Abstract
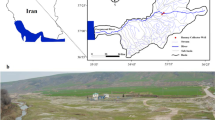
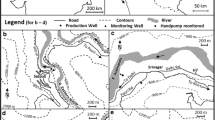
This study approach seeks to characterize the hydraulic interactions between the Nile and the Quaternary aquifer via riverbank filtration (RBF) in Abu Tieg area, Assuit Governorate. The substantial removal/reduction of the most problematic substances during percolation of Nile water into abstraction wells was investigated using physico-chemical and biological indicators. Four sites with 11 municipal wells (20–750 m from the Nile) tapping the alluvial aquifer that is fed by the riverbank infiltrate were monitored. Bank-filtrated water was compared with those of the Nile and groundwater. Results showed that infiltrated Nile water ratio into the wells ranged from 39 to 80% reflecting the effect of distance from the Nile. Removal efficiency of total algal, total and faecal coliforms in bank-filtered water was 99.9%, while turbidity removal ranged from 93 to 98%. Fe, Mn and Zn in the bank-filtered water were relatively higher than those in the Nile, but were still under the allowable standards except those of Mn. LSI and WQI for the bank-filtered water indicated that the water was ranked as non-corrosive and of excellent quality. Comparison of physico-chemical and microbiological characteristics of the bank-filtered water with those of the Nile and groundwater showed the high efficiency of RBF as a treatment technology with minimal cost compared to conventional methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla F and Shamrukh M 2011 Riverbank filtration as a new treatment technology in Nile Valley: Case study, Abu Tieg City, Assiut, Egypt; In: Riverbank filtration for water security in desert countries (eds) Ray C and Shamrukh M, Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 255–266.
Abdel-Lah A and Shamrukh M 2006 Riverbank filtration: A promise method for water supply from Nile, Egypt; In: Proceedings of 7th International Symposium on Water Supply Technology, Yokohama, Japan, November, pp. 385–395.
Adeogun A O 2012 Impact of industrial effluent on water quality and gill pathology of Clarias gariepinus from Alaro stream, Ibadan, southwest Nigeria; European J. Sci. Res. 76 83–94.
Akoteyon I, Omotayo A, Soladoye O and Olaoye H O 2011 Determination of water quality index and suitability of urban river for municipal water supply in Lagos, Nigeria; European J. Sci. Res. 54 (2) 263–271.
American Public Health Association (APHA) 1998 Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 17th edn; APHA, Washington, DC.
ATSDR 1992 The agency for toxic substances and disease registry; A Public Health Assessment Guidance Manual, US Dept. of Health and Human Services, Atlanta, Georgia.
Avvannavar S and Shrihari S 2008 Evaluation of water quality index for drinking purposes for river Netravathi, Mangalore; South India Environ. Monit. Assess. 143 279–290.
Balan I, Shivakumar M and Kumar P 2012 An assessment of groundwater quality using water quality index in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; Chronicles of Young Scientists 3 (2) 146–150.
Bartak R, Grischek T, Ghodeif K and Wahaab R 2014 Shortcomings of the RBF pilot site in Dishna, Egypt; J. Hydrol. Eng., doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001137 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001137.
Dawoud M and Ismail S 2013 Saturated and unsaturated River Nile/groundwater aquifer interaction systems in the Nile Valley, Egypt; Arabian J. Geosci. 6 2119– 2130.
Deininger R, Lee J, Ancheta A and Somana C 2002 Public health aspects of riverbank filtration; In: River bank filtration: Understanding contaminant biogeochemistry and pathogens removal (ed.) Ray C (The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publisher) Earth Environ. Sci., NATO Science Series 14 153–176.
Doussan C, Poitevin G, Ledoux E and Detay M 1997 Riverbank filtration: Modeling of the changes in water chemistry with emphasis on nitrogen species; J. Contam. Hydrol. 25 129–156.
Egyptian Higher Committee of Water (EHCW) 2007 Egyptian standards for drinking and domestic water according to the Act 27/1978 in regulating of the public water supplies; Egyptian Governmental Press, Egypt.
El Miligy E M 2004 Groundwater resources evaluation of Assiut area; Ph.D. thesis, Fac. Sci., Assiut University, Egypt.
Farrag A A 2005 The hydraulic and hydrogeological impacts of the Nile system on the groundwater in Upper Egypt, Assuit University; Bull. Environ. Res. 8 87–102.
Fleisher J M, Kay D, Wyer D and Godfree A F 1998 Estimates of the severity of illness associated with bathing in marine recreational waters contaminated with domestic sewage; Int. J. Epidemiol. 27 722–726.
Giannoulis N, Maipa V, Konstantinou I, Albanis T and Dimoliatis I 2005 Microbiological risk assessment of Agios Georgios source supplies in north western Greece based on faecal coliform determination and sanitary inspection survey; Chemosphere 58 1269–1276.
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) 1991 Chlorinated drinking water; Chlorination by-products; Some other halogenated compounds; Cobalt and cobalt compounds; IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Lyon, France, 52 544p.
Ibrahim H A, Ebraheem A M, Abu El Ella E M, Bakheit A A and El Hussaini A H 1995 The study of groundwater resources along the plain of the River Nile (from Aswan to Assiut) using geoelectrical resistivity methods. Proceedings of the 1st inter. Conf.: The environment and development in Africa, 21–24 October, Assiut University, Egypt, pp. 273–300.
Kahler H I 1944 Once through and recirculation cooling water studies; Proceedings, Engineers Society Western Pcnna, pp. 39–62.
Kim S, Corapcioglu M and Kim D 2003 Effect of dissolved organic matter and bacteria on contaminant transport in riverbank filtration; J. Contam. Hydrol. 66 1–23.
Korany E A, Tempel R N, Gomaa M A and Mohamed R 2013 Detecting the roles of the physiochemical processes on groundwater evolution, Assiut area, Egypt – applications of hydrogeochemical and isotopic approaches; Egyptian J. Geol. 57 63–83.
Kuehn W and Mueller U 2000 Riverbank filtration: An overview; J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 92 60–69.
Langelier F 1936 The analytical control of anticorrosion water treatment; J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 28 1500–1521.
Macler A B and Merkel C J 2000 Current knowledge on groundwater microbial pathogens and their control; Hydrogeol. J. 8 29–40.
Mohod C and Dhote J 2013 Review of heavy metals in drinking water and their effect on human health; IJIRSET 2 2992–2996.
Morris R, Naumova E, Levin R and Munasinghe L 1996 Temporal variation in drinking water turbidity and diagnosed gastroenteritis in Milwaukee; Am. J. Public Health 86 237–239.
Mousa S E, Attia F A and Abu ElFotouh A M 1994 Geological and hydrogeological study on the Quaternary aquifer in the Nile Valley between Assiut and Sohage Governorates; Egyptian Geol. J. 38 1–20.
Nieuwenhuijsen K, de Boer A, Spelten E and Sprangers M A et al. 2009 The role of neuropsychological functioning in cancer survivors’ return to work one year after diagnosis; Psychooncology 18 589–597.
Pressman G, Richardson D, Speth F, Miltner J, Narotsky G, Hunter S, Rice E, Teuschler K, McDonald A, Parvez S, Krasner W, Weinberg S, McKague B, Parrett J, Bodin N, Chinn R, Lee T and Simmons E 2010 Concentration, chlorination, and chemical analysis of drinking water for disinfection byproduct mixtures health effects research: U.S. EPA’s Four Lab Study; Environ. Sci. Technol. 44 7184–7192.
Ray C, Melin G and Linsky R B 2002 Riverbank Filtration: Improving Source Water Quality; Kluwer, The Netherlands.
Richardson R M, Sun D and Bullock M R 2007 Neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury; Neurosurgery Clinics of North America 18 169–181.xi.
Robertson W D, Cherry J A and Sudicky E A 1991 Ground-water contamination from two small septic systems on sand aquifers; Ground Water 29 82–92.
Said R 1981 The geological evolution of the River Nile; Springer-Verlag, New York, Heidelbeirg, Berlin.
Sawyer C and McCarty P 1967 Chemistry and Sanitary Engineers, 2nd edn; McCraw-Hill, New York, 518p.
Schmidt C K, Lange F T, Brauch H G and Kühn W 2003 Experiences with riverbank filtration and infiltration in Germany; DVGW-Water Technology Center, TZW, Germany.
Shamrukh M and Abdel-Wahab A 2008 Riverbank filtration for sustainable water supply: Application to a large-scale facility on the Nile River; Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 10 (4) 351–358.
Shamrukh M and Abdel-Wahab A 2009 Water Pollution and Riverbank Filtration for Water Supply along River Nile, Egypt; NATO Advanced Research Workshop ‘Riverbank Filtration for Water Security in Desert Countries’, Luxor, Egypt, 24–27 October.
Shamrukh M and Abdel-Wahab A 2011 Water pollution and riverbank filtration for water supply along river Nile, Egypt; In: Riverbank filtration for water security in desert countries (eds) Ray C and Shamrukh M, Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 255– 266.
Shehata A, Ali H and Wahba Z 2008 Distribution pattern of Nile water algae with reference to its treatability in drinking water; J. Appl. Sci. Res. 4 (6) 722–730.
Seth R, Mohan M, Singh P, Singh R, Dobhal R, Singh K and Gupta S 2014 Water quality evaluation of Himalayan rivers of Kumaun region, Uttarakhand, India; Appl. Water Sci., 10.1007/s13201-014-0213-7.
Stuyfzand P J 1998 Fate of pollutants during artificial recharge and bank filtration in the Netherlands; In: Artificial Recharge of Groundwater (ed.) Peters J H, Water Research Association, Medmenham, England, pp. 119–125.
Todd D 1980 Ground Water Hydrology, 2nd edn; Wiley, New York.
Ozoko D 2015 Corrosion potentials of natural waters in Abakaliki, Ebonyi State, Nigeria; J. Natural Sci. Res. 5 (9) 108–114.
Valiela I, Collins G, Kremer J, Lajtha K, Geist M, Seely B, Brawley J and Sham C H 1997 Nitrogen loading from coastal watersheds to receiving estuaries: new method and application; Ecol. Appl. 7 (2) 358– 380.
van der Kooij D, Groennou J T, Kruithof J C, Noordam P C, Noordsij A, Stuyfzand P J and van der Gaag M A 1985 Water quality aspects of river bank filtration in the Netherlands; Water Supply 3 41–50.
Wilhelm S R, Schiff S L and Cherry J A 1994b Biogeochemical evolution of domestic waste water in septic systems: 1. Conceptual model; Ground Water 32 905–916.
World Health Organization (WHO) 2008 Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality; 3rd edn, Incorporating the first and second Addenda, Volume 1, Geneva.
Zia M, Iqbal M, Nawaz H and Samin G 1999 Langelier calcium carbonate saturometry determination by table values; Int. J. Agri. Biol. 1 353–355.
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank the staff of the central laboratory of Health Ministry in Cairo, Assiut Holding Company for drinking water and wastewater. Dr Scheytt, Mrs Pieper and Mr Yildiz from the Department of Applied Geosciences of TU Berlin, for their help. The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding through research group (RGP-1437-012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Rajib Maity
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdalla, F., Shamrukh, M. Quantification of River Nile/Quaternary aquifer exchanges via riverbank filtration by hydrochemical and biological indicators, Assiut, Egypt. J Earth Syst Sci 125, 1697–1711 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0755-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0755-1