Abstract
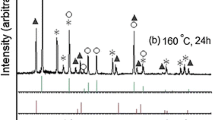
Synthesis of zinc titanates was carried out using a simple precipitation method followed by calcination at different temperatures to obtain different phases of the material. The phase transition characteristics, presence of functional groups, structural aspects and optical bandgaps with respect to calcination temperature were studied by thermal analysis, EDAX, FT-IR, powder XRD, Raman and UV-Vis spectroscopy respectively. The compound on heat treatment at 100∘C for 24 h showed broadened peaks in XRD. With increasing temperature of calcination, the compound appeared to turn to crystalline phase and cubic ZnTiO3 phase was observed at 600∘C. Partial phase transformation of cubic phase ZnTiO3 into hexagonal ilmenite type ZnTiO3 was observed in the temperature range 700∘C to 900∘C. At 1000∘C both cubic and hexagonal ilmenite phases decomposed into cubic phase Zn2TiO 4 and rutile TiO2. FT-IR showed M-O bonds in the range of 400 cm −1 to 700 cm −1. Raman spectra of cubic defect spinel ZnTiO3 and cubic inverse spinel Zn2TiO4 were found to be similar. The optical bandgap calculated using diffuse reflectance spectra was found to be in the range of 3.59 to 3.84 eV depending on calcination temperature.

Zinc titanates were synthesized by a simple precipitation reaction and characterized using thermal analysis, EDAX, powder XRD, FT-IR, Raman and DRS studies. Calcination temperature influences phase transition and optical properties. Raman spectra of cubic ZnTiO3 and cubic Zn2TiO4 are similar due to similarity in their crystal structure and lattice parameters.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pineda M, Fierro J L G, Palacios J M, Cilleruelo C, Garcia E and Ibarra J V 1997 Appl. Surf. Sci. 119 1
Pal N, Paul M and Bhaumik A 2011 Appl. Catal., A. 393 153
Wu S P, Luo J H and Cao S X 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 502 147
Yadav B C, Yadav A, Singh S and Singh K 2013 Sens. Actuators B. 177 605
Obayashi H, Sakurai Y and Gejo T 1976 J. Solid State Chem. 17 299
Wang N, Li X, Wang Y, Hou Y, Zou X and Chen G 2008 Mater. Lett. 62 3691
Darzi S J and Mahjoub A R 2009 J. Alloys Compd. 486 805
McCord A T and Saunder H F 1945 U.S Patent 2379019
Steinike U and Wallis B 1997 Cryst. Res. Technol. 32 187
Jain P K, Kumar D, Kumar A and Kaur D 2010 Opto. Mater. Adv. Mater. 4 299
Manik S K and Pradhan S K 2006 Physica E 33 69
Mrazek J, Spanhel L, Chadyron G and Matejec V 2010 J. Phys. Chem. C. 114 2843
Hou L, Hou Y D, Zhu M K, Tang J, Liu J B, Wang H and Yan H 2005 Mater. Lett. 59 197
Nolan N T, Seery M K and Pillai S C 2011 Chem. Mater. 23 1496
Chai Y L, Chang Y S, Chen G J and Hsiao Y J 2008 Mater. Res. Bull. 43 1066
Wang C L, Hwang W S, Chang K M, Ko H H, Hisn C S, Huang H H and Wang M C 2011 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12 935
Lee Y C and Chen P S 2013 Thin Solid Films. 531 222
Ramirez E G, Chaparro M M and Angel O Z 2010 Appl. Phys. A. 108 291
Phani A R, Passacantando M and Santucci S 2007 J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 68 317
Liu X 2012 Mater. Lett. 80 69
Liu Z, Zhou D, Gong S and Li H 2009 J. Alloys Compd. 475 840
Kim H T, Kim S H, Nahm S and Byun J D 1999 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82 3043
Cassaignon S, Koelsch M and Jolivet J P 2007 J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 68 695
Svehla G 1979 In Vogel’s Text book of macro and semimicro Qualitative Inorganic Analysis 5 th edition (London and New York: Longman) p 272 and 532
Zhong S L, Xu R, Wang L, Li Y and Zhang L F 2011 Mater. Res. Bull. 46 2385
Chamberland B L and Silverman S 1979 J. Less. Common. Met. 65 P41
Yuan Z, Huang F, Sun J and Zhou Y 2002 Chem. Lett. 31 408
Sharma Y, Sharma N, Rao G V S and Chowdari B V R 2009 J. Power Sources 192 627
Lu W and Schmidt H 2005 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25 919
Yang J and Swisher J H 1996 Mater. Charact. 37 153
Wang C T and Lin J C2008 Appl. Surf. Sci. 254 4500
Yamaguchi O, Morimi M, Kawabata H and Shimizu K 1987 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 70 C-97
Li G, Li L, Goates J B and Woodfield B F 2009 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 8659
Zheng M, Xing X., Deng J, Li L, Zhao J, Qiao L and Fang C 2007 J. Alloys Compd. 456 353
Wang L, Kang H, Xue D and Liu C 2009 J. Cryst. Growth. 311 611
Jeong T S, Han M S and Youn C J 2004 J. Appl. Phys. 96 175
Wang Z, Saxena S K and Zha C S 2002 Phys. Review B. 66 024103
Krylova G, Brioude A, Girard S A, Mrazek J and Spanhel L 2010 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12 15101
Huo Y and Hu Y H 2012 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51 1083
Shi L and Lin H 2011 Langmuir 27 3977
Acknowledgments
The authors thank VIT-SIF for thermal analysis, powder XRD, FT-IR and DRS, and Dr. R.P. Vijayalakshmi, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati for Raman spectral data. One of the authors, B. Lokesh thanks VIT University for providing financial support to carry out the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BUDIGI, L., NASINA, M.R., SHAIK, K. et al. Structural and optical properties of zinc titanates synthesized by precipitation method. J Chem Sci 127, 509–518 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-015-0802-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-015-0802-5