Abstract
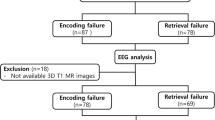
Persons with drug refractory TLE have the option of being managed by surgery. They may develop memory impairment with specific etiology of mesial temporal sclerosis and anterior temporal lobe resection (ATLR). The study evaluated the semantic verbal memory outcomes in pre- and post-surgery temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) patients using functional MRI and voxel morphometric methods. Twenty consecutive persons with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) and 20 healthy controls were recruited after obtaining the institute ethics approval. The fMRI scans were performed on a 1.5 T MR Scanner using standardized semantic verbal memory tasks using a native Hindi paradigm, before and after an anterior temporal lobectomy (in cases). A task-based functional connectivity (FC) was estimated using a conn toolbox. Data analysis was carried out using the statistical parametric imaging (SPM12) and CAT12 toolbox. Post-surgery TLE group showed increased robust FC in the right middle and posterior temporal regions as compared to pre-surgery session. A significant reduction in grey matter volume was observed in the left temporal lobe post-operatively as compared to pre-surgery and healthy control groups. In the post-surgery TLE group, neuropsychological scores were reduced in specific PGI domains such as visuospatial, working memory, and executive functioning. Our results may help in understanding of memory reorganization in TLE post-operatively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonelli SB, Thompson PJ, Koepp MJ and Duncan JS 2013 Memory reorganization following anterior temporal lobe resection: a longitudinal functional MRI study. Brain 136 1889–1900
Button KS, Ioannidis JP, Mokrysz C, Nosek BA, Flint J, Robinson ES and Munafò MR 2013 Power failure: why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14 365–376
Chaudhary K, Ramanujam B, Kumaran SS, Chandra PS and Tripathi M 2017 Does education play a role in language reorganization after surgery in drug refractory temporal lobe epilepsy: An fMRI-based study? Epilepsy Res. 136 88–96
Frings L, Wagner K, Halsband U, Schwarzwald R and Zentner J 2008 Lateralization of hippocampal activation differs between left and right temporal lobe epilepsy persons and correlates with postsurgical verbal learning decrement. Epilepsy Res. 78 161–170
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline JB, Frith C and Frackowiak RS 1995 Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp. 2 189–210
Gaelle E, Xiaosong HeS and perling M 2016 Gray Matter Abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy: relationships with resting-state functional connectivity and episodic memory performance. PloS One 11 e0154660
Gaillard WD, Balsamo L, Xu B, McKinney C, Papero PH and Theodore WH 2004 fMRI language task panel improves determination of language dominance. Neurology 63 1403–1408
Gaser C and Dahnke R 2016 CAT - a computational anatomy toolbox for the analysis of structural MRI data. Paper Presented at the 22nd Annual Meeting of the Organisation for Human Brain Mapping Geneva, Switzerland
Gleissner U, Helmstaedter C, Schramm J and Elger CE 2004 Memory outcome after selective amygdalohippocampectomy in persons with temporal lobe epilepsy: one-year follow-up. Epilepsia 45 960–962
Helmstaedter C, Brosch T, Kurthen M and Elger CE 2004 The impact of sex and language dominance on material‐specific memory before and after left temporal lobe surgery. Brain 127 1518–1525
Ivanova A, Zaidel E, Salamon N, Bookheimer S, Uddin LQ and de Bode S 2017 Intrinsic functional organization of putative language networks in the brain following left cerebral hemispherectomy. Brain Struct. Funct. 222 3795–3805
Janecek JK, Swanson SJ and Sabsevitz DS 2013 Language lateralization by fMRI and Wada testing in 229 persons with epilepsy: rates and predictors of discordance. Epilepsia 54 314–322
Keller SS, Wieshmann UC, Mackay CE, Denby CE, Webb J and Roberts N 2002 Voxel based morphometry of grey matter abnormalities in persons with medically intractable temporal lobe epilepsy: effects of side of seizure onset and epilepsy duration. JNNP 73 648–655
Mueller SG, Laxer KD, Cashdollar N, Buckley S, Paul C and Weiner MW 2006 Voxel-based optimized morphometry (VBM) of gray and white matter in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsia 47 900–9007
Oldfield RC 1971 The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9 97–113
Parra-Díaz P and García-Casares N 2017 Memory assessment in persons with temporal lobe epilepsy to predict memory impairment after surgery: A systematic review. Neurologia doi: 10.1016/j.nrl.2017.02.012
Pershad D and Wig NN 1994 Revised Manual for PGI memory scale (PGIMS) (National Psychological Corporation)
Powell H, Richardson M, Symms MR, Boulby PA and Thompson PJ 2008 Preoperative fMRI predicts memory decline following anterior temporal lobe resection. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79 686–693
Puka K and Smith ML 2016 Predictors of language skills in the long term after pediatric epilepsy surgery. Epilepsy Behav. 63 1–8
Rao SL, Subbakrishna DK and Gopukumar K 2004 NIMHANS neuropsychology battery (manual) (National Institute of Mental Health and Neuroscience)
Sidhu MK, Stretton J, Winston GP, Bonelli S and Centeno M 2013 A functional magnetic resonance imaging study mapping the episodic memory encoding network in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 136 1868–1888
Sidhu MK, Stretton J, Winston GP, McEvoy AW, Symms M, Thompson PJ and Duncan JS 2016 Memory network plasticity after temporal lobe resection: a longitudinal functional imaging study. Brain 139 415–430
Sidhu MK, Stretton J, Winston GP, Symms M and Thompson PJ 2015a Memory fMRI predicts verbal memory decline after anterior temporal lobe resection. Neurology 84 1512–1519
Sidhu MK, Stretton J, Winston GP, Symms M and Thompson PJ 2015b Factors affecting reorganisation of memory encoding networks in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 110 1–9
Smith AD, Michelle A, Ensign E, Jimenez SS, Millett D and Liu C 2018 Epilepsy surgery in the underserved Hispanic population improves depression, anxiety, and quality of life. Epilepsy Behav. 83 1–6
Szaflarski JP, David G, Binder JR, Swanson SJ, French JA and Theodore WH 2017 Practice guideline summary: Use of fMRI in the presurgical evaluation of persons with epilepsy. Neurology 88 1–8
Towgood K, Barker GJ, Caceres A and Crum WR 2015 Bringing memory fMRI to the clinic: comparison of seven memory fMRI protocols in temporal lobe epilepsy. Hum Brain Mapp. 36 1595–608
Wilke M and Lidzba K 2007 LI-tool: a new toolbox to assess lateralization in functional MR. J. Neurosci. Methods 163 128–36
Acknowledgements
The research presented in this paper was funded by Department of Science and Technology-Cognitive Science Research Initiative (Sanction order no; SR/CSI/49/2013), New Delhi, India. We thank all our clinical research team and staff of Epilepsy clinic and NMR&MRI facility centre at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, (New Delhi, India) for their invaluable help, and all our persons and controls for their participation in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Aurnab Ghose
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, K., Tripathi, M., Chandra, P.S. et al. Evaluation of memory in persons with mesial temporal lobe sclerosis: A combined fMRI and VBM study. J Biosci 45, 74 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00041-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00041-6