Abstract
The deactivation mechanism of the simultaneous removal of COS and \(\hbox {CS}_{2}\) over a Fe–Cu–Ni/MCSAC catalyst was investigated using SEM/EDS, XPS and in situ DRIFTS methods. The results show that the catalytic hydrolysis of COS and \(\hbox {CS}_{2}\) over the Fe–Cu–Ni/MCSAC catalyst involves two steps: hydrolysis of \(\hbox {COS}/\hbox {CS}_{2}\) and oxidation of \(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}\). The SEM/EDS and XPS results indicate that that catalytic hydrolysis of \(\hbox {CS}_{2}\) can be achieved by the actions of alkaline groups and active components. When \(\hbox {O}_{2}\) was introduced into the system, oxidation of \(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}\) occurred \(\textit{via}\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}\rightarrow \hbox {S}\rightarrow \hbox {SO}_{4}^{2-}/\hbox {sulphate}\). In situ DRIFTS experiments indicated that the formation of sulphate may occur as follows: (a) \(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}+\hbox {O}_{2}\rightarrow \hbox {S}+\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {O}\), (b) S+\(\hbox {O}_{2}\rightarrow \hbox {S}\)–O, (c) –COO+\(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}\rightarrow \)–CH+S–O, (d) C–OH+\(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}\rightarrow \)–CH+S–O. The in situ DRIFTS experiments also indicated that the C–OH groups, –COO groups and \(\hbox {O}_{2}\) played important roles in the deactivation of the catalyst, which was consistent with the XPS results. Meanwhile, the \(\hbox {SO}_{4}^{2-}/\hbox {sulphate}\) content increased during the reaction, which led to its occupancy of the catalyst’s surface activity sites. Additionally, the alkaline groups and active components were removed, which could also result in the deactivation of the catalysts.
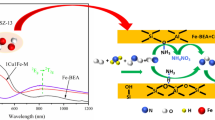
Graphical Abstract
SYNOPSIS The deactivation mechanism of the simultaneous removal of COS and \(\hbox {CS}_{2}\) over a Fe–Cu–Ni/MCSAC catalyst was investigated using SEM/EDS, XPS and in situ DRIFTS methods. In situ DRIFTS experiments indicated that the formation of sulphate may occur as follows: (a) \(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}+\hbox {O}_{2}\rightarrow \hbox {S}+\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {O}\), (b) S+\(\hbox {O}_{2}\rightarrow \hbox {S}\)–O, (c) –COO+\(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}\rightarrow \)–CH+S–O, (d) C–OH+\(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {S}\rightarrow \)–CH+S–O.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leman L J, Orgel L E and Ghadiri M R 2006 Amino acid dependent formation of phosphate anhydrides in water mediated by carbonyl sulfide J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 20
Sun X, Ning P, Tang X L, Yi H H, Li K, He D, Xu X M, Huang B and Lai R Y 2014 Simultaneous catalytic hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide and carbon disulfide over \(\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\)–K/CAC catalyst at low temperature J. Energy Chem. 23 221
Chowanietz V, Pasel C, Eckardt T, Siegel A and Bathen D 2016 Formation of carbonyl sulfide (COS) on different adsorbents in natural gas treatment plants Oil Gas Eur. Mag. 42 82
Zhao S Z, Yi H H, Tang X L, Gao F Y, Yu Q J, Zhou Y S, Wang J G, Huang Y H and Yang Z Y 2016 Enhancement effects of ultrasound assisted in the synthesis of NiAl hydrotalcite for carbonyl sulfide removal Ultrason. Sonochem. 32 336
Qiu J, Ning P, Wang X Q, Li K, Liu W, Chen W and Wang L L 2014 Removing carbonyl sulfide with metal-modified activated carbon Front. Env. Sci. Eng. 10 11
Kuznetsov D L, Filatov I E and Uvarin V V 2016 Processes of carbon disulfide degradation under the action of a pulsed corona discharge Tech. Phys. Lett. 42 822
Yegiazarov Y, Clark J, Potapova L, Radkevich V, Yatsimirsky V and Brunel D 2005 Adsorption-catalytic process for carbon disulfide removal from air Catal. Today 102 242
Huang H M, Young N, Williams B P, Taylor S H and Hutchings G 2006 High temperature COS hydrolysis catalysed by \(\upgamma -\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\) Catal. Lett. 110 243
Liu Y C, He H and Ma Q X 2008 Temperature dependence of the heterogeneous reaction of carbonyl sulfide on magnesium oxide J. Phys. Chem. A 112 2820
Rhodes C, Riddel S A, West J, Williams B P and Hutchings G J 2000 The low-temperature hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide and carbon disulfide: a review Catal. Today 59 443
Ning P, Yu L L, Yi H H, Tang X L, Li H, Wang H Y and Yang L N 2010 Effect of Fe/Cu/Ce loading on the coal-based activated carbons for hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide J. Rare Earth 28 205
Zhu Y Y, Kolar P, Shah S B, Cheng J J and Lim P K 2016 Avocado seed-derived activated carbon for mitigation of aqueous ammonium Ind. Crop. Prod. 92 34
He Q, Dai J L, Zhu L, Xiao K J and Yin Y R 2016 Synthesis and lead absorption properties of sintered activated carbon supported zero-valent iron nanoparticle J. Alloy. Compd. 687 326
Balsamo M, Cimino S, Falco G D, Erto A and Lisi L 2016 ZnO–CuO supported on activated carbon for \(\text{ H }_{2}\text{ S }\) removal at room temperature Chem. Eng. J. 304 399
Li K, Song X, Ning P, Yi H H, Tang X L and Wang C 2014 Energy utilization of yellow phosphorus tail gas: simultaneous catalytic hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide and carbon disulfide at low temperature Energy Technol. 3 136
Ning P, Li K, Yi H H, Tang X L, Peng J H, He D, Wang H Y and Zhao S Z 2012 Simultaneous catalytic hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide and carbon disulfide over modified microwave coal-based active carbon catalysts at low temperature J. Phys. Chem. C 116 17055
Yi H H, Li K, Tang X L, Ning P, Peng J H, Wang C and He D 2013 Simultaneous catalytic hydrolysis of low concentration of carbonyl sulfide and carbon disulfide by impregnated microwave activated carbon at low temperatures Chem. Eng. J. 230 220
Li K, Liu G, Gao T Y, Lu F, Tang L H, Liu S J and Ning P 2016 Surface modification of Fe/MCSAC catalysts with coaxial cylinder dielectric barrier discharge plasma for low-temperature catalytic hydrolysis of \(\text{ CS }_{2}\) Appl. Catal. A 527 171
Guo H B, Tang L H, Li K, Ning P, Sun X, Liu G, Bao S Y, Zhu T T, Jin X, Duan Z Y and Li Q S 2016 The hydrolysis mechanism and kinetic analysis for COS hydrolysis: A DFT study Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 10 427
Yi H H, Zhao S Z, Tang X L, Song C Y, Gao F Y, Zhang B W, Wang Z X and Zuo Y R 2014 Low-temperature hydrolysis of carbon disulfide using the Fe-Cu/AC catalyst modified by non-thermal plasma Fuel 128 268
Li X H, Ren S J, Wei X G, Zeng Y, Gao G W, Y. Ren, Zhu J, Lau K C and Li W K 2014 Concerted or stepwise mechanism? New insight into the water-mediated neutral hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide J. Phys. Chem. A 118 3503
Wang H Y, Yi H H, Tang X L, Yu L L, He D, Zhao S Z and K Li 2013 Reactivation of CoNiAl calcined hydrotalcite-like compounds for hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52 9331
George Z M 1974 Kinetics of cobalt-molybdate-catalyzed reactions of \(\text{ SO }_{2}\) with \(\text{ H }_{2}\text{ S }\) and COS and the hydrolysis of COS J. Catal. 32 261
Akimoto M and Lana I G D 1980 Role of reduction sites in vapor-phase hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide over alumina catalysts J. Catal. 62 84
Ju S 1998 Hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide and carbon disulfide over alumina based catalysts I. Study on activities of COS and \(\text{ CS }_{2}\) hydrolysis J. Nat. Gas Chem. 7 16
Hoggan P E, Aboulayt A, Pieplu A, Nortier P and Lavalley J C 1994 Mechanism of COS hydrolysis on alumina J. Catal. 149 300
Wilson C and Hirst D M 1995 High-level ab initio study of the reaction of OCS with OH radicals J. Chem. Soc. Faraday T. 91 793
Sakanishi K, Wu Z H, Matsumura A, Saito I, Hanaoka T, Minowa T, Tada M and Iwasaki T 2005 Simultaneous removal of \(\text{ H }_{2}\text{ S }\) and COS using activated carbons and their supported catalysts Catal. Today 104 94
Aboulayt A, Mauge F, Hoggan P E and Lavalley J C 1996 Combined FTIR, reactivity and quantum chemistry investigation of COS hydrolysis at metal oxide surfaces used to compare hydroxyl group basicity Catal. Lett. 39 213
Li W, Peng J, Zhang L, Yang K, Xia H, Zhang S and Guo S H 2008 Preparation of activated carbon from coconut shell chars in pilot-scale microwave heating equipment at 60 Kw Waste Manage. 29 756
Luo Y R 2007 Comprehensive Handbook of Chemical Bond Energies (Boca Raton: CRC Press)
Cottrell T L 1958 The Strengths of Chemical Bonds \(2^{{\rm nd}}\) edn. (London: Butterworths Scientific Publications)
U.S. Dept. of Commerce 1970 National standard reference data series, National Bureau of Standards, Washington.
Benson S W 1965 III-Bond energies J. Chem. Educ. 42 502
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51408282, 21667015), China Scholarship Council (201508530017, 201608530169, 201608740011) and the Analysis and Testing Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Song, X., Wang, C. et al. Deactivation mechanism of the simultaneous removal of carbonyl sulphide and carbon disulphide over Fe–Cu–Ni/MCSAC catalysts. J Chem Sci 129, 1893–1903 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-017-1397-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-017-1397-9