Abstract
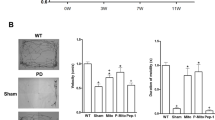
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) gene therapy could offer a disease-modifying treatment for Parkinson’s disease (PD). Here, we report that plasmid DNA nanoparticles (NPs) encoding human GDNF administered intranasally to rats induce transgene expression in the brain and protect dopamine neurons in a model of PD. To first test whether intranasal administration could transfect cells in the brain, rats were sacrificed 1 week after intranasal pGDNF NPs or the naked plasmid. GDNF ELISA revealed significant increases in GDNF expression throughout the brain for both treatments. To assess whether expression was sufficient to protect dopamine neurons, naked pGDNF and pGDNF DNA NPs were given intranasally 1 week before a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion in a rat model of PD. Three to four weeks after the lesion, amphetamine-induced rotational behavior was reduced, and dopaminergic fiber density and cell counts in the lesioned substantia nigra and nerve terminal density in the lesioned striatum were significantly preserved in rats given intranasal pGDNF. The NPs afforded a greater level of neuroprotection than the naked plasmid. These results provide proof-of-principle that intranasal administration of pGDNF DNA NPs can offer a non-invasive, non-viral gene therapy approach for early-stage PD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin LF, Doherty DH, Lile JD, Bektesh S, Collins F (1993) GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science 260(5111):1130–1132
Kirik D, Georgievska B, Bjorklund A (2004) Localized striatal delivery of GDNF as a treatment for Parkinson disease. Nat Neurosci 7(2):105–110. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1175
Tomac A, Lindqvist E, Lin LF, Ogren SO, Young D, Hoffer BJ, Olson L (1995) Protection and repair of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system by GDNF in vivo. Nature 373(6512):335–339. https://doi.org/10.1038/373335a0
Kearns CM, Gash DM (1995) GDNF protects nigral dopamine neurons against 6-hydroxydopamine in vivo. Brain Res 672(1–2):104–111
Love S, Plaha P, Patel NK, Hotton GR, Brooks DJ, Gill SS (2005) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor induces neuronal sprouting in human brain. Nat Med 11(7):703–704. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0705-703
Slevin JT, Gerhardt GA, Smith CD, Gash DM, Kryscio R, Young B (2005) Improvement of bilateral motor functions in patients with Parkinson disease through the unilateral intraputaminal infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosurg 102(2):216–222. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.2.0216
Nutt JG, Burchiel KJ, Comella CL, Jankovic J, Lang AE, Laws ER Jr, Lozano AM, Penn RD et al (2003) Randomized, double-blind trial of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in PD. Neurology 60(1):69–73
Gill SS, Patel NK, Hotton GR, O'Sullivan K, McCarter R, Bunnage M, Brooks DJ, Svendsen CN et al (2003) Direct brain infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson disease. Nat Med 9(5):589–595. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm850
Lang AE, Gill S, Patel NK, Lozano A, Nutt JG, Penn R, Brooks DJ, Hotton G et al (2006) Randomized controlled trial of intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor infusion in Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 59(3):459–466. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20737
Patel NK, Bunnage M, Plaha P, Svendsen CN, Heywood P, Gill SS (2005) Intraputamenal infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in PD: a two-year outcome study. Ann Neurol 57(2):298–302. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20374
Marks WJ Jr, Ostrem JL, Verhagen L, Starr PA, Larson PS, Bakay RA, Taylor R, Cahn-Weiner DA et al (2008) Safety and tolerability of intraputaminal delivery of CERE-120 (adeno-associated virus serotype 2-neurturin) to patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: an open-label, phase I trial. Lancet Neurol 7(5):400–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(08)70065-6
Bartus RT, Baumann TL, Siffert J, Herzog CD, Alterman R, Boulis N, Turner DA, Stacy M et al (2013) Safety/feasibility of targeting the substantia nigra with AAV2-neurturin in Parkinson patients. Neurology 80(18):1698–1701. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182904faa
Stroke NIoNDa (2012) AAV2-GDNF for advanced Parkinson’s disease. National Library of Medicine (US), Bethesda (MD) https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01621581. 2016
Trust NBN (2013) An extension study to assess the safety and efficacy of intermittent bilateral intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) infusions administered via onvection enhanced delivery (CED) in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. European Medicines Agency. https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2013-001881-40/GB. 2016
Thorne RG, Pronk GJ, Padmanabhan V, Frey WH 2nd (2004) Delivery of insulin-like growth factor-I to the rat brain and spinal cord along olfactory and trigeminal pathways following intranasal administration. Neuroscience 127(2):481–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.05.029
Thorne RG, Hanson LR, Ross TM, Tung D, Frey WH 2nd (2008) Delivery of interferon-beta to the monkey nervous system following intranasal administration. Neuroscience 152(3):785–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.013
Dhuria SV, Hanson LR, Frey WH 2nd (2010) Intranasal delivery to the central nervous system: mechanisms and experimental considerations. J Pharm Sci 99(4):1654–1673. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21924
Migliore MM, Vyas TK, Campbell RB, Amiji MM, Waszczak BL (2010) Brain delivery of proteins by the intranasal route of administration: a comparison of cationic liposomes versus aqueous solution formulations. J Pharm Sci 99(4):1745–1761. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21939
Kim ID, Shin JH, Kim SW, Choi S, Ahn J, Han PL, Park JS, Lee JK (2012) Intranasal delivery of HMGB1 siRNA confers target gene knockdown and robust neuroprotection in the postischemic brain. Mol Ther 20(4):829–839. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2011.291
Jiang Y, Wei N, Zhu J, Zhai D, Wu L, Chen M, Xu G, Liu X (2012) A new approach with less damage: intranasal delivery of tetracycline-inducible replication-defective herpes simplex virus type-1 vector to brain. Neuroscience 201:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.10.043
Harmon BT, Aly AE, Padegimas L, Sesenoglu-Laird O, Cooper MJ, Waszczak BL (2014) Intranasal administration of plasmid DNA nanoparticles yields successful transfection and expression of a reporter protein in rat brain. Gene Ther 21(5):514–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2014.28
Bender TS, Migliore MM, Campbell RB, John Gatley S, Waszczak BL (2015) Intranasal administration of glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) rapidly and significantly increases whole-brain GDNF level in rats. Neuroscience 303:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.016
Malerba F, Paoletti F, Capsoni S, Cattaneo A (2011) Intranasal delivery of therapeutic proteins for neurological diseases. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 8(10):1277–1296. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2011.588204
Lochhead JJ, Thorne RG (2012) Intranasal delivery of biologics to the central nervous system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(7):614–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2011.11.002
Aly AE, Waszczak BL (2015) Intranasal gene delivery for treating Parkinson’s disease: overcoming the blood-brain barrier. Expert Opin Drug Deliv:1–19
Li Y, Field PM, Raisman G (2005) Olfactory ensheathing cells and olfactory nerve fibroblasts maintain continuous open channels for regrowth of olfactory nerve fibres. Glia 52(3):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20241
Bedussi B, van der Wel NN, de Vos J, van Veen H, Siebes M, VanBavel E, Bakker EN (2017) Paravascular channels, cisterns, and the subarachnoid space in the rat brain: a single compartment with preferential pathways. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37(4):1374–1385. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678x16655550
Lochhead JJ, Wolak DJ, Pizzo ME, Thorne RG (2015) Rapid transport within cerebral perivascular spaces underlies widespread tracer distribution in the brain after intranasal administration. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35(3):371–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2014.215
Migliore MM, Ortiz R, Dye S, Campbell RB, Amiji MM, Waszczak BL (2014) Neurotrophic and neuroprotective efficacy of intranasal GDNF in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 274:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.019
Thorne RG, Frey WH 2nd (2001) Delivery of neurotrophic factors to the central nervous system: pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet 40(12):907–946. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200140120-00003
Yurek DM, Fletcher AM, Smith GM, Seroogy KB, Ziady AG, Molter J, Kowalczyk TH, Padegimas L et al (2009) Long-term transgene expression in the central nervous system using DNA nanoparticles. Mol Ther 17(4):641–650. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2009.2
Liu G, Li D, Pasumarthy MK, Kowalczyk TH, Gedeon CR, Hyatt SL, Payne JM, Miller TJ et al (2003) Nanoparticles of compacted DNA transfect postmitotic cells. J Biol Chem 278(35):32578–32586. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M305776200
Fink TL, Klepcyk PJ, Oette SM, Gedeon CR, Hyatt SL, Kowalczyk TH, Moen RC, Cooper MJ (2006) Plasmid size up to 20 kbp does not limit effective in vivo lung gene transfer using compacted DNA nanoparticles. Gene Ther 13(13):1048–1051
Ziady AG, Gedeon CR, Miller T, Quan W, Payne JM, Hyatt SL, Fink TL, Muhammad O et al (2003) Transfection of airway epithelium by stable PEGylated poly-L-lysine DNA nanoparticles in vivo. Mol Ther 8(6):936–947
Cai X, Conley SM, Nash Z, Fliesler SJ, Cooper MJ, Naash MI (2010) Gene delivery to mitotic and postmitotic photoreceptors via compacted DNA nanoparticles results in improved phenotype in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. FASEB J 24(4):1178–1191. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-139147
Farjo R, Skaggs J, Quiambao AB, Cooper MJ, Naash MI (2006) Efficient non-viral ocular gene transfer with compacted DNA nanoparticles. PLoS One 1:e38. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000038
Yurek DM, Fletcher AM, McShane M, Kowalczyk TH, Padegimas L, Weatherspoon MR, Kaytor MD, Cooper MJ et al (2011) DNA nanoparticles: detection of long-term transgene activity in brain using bioluminescence imaging. Mol Imaging 10(5):327–339. https://doi.org/10.2310/7290.2010.00053
Fletcher AM, Kowalczyk TH, Padegimas L, Cooper MJ, Yurek DM (2011) Transgene expression in the striatum following intracerebral injections of DNA nanoparticles encoding for human glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuroscience 194:220–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.072
Wang Y, Geng Z, Zhao L, Huang SH, Sheng AL, Chen ZY (2008) GDNF isoform affects intracellular trafficking and secretion of GDNF in neuronal cells. Brain Res 1226:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.05.087
Ungerstedt U (1968) 6-Hydroxy-dopamine induced degeneration of central monoamine neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 5(1):107–110
Ungerstedt U (1973) Selective lesions of central catecholamine pathways: application in functional studies. Neurosci Res (N Y) 5:73–96
Bové J, Prou D, Perier C, Przedborski S (2005) Toxin-induced models of Parkinson’s disease. NeuroRx 2(3):484–494
Zhang Z, Miyoshi Y, Lapchak PA, Collins F, Hilt D, Lebel C, Kryscio R, Gash DM (1997) Dose response to intraventricular glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor administration in parkinsonian monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282(3):1396–1401
Manfredsson FP, Tumer N, Erdos B, Landa T, Broxson CS, Sullivan LF, Rising AC, Foust KD et al (2009) Nigrostriatal rAAV-mediated GDNF overexpression induces robust weight loss in a rat model of age-related obesity. Mol Ther 17(6):980–991. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2009.45
Olanow CW, Bartus RT, Volpicelli-Daley LA, Kordower JH (2015) Trophic factors for Parkinson’s disease: to live or let die. Mov Disord 30(13):1715–1724. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26426
Yurek D, Hasselrot U, Sesenoglu-Laird O, Padegimas L, Cooper M (2017) Intracerebral injections of DNA nanoparticles encoding for a therapeutic gene provide partial neuroprotection in an animal model of neurodegeneration. Nanomedicine 13(7):2209–2217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2017.06.010
Okragly AJ, Haak-Frendscho M (1997) An acid-treatment method for the enhanced detection of GDNF in biological samples. Exp Neurol 145(2 Pt 1):592–596. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1997.6500
Lin LF, Zhang TJ, Collins F, Armes LG (1994) Purification and initial characterization of rat B49 glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurochem 63(2):758–768
Georgievska B, Kirik D, Bjorklund A (2002) Aberrant sprouting and downregulation of tyrosine hydroxylase in lesioned nigrostriatal dopamine neurons induced by long-lasting overexpression of glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor in the striatum by lentiviral gene transfer. Exp Neurol 177(2):461–474
Rosenblad C, Georgievska B, Kirik D (2003) Long-term striatal overexpression of GDNF selectively downregulates tyrosine hydroxylase in the intact nigrostriatal dopamine system. Eur J Neurosci 17(2):260–270
Georgievska B, Kirik D, Bjorklund A (2004) Overexpression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor using a lentiviral vector induces time- and dose-dependent downregulation of tyrosine hydroxylase in the intact nigrostriatal dopamine system. J Neurosci 24(29):6437–6445. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1122-04.2004
Eslamboli A, Georgievska B, Ridley RM, Baker HF, Muzyczka N, Burger C, Mandel RJ, Annett L et al (2005) Continuous low-level glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor delivery using recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors provides neuroprotection and induces behavioral recovery in a primate model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 25(4):769–777. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4421-04.2005
Redmond DE Jr, McEntire CR, Kingsbery JP, Leranth C, Elsworth JD, Bjugstad KB, Roth RH, Samulski RJ et al (2013) Comparison of fetal mesencephalic grafts, AAV-delivered GDNF, and both combined in an MPTP-induced nonhuman primate Parkinson’s model. Mol Ther 21(12):2160–2168. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2013.180
Kozlowski DA, Miljan EA, Bremer EG, Harrod CG, Gerin C, Connor B, George D, Larson B et al (2004) Quantitative analyses of GFRalpha-1 and GFRalpha-2 mRNAs and tyrosine hydroxylase protein in the nigrostriatal system reveal bilateral compensatory changes following unilateral 6-OHDA lesions in the rat. Brain Res 1016(2):170–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2004.05.003
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the expertise and technical assistance of Alexandra Christodoulou in performing the BIOQUANT analyses of microscopic images.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research and a Northeastern University Tier 1 grant (BLW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of Interests
AEA, BTH, and BLW declare no conflict of interest. MJC and OSL are current employees of Copernicus Therapeutics, and LP is a past employee. MJC and OSL hold stock/stock options in the company.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aly, A.EE., Harmon, B.T., Padegimas, L. et al. Intranasal Delivery of pGDNF DNA Nanoparticles Provides Neuroprotection in the Rat 6-Hydroxydopamine Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 56, 688–701 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1109-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1109-6