Abstract
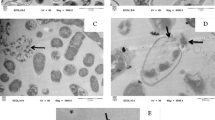
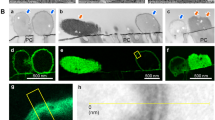
In the last decade the detection of the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics treatment, developed by different kind of bacteria, is becoming a huge problem. We hereby present a different approach to the current problem of detection of bacteria resistance to antibiotics. Our aims were to use the atomic force microscopy (AFM) to investigate bacteria morphological changes in response to antibiotics treatment and explore the possibility of reducing the time required to obtain information on their resistance. In particular, we studied Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria provided by the Lavagna Hospital ASL4 Liguria (Italy), where there are cases linked with antibiotics resistance of the Klebsiella pneumoniae. By comparing AFM images of bacteria strains treated with different antibiotics is possible to identify unambiguously the Klebsiella pneumoniae strains resistant to antibiotics. In fact, the analysis of the AFM images of the antibiotic-sensitive bacteria shows clearly the presence of morphological alterations in the cell wall. While in the case of the antibiotic-resistant bacteria morphological alterations are not present. This approach is based on an easy and potentially rapid AFM analysis.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MD, Nickel GC, Bajaksouzian S, Lavender H, Murthy AR, Jacobs MR and Bonomo RA 2009 Resistance to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii associated with mutations in the PmrAB two-component system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 3628–3634
Allison DP, Sullivan CJ, Mortensen NP, Retterer ST and Doktycz M 2011 Bacterial immobilization for imaging by atomic force microscopy. J. Vis. Exp. 54 e2880
Beceiro A, Moreno A, Fernández N, Vallejo JA, Aranda J, Adler B, Harper M, Boyce JD and Bou G 2014 Biological cost of different mechanisms of colistin resistance and their impact on virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58 518–526
Blair JM A., Webber MA, Baylay AJ, Ogbolu DO and Piddock LJ V 2015 Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 13 42–51
Bolshakova AV, Kiselyova OI, Filonov AS, Frolova OY, Lyubchenko YL and Yaminsky IV 2001 Comparative studies of bacteria with an atomic force microscopy operating in different modes. Ultramicroscopy 86 121–128
Braga PC and Ricci D 1998 Atomic Force Microscopy: Application to investigation of Escherichia coli morphology before and after exposure to Cefodizime. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42 18–22
Cannatelli A, Giani T, D’Andrea MM, Di Pilato V, Arena F, Conte V and Rossolini GM 2014 MgrB inactivation is a common mechanism of colistin resistance in KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of clinical origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58 5696–5703
Cleven BEE, Palka-Santini M, Gielen J, Meembor S, Krönke M and Krut O 2006 Identification and characterization of bacterial pathogens causing bloodstream infections by DNA microarray. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44 2389–2397
Decré D, Verdet C, Emirian A, Le Gourrierec T, Petit J-C, Offenstadt G and Arlet G 2011 Emerging severe and fatal infections due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in two university hospitals in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49 3012–3014
Doumith M, Ellington MJ, Livermore DM and Woodford N 2009 Molecular mechanisms disrupting porin expression in ertapenem-resistant Klebsiella and Enterobacter spp. clinical isolates from the UK. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 63 659–667
Epand RM, Walker C, Epand RF and Magarvey NA 2016 Molecular mechanisms of membrane targeting antibiotics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembranes 1858 980–987
Fantner GE, Barbero RJ, Gray DS and Belcher AM 2010 Kinetics of antimicrobial peptide activity measured on individual bacterial cells using high-speed atomic force microscopy. Nat. Nanotech. 5 280–285
Formosa C, Herold M, Vidaillac C, Duval RE and Dague E 2015 Unravelling of a mechanism of resistance to colistin in Klebsiella pneumoniae using atomic force microscopy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 70 2261–2270
Hanson C, Sieverts M, Tew K, Dykes A, Salisbury M and Vargis E 2016 The use of microfluidics and dielectrophoresis for separation, concentration, and identification of bacteria. Proc. SPIE 9705, Microfluidics, BioMEMS, and Medical Microsystems XIV, 97050E
Horvat RT 2010 Review of antibiogram preparation and susceptibility testing systems. Hosp. Pharm. 45 S6–S9
Ierardi V, Niccolini A, Alderighi M, Gazzano A, Martelli F and Solaro R 2008 AFM characterization of rabbit spermatozoa. Microsc. Res. Tech. 71 529–535
Kumarasamy KK, Toleman MA, Walsh TR, Bagaria J, Butt F, Balakrishnan R and Woodford N 2010 Emergence of a new antibiotic resistance mechanism in India, Pakistan, and the UK: a molecular, biological, and epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 10 597–602
Lekka M, Gil D, Pogoda K, Dulińska-Litewka J, Jach R, Gostek J and Laidler P 2012 Cancer cell detection in tissue sections using AFM. Arch. Biochem.Biophys. 518 151–156
Li A, Lee PY, Ho B, Ding JL and Lim CT 2007 Atomic force microscopy study of the antimicrobial action of Sushi peptides on Gram negative bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1768 411–418
Lim LM, Ly N, Anderson D, Yang JC, Macander L, Jarkowski A and Tsuji BT 2010 Resurgence of Colistin: A review of resistance, toxicity, pharmacodynamics, and dosing. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Therapy 30 1279–1291
Liu Y-Y, Wang Y, Walsh TR, Yi L-X, Zhang R, Spencer J and Shen J 2015 Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: a microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect Dis. 16 161–168
Longo G, Alonso Sarduy L, Rio LM, Bizzini A, Trampuz A, Notz J, Kasas S 2013 Rapid detection of bacterial resistance to antibiotics using AFM cantilevers as nanomechanical sensors. Nat. Nanotech. 8 522–526
Marchese A, Coppo E, Barbieri R and Debbia E 2010 Emergence of KPC-2 Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains and spread of an isolate of sequence type 258 in the neuro-rehabilitation unit of an Italian hospital. J. Chemother. 22 212–214
Matsumoto Y, Sakakihara S, Grushnikov A, Kikuchi K, Noji H, Yamaguchi A and Nishino K 2016 A microfluidic channel method for rapid drug-susceptibility testing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 11 e0148797
Ohlsson P, Evander M, Petersson K, Mellhammar L, Lehmusvuori A, Karhunen U and Laurell T 2016 Integrated acoustic separation, enrichment, and microchip polymerase chain reaction detection of bacteria from blood for rapid sepsis diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 88 9403–9411
Rice KC and Bayles KW 2008 Molecular Control of bacterial death and lysis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 72 85–109
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW 2012 NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. [10.1038/nmeth.2089]. Nat. Methods 9 671–675
Soon RL, Nation RL, Hartley PG, Larson I and Li J 2009 Atomic force microscopy investigation of the morphology and topography of colistin-heteroresistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains as a function of growth phase and in response to colistin treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 4979–4986
Tissari P, Zumla A, Tarkka E, Mero S, Savolainen L, Vaara M and Gant V 2010 Accurate and rapid identification of bacterial species from positive blood cultures with a DNA-based microarray platform: an observational study. Lancet 375 224–230
van Helvert S and Friedl P 2016 Strain Stiffening of fibrillar collagen during individual and collective cell migration identified by AFM nanoindentation. ACS Appl. Math. Interfaces 8 21946–21955
Vrioni G, Daniil I, Voulgari E, Ranellou K, Koumaki V, Ghirardi S and Tsakris A 2012 Comparative evaluation of a prototype chromogenic medium (ChromID CARB(A) for detecting Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in surveillance rectal swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 50 1841–1846
Waldeisen JR, Wang T, Mitra D and Lee LP 2011 A real-time PCR antibiogram for drug-resistant sepsis. PLoS ONE 6 e28528
Wiegand I, Hilpert K and Hancock REW 2008 Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc 3 163–175
Yigit H, Queenan AM, Anderson GJ, Domenech-Sanchez A, Biddle JW, Steward CD and Tenover FC 2001 Novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase, KPC-1, from a Carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45 1151–1161
Zhang SX, Rawte P, Brown S, Lo S, Siebert H, Pong-Porter S and Jamieson FB 2011 Evaluation of CLSI agar dilution method and trek sensititre broth microdilution panel for determining antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49 704–706
Zhihua L, Xuetao H, Jiyong S, Xiaobo Z, Xiaowei H, Xucheng Z, Povey M 2016 Bacteria counting method based on polyaniline/bacteria thin film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 81 75–79
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr Marco Solari (Chemilab Chiavari) for helping them with bacteria handling methods, Dr Mario Lambruschini, nicknamed ‘Sassaroli’, for his useful advice on antibiotics treatments, DrNicola Rossi (Basilea University) and Dr Luca Repetto (University of Genoa) for the valuable discussion on the ideas underlying this work. The Lavagna Hospital states that for this work no grant has been received from any funding agency in the public, commercial, and not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by SRI RAMA KOTI AINAVARAPU.
Corresponding editor: Sri Rama Koti Ainavarapu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ierardi, V., Domenichini, P., Reali, S. et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae antibiotic resistance identified by atomic force microscopy. J Biosci 42, 623–636 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-017-9713-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-017-9713-6