications of some long-term data sets for precipitation; Chem. Geol. 430 78–89.
Eastoe C J and Guilbert J M 1992 Stable chlorine isotopes in hydrothermal processes; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56(12) 4247–4255.
Eastoe C J, Long A and Knauth L P 1999 Stable chlorine isotopes in the Palo Duro Basin, Texas: Evidence for preservation of Permian evaporite brines; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 63(9) 1375–1382.
Eastoe C, Peryt T, Petrychenko Y and Geisler-Cussey D 2007 Stable chlorine isotopes in Phanerozoic evaporites; Appl. Geochem. 22(3) 575–588.
Eggenkamp H G M and Schuiling R D 1995 Δ 37c1 variations in selected minerals: A possible tool for exploration; J. Geochem. Explor. 55(1–3) 249–255.
Eggenkamp H G M, Kreulen R and Van Groos A F K 1995 Chlorine stable isotope fractionation in evaporites; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59(24) 5169–5175.
Fontes J C and Matray J M 1993 Geochemistry and origin of formation brines from the Paris Basin, France: 2 Saline solutions associated with oil fields; Chem. Geol. 109(1–4) 149–175.
Gleeson S A and Smith M P 2009 The sources and evolution of mineralising fluids in iron oxide-copper-gold systems, Norrbotten, Sweden: Constraints from Br/Cl ratios and stable Cl isotopes of fluid inclusion leachates; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 73(19) 5658–5672.
Godon A, Jendrzejewski N, Eggenkamp H G M, Banks D A, Ader M and Coleman M L 2004 A cross-calibration of chlorine isotopic measurements and suitability of seawater as the international reference material; Chem. Geol. 207(1–2) 1–12.
Grandia F 2003 Geochemistry of the fluids related to epigenetic carbonate-hosted Zn–Pb deposits in the Maestrat Basin, Eastern Spain: Fluid inclusion and isotope (Cl, C, O, S, Sr) evidence; Econ. Geol. 98(5) 933–954.
Han J L, Han F Q, Hussain S A, Liu W Y, Nian X Q and Mao Q F 2018 Origin of boron and brine evolution in saline springs in the Nangqen Basin, Southern Tibetan Plateau; Geofluids 2018 1–12.
Hemming N G and Hanson G N 1992 Boron isotopic composition and concentration in modern marine carbonates; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56(1) 537–543.
Horton B K, Zhou J Y, Spurlin M S and Wang J H 2000 Paleogene deposystems and basin evolution in the eastern Tibetan Plateau: Nangqian and Xialaxiu basins; Earth Sci. Front. 7(suppl.) 282–283.
Jiang Y H, Jiang S Y, Ling H F and Zhang D B 2006 Low-degree melting of a metasomatized lithospheric mantle for the origin of Cenozoic Yulong monzogranite-porphyry, east Tibet: Geochemical and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf isotopic constraints; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 241(3) 617–633.
Kaufmann R S, Frape S K, Mcnutt R and Eastoe C 1993 Chlorine stable isotope distribution of Michigan Basin formation waters; Appl. Geochem. 8 403–407.
Kaufmann R, Long A, Bentley H and Davis S 1984 Natural chlorine isotope variations; Nature 309 338–340.
Koehler G and Wassenaar L I 2010 The stable isotopic composition (37Cl/35Cl) of dissolved chloride in rainwater; Appl. Geochem. 25(1) 91–96.
Liu W G and Xiao Y K 1996 Chlorine isotopic composition in Qaidam Basin; Geochimica 25(3) 296–303.
Liu W G, Xiao Y K, Wang Q Z, Qi H P, Wang Y H, Zhou Y M and Shirodkar P V 1997 Chlorine isotopic geochemistry of salt lakes in the Qaidam Basin, China; Chem. Geol. 136(3) 271–279.
Liu W G, Peng Z C and Xiao Y K 1998 Boron and chlorine isotopic determinations and applications for earth sciences; Adv. Earth Sci. 13(6) 38–45.
Luo C G, Xiao Y K, Ma H Z, Ma Y Q, Zhang Y L and He M Y 2012 Stable isotope fractionation of chlorine during evaporation of brine from a saline lake; Chin. Sci. Bull. 57(15) 1833–1843.
Luo C G, Xiao Y K, Wen H J, Ma H Z, Ma Y Q, Zhang Y L and He M Y 2015 Reply to the comment on the paper ‘Stable isotope fractionation of chlorine during the precipitation of single chloride minerals’; Appl. Geochem. 54 117–118.
Lv Y Y, Zheng M P, Zhao P and Xu R H 2014 Geochemical processes and origin of boron isotopes in geothermal water in the Yunnan-Tibet geothermal zone; Earth Sci. 57(12) 2934–2944.
Magenheim A J, Spivack A J, Volpe C and Ransom B 1994 Precise determination of stable chlorine isotopic ratios in low-concentration natural samples; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 58(14) 3117–3121.
Nahnybida T, Gleeson S A, Rusk B G and Wassenaar L I 2009 Cl/Br ratios and stable chlorine isotope analysis of magmatic-hydrothermal fluid inclusions from Butte, Montana and Bingham Canyon, Utah; Miner. Deposita 44(8) 837–848.
Qi Z, Li Y, Wang C, Sun T and Zhang J 2017 Organic geochemistry of the Paleocene-Eocene oil shales of the Gongjue formation, Nangqian basin, east-central Tibetan plateau; Oil Shale 34(1) 1–14.
Richard A, Banks D A, Mercadier J, Boiron M C, Cuney M and Cathelineau M 2011 An evaporated seawater origin for the ore-forming brines in unconformity-related uranium deposits (Athabasca Basin, Canada): Cl/Br and δ 37Cl analysis of fluid inclusions; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 75(10) 2792–2810.
Risacher F, Alonso H and Salazar C 2003 The origin of brines and salts in Chilean salars: A hydrochemical review; Earth-Sci. Rev. 63 249–293.
Rodríguez A, Bergen J and Eggenkamp H G M 1997 Isotopic compositions of chlorine in brine and saline minerals; Chin. Sci. Bull. 42(5) 406–409.
Sharp Z D, Barnes J D, Brearley A J, Chaussidon M, Fischer T P and Kamenetsky V S 2007 Chlorine isotope homogeneity of the mantle, crust and carbonaceous chondrites; Nature 446(7139) 1062–1065.
Spurlin M S, Yin A, Horton B K, Zhou J Y and Wang J H 2015 Structural evolution of the Yushu–Nangqian region and its relationship to syncollisional igneous activity, east-central Tibet; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 117(9–10) 1293–1317.
Tan H B, Ma H Z, Xiao Y K, Wei H Z and Zhang X Y 2005 Characteristics of chlorine isotope distribution and analysis on sylvinite deposit formation based on ancient salt rock in the western Tarim Basin; Sci. China: Earth Sci. 48(11) 1913–1920.
Vengosh A, Chivas A R and Mcculloch M T 1989 Direct determination of boron and chlorine isotopic compositions in geological materials by negative thermal-ionization mass spectrometry; Chem. Geol. Isot. Geosci. 79(4) 333–343.
Xiao Y K, Liu W G and Zhang C G 1994 The preliminary investigation on chlorine isotopic fractionation during the crystallization of saline minerals in salt lake; J. Salt Lake Res. 2(3) 27–34 (in Chinese).
Xiao Y K, Liu W G, Qi H P and Wang Y H 1998 The new methods for isotopic measurement of elements by mass spectrometry and investigation of its application; J. Salt Lake Res. 6(2–3) 73–85 (in Chinese).
Xiao Y K, Wei H Z and Yin D Z 2000 Progress on isotopic geochemistry of boron and chlorine in salt lakes; J. Salt Lake Res. 8(1) 30–40 (in Chinese).
Xu J X, Ma H Z, Xiao Y K, Tan H B, Li T W, Sun Z G and Fan Q S 2008 Stable chlorine isotope and Its research on applied geochemistry; J. Salt Lake Res. 16(1) 51–59 (in Chinese).
Yang D X 1988 The determinations of plateau age by 40Ar/39Ar dating on Cenozoic calc–alkalic trachytes of Nangqen Basin, Northern transverse mountains; In: Contribution to the Geology of the Qinghai–Xizang (Tibet) Plateau, Geological Publishing House, Beijing 19 9–44 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dr Ma Yunqi, Associate Research Fellow, for providing valuable suggestions and the help during the laboratory experiments. This research was supported by the science and technology project of the Qinghai province (grant no. 2014-ZJ-702).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Rajneesh Bhutani
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, JL., Hussain, SA. & Han, FQ. Stable chlorine isotopes in saline springs from the Nangqen basin, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Brine genesis and evolution. J Earth Syst Sci 128, 206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1236-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1236-0