Abstract
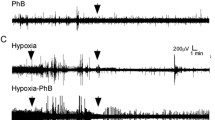
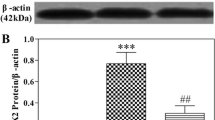
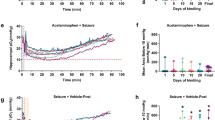
Neuregulin 1 (NRG1)–induced activation of ErbB4 in parvalbumin (PV) inhibitory interneurons is reported to serve as a critical endogenous negative-feedback mechanism to repress brain epileptogenesis. Here, we investigated the seizure susceptibility and the role of NRG1-ErbB4 signaling in PV interneurons in the suppression of epileptic seizures for rats subject to early life hypoxia. Neonatal postnatal day 5 (P5) rats were exposed to intermittent hypoxia (IH) or control (CON) room air for 10 days. In the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of P54 rats, we determined the impact of neonatal IH exposures on the expression of PV, NRG1, ErbB4, and phosphorylated ErbB4 (p-ErbB4) during the seizure induction. Seizure susceptibility tests with the common convulsant agent pentylenetetrazole (PEN) at P54 revealed that rats subject to neonatal hypoxia exposure developed faster and more serious epileptic seizures. Neonatal IH exposures (1) decreased the number of PV cells in the PFC of P54 rats; (2) interrupted the expression of NRG1 gene; and (3) altered the activity of NRG1 on PV interneurons in the PFC after the seizure induction. Intracerebroventricular delivery of exogenous NRG1 before seizure induction by PEN significantly reduced the seizure susceptibility for neonatal IH-exposed rats. The ErbB4 inhibitor AG1478 inhibited the exogenous NRG1’s effects on seizure susceptibility. Environmental enrichment (EE) rescued the abovementioned pathophysiological alterations and significantly attenuated the epileptic seizures after the seizure induction for neonatal IH-exposed rats. Our study indicated early life hypoxia exposure might increase the seizure susceptibility for rats and contribute to pathophysiological dysfunction of NRG1-ErbB4 signaling in PV interneurons in the suppression of epileptic seizures. EE might attenuate the increased seizure susceptibility for neonatal IH-exposed rats through rescuing pathophysiological alterations of NRG1-ErbB4 signaling in PV interneurons.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atik A, Harding R, De Matteo R, Kondos-Devcic D, Cheong J, Doyle LW, Tolcos M (2017) Caffeine for apnea of prematurity: Effects on the developing brain. Neurotoxicology 58:94–102
Laouafa S, Iturri P, Arias-Reyes C, Marcouiller F, Gonzales M, Joseph V, Bairam A, Soliz J (2019) Erythropoietin and caffeine exert similar protective impact against neonatal intermittent hypoxia: apnea of prematurity and sex dimorphism. Exp Neurol 320:112985
Morton SU, Smith VC (2016) Treatment options for apnoea of prematurity. Arch Dis Child-Fetal 101:F352–F356
Bartos M, Vida I, Jonas P (2007) Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:45–56
Komitova M, Xenos D, Salmaso N, Tran KM, Brand T, Schwartz ML, Ment L, Vaccarino FM (2013) Hypoxia-induced developmental delays of inhibitory interneurons are reversed by environmental enrichment in the postnatal mouse forebrain. J Neurosci 33:13375–13387
Lewis DA, Curley AA, Glausier JR, Volk DW (2012) Cortical parvalbumin interneurons and cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia Trends. Neurosci 35:57–67
Liang D, Li G, Liao X, Yu D, Wu J, Zhang M (2016) Developmental loss of parvalbumin-positive cells in the prefrontal cortex and psychiatric anxiety after intermittent hypoxia exposures in neonatal rats might be mediated by NADPH oxidase-2. Behav Brain Res 296:134–140
Sohal VS, Zhang F, Yizhar O, Deisseroth K (2009) Parvalbumin neurons and gamma rhythms enhance cortical circuit performance. Nature 459:698–702
Whittington MA, Cunningham MO, LeBeau FE, Racca C, Traub RD (2011) Multiple origins of the cortical gamma rhythm. Dev Neurobiol 71:92–106
Schwaller B, Tetko IV, Tandon P, Silveira DC, Vreugdenhil M, Henzi T, Potier M-C, Celio MR et al (2004) Parvalbumin deficiency affects network properties resulting in increased susceptibility to epileptic seizures. Mol Cell Neurosci 25:650–663
Galeano P, Romero JI, Luque-Rojas MJ, Suarez J, Holubiec MI, Bisagno V, Santín LJ, De Fonseca FR et al (2013) Moderate and severe perinatal asphyxia induces differential effects on cocaine sensitization in adult rats. Synapse 67:553–567
Goussakov I, Synowiec S, Yarnykh V, Drobyshevsky A (2019) Immediate and delayed decrease of long term potentiation and memory deficits after neonatal intermittent hypoxia. Int J Dev Neurosci 74:27–37
Wang H, Liu F, Chen W, Sun X, Cui W, Dong Z, Zhao K, Zhang H et al (2018) Genetic recovery of ErbB4 in adulthood partially restores brain functions in null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:13105–13110
Tan GH, Liu YY, Hu XL, Yin DM, Mei L, Xiong ZQ (2011) Neuregulin 1 represses limbic epileptogenesis through ErbB4 in parvalbumin-expressing interneurons. Nat Neurosci 15:258–266
Huang YZ, Won S, Ali DW, Wang Q, Tanowitz M, Du QS, Pelkey KA, Yang DJ et al (2000) Regulation of neuregulin signaling by PSD-95 interacting with ErbB4 at CNS synapses. Neuron 26:443–455
Yau HJ, Wang HF, Lai C, Liu FC (2003) Neural development of the neuregulin receptor ErbB4 in the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus: preferential expression by interneurons tangentially migrating from the ganglionic eminences. Cereb Cortex 13:252–264
Woo RS, Li XM, Tao Y, Carpenter-Hyland E, Huang YZ, Weber J, Neiswender H, Dong XP (2007) Neuregulin-1 enhances depolarization-induced GABA release. Neuron 54:599–610
Wen L, Lu YS, Zhu XH, Li XM, Woo RS, Chen YJ, Yin DM, Lai C et al (2010) Neuregulin 1 regulates pyramidal neuron activity via ErbB4 in parvalbumin-positive interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:1211–1216
Eilam R, Pinkas-Kramarski R, Ratzkin BJ, Segal M, Yarden Y (1998) Activity-dependent regulation of Neu differentiation factor neuregulin expression in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1888–1893
Ozaki M, Itoh K, Miyakawa Y, Kishida H, Hashikawa T (2004) Protein processing and releases of neuregulin-1 are regulated in an activity-dependent manner. J Neurochem 91:176–188
McNamara JO, Huang YZ, Leonard AS (2006) Molecular signaling mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis. Sci Stke 356:re12
Morimoto K, Fahnestock M, Racine RJ (2004) Kindling and status epilepticus models of epilepsy: rewiring the brain. Prog Neurobiol 73:1–60
Holmes GL, Gairsa JL, Chevassus-au-Louis N, Ben-Ari Y (1998) Consequences of neonatal seizures in the rat: morphological and behavioral effects. Ann Neurol 44:845–857
Dube C, Chen K, Eghbal-Ahmadi M, Brunson K, Soltesz I, Baram TZ (2000) Prolonged febrile seizures in the immature rat model enhance hippocampal excitability long term. Ann Neurol 47:336–344
Jensen FE, Applegate CD, Holtzman D, Belin TR, Burchfiel JL (1991) Epileptogenic effect of hypoxia in the immature rodent brain. Ann Neurol 29:629–637
Hei Y, Chen R, Mao X, Wang J, Long Q, Liu W (2019) Neuregulin1 attenuates cognitive deficits and hippocampal CA1 neuronal apoptosis partly viaErbB4 receptor in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Behav Brain Res 365:141–149
Lau D, Vega-Saenz D, Miera EC, Contreras D, Ozaita A, Harvey M, Chow A, Noebels JL et al (2000) Impaired fast-spiking, suppressed cortical inhibition, and increased susceptibility to seizures in mice lacking Kv3.2 K+ channel proteins. J. Neurosci 20:9071–9085
Nithianantharajah J, Hannan AJ (2006) Enriched environments, experience-dependent plasticity and disorders of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:697–709
Wang Y, Liang J, Chen L, Shen Y, Zhao J, Xu C, Wu X, Cheng H et al (2018) Pharmaco-genetic therapeutics targeting parvalbumin neurons attenuate temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 117:149–160
Funding
This work was supported by the grants from the Research Fun of Ruijin Hospital North, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University (No. 2016ZY11) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81701090) and Scientific Research Project of Sichuan Provincial Health Committee (No. 17PJ492)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception: DL and MQZ; research design: MQZ, BBL; collection of data: YFL, YF; data analyses and interpretation: WD and DL; preparation of figures: FFL and YF; manuscript writing: MQZ and BBL.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Teaching Hospital of Chengdu University of T.C.M, Chengdu, China, and was conducted in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines and the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals from the National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, USA).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, D., Fan, F., Ding, W. et al. Increased Seizure Susceptibility for Rats Subject to Early Life Hypoxia Might Be Associated with Brain Dysfunction of NRG1-ErbB4 Signaling in Parvalbumin Interneurons. Mol Neurobiol 57, 5276–5285 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02100-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02100-3