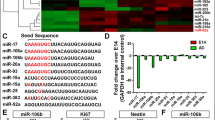
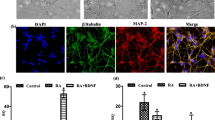
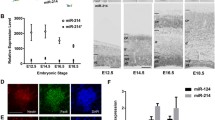
Abstract
Neuronal PAS domain protein 4 (Npas4) is a brain-specific transcription factor whose expression is enriched in neurogenic regions of the brain. In addition, it was demonstrated that Npas4 expression is dynamic and highly regulated during neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells (ESCs). While these findings implicate a role for Npas4 in neurogenesis, the underlying mechanisms of regulation remain unknown. Given that growing evidence suggests that microRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in both embryonic and adult neurogenesis, we reasoned that miRNAs are good candidates for regulating Npas4 expression during neural differentiation of ESCs. In this study, we utilized the small RNA sequencing method to profile miRNA expression during neural differentiation of mouse ESCs. Two differentially expressed miRNAs were identified to be able to significantly reduce reporter gene activity by targeting the Npas4 3’UTR, namely miR-744 and miR-224. More importantly, ectopic expression of these miRNAs during neural differentiation resulted in downregulation of endogenous Npas4 expression. Subsequent functional analysis revealed that overexpression of either miR-744 or miR-224 delayed early neural differentiation, reduced GABAergic neuron production and inhibited neurite outgrowth. Collectively, our findings indicate that Npas4 not only functions at the early stages of neural differentiation but may also, in part, contribute to neuronal subtype specification and neurite development.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flood WD, Moyer RW, Tsykin A, Sutherland GR, Koblar SA (2004) Nxf and Fbxo33: novel seizure-responsive genes in mice. Eur J Neurosci 20(7):1819–1826. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03646.x
Moser M, Knoth R, Bode C, Patterson C (2004) LE-PAS, a novel Arnt-dependent HLH-PAS protein, is expressed in limbic tissues and transactivates the CNS midline enhancer element. Mol Brain Res 128(2):141–149. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.06.023
Ooe N, Saito K, Mikami N, Nakatuka I, Kaneko H (2004) Identification of a novel basic helix-loop-helix-PAS factor, NXF, reveals a Sim2 competitive, positive regulatory role in dendritic-cytoskeleton modulator Drebrin gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 24(2):608–616. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.2.608-616.2004
Kewley RJ, Whitelaw ML, Chapman-Smith A (2004) The mammalian basic helix-loop-helix/PAS family of transcriptional regulators. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(2):189–204. doi:10.1016/s1357-2725(03)00211-5
Hester I, McKee S, Pelletier P, Thompson C, Storbeck C, Mears A, Schulz JB, Hakim AA, Sabourin LA (2007) Transient expression of Nxf, a bHLH-PAS transactivator induced by neuronal preconditioning, confers neuroprotection in cultured cells. Brain Res 1135(1):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.11.083
Shamloo M, Soriano L, von Schack D, Rickhag M, Chin DJ, Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Gido G, Urfer R, Wieloch T, Nikolich K (2006) Npas4, a novel helix-loop-helix PAS domain protein, is regulated in response to cerebral ischemia. Eur J Neurosci 24(10):2705–2720. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05172.x
Lin Y, Bloodgood BL, Hauser JL, Lapan AD, Koon AC, Kim T-K, Hu LS, Malik AN, Greenberg ME (2008) Activity-dependent regulation of inhibitory synapse development by Npas4. Nature 455(7217):1198–1204. doi:10.1038/nature07319
Zhang S-J, Zou M, Lu L, Lau D, Ditzel DAW, Delucinge-Vivier C, Aso Y, Descombes P, Bading H (2009) Nuclear calcium signaling controls expression of a large gene pool: identification of a gene program for acquired neuroprotection induced by synaptic activity. PLoS Genet 5(8):e1000604. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000604
Spiegel I, Mardinly AR, Gabel HW, Bazinet JE, Couch CH, Tzeng CP, Harmin DA, Greenberg ME (2014) Npas4 regulates excitatory-inhibitory balance within neural circuits through cell-type-specific gene programs. Cell 157(5):1216–1229. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.058
Leong WK, Klaric TS, Lin Y, Lewis MD, Koblar SA (2013) Upregulation of the neuronal Per-Arnt-Sim domain protein 4 (Npas4) in the rat corticolimbic system following focal cerebral ischemia. Eur J Neurosci 37(11):1875–1884. doi:10.1111/ejn.12163
Bloodgood BL, Sharma N, Browne HA, Trepman AZ, Greenberg ME (2013) The activity-dependent transcription factor NPAS4 regulates domain-specific inhibition. Nature 503(7474):121–125. doi:10.1038/nature12743
Pruunsild P, Sepp M, Orav E, Koppel I, Timmusk T (2011) Identification of cis-elements and transcription factors regulating neuronal activity-dependent transcription of human BDNF gene. J Neurosci 31(9):3295–3308. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.4540-10.2011
Ji W, Zhang X, Ji L, Wang K, Qiu Y (2015) Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 on the neuronal differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells. Mol Med Report 12(4):4981–4988. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.4099
Lee J, Duan W, Mattson MP (2002) Evidence that brain‐derived neurotrophic factor is required for basal neurogenesis and mediates, in part, the enhancement of neurogenesis by dietary restriction in the hippocampus of adult mice. J Neurochem 82(6):1367–1375. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.01085.x
Vicario-Abejón C, Johe KK, Hazel TG, Collazo D, McKay RD (1995) Functions of basic fibroblast growth factor and neurotrophins in the differentiation of hippocampal neurons. Neuron 15(1):105–114. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(95)90068-3
Klaric TS, Thomas PQ, Dottori M, Leong WK, Koblar SA, Lewis MD (2014) A reduction in Npas4 expression results in delayed neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 5(3):64. doi:10.1186/scrt453
Mehler MF, Mattick JS (2007) Noncoding RNAs and RNA editing in brain development, functional diversification, and neurological disease. Physiol Rev 87(3):799–823. doi:10.1152/physrev.00036.2006
Chekulaeva M, Filipowicz W (2009) Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in animal cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21(3):452–460. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.04.009
Flynt AS, Lai EC (2008) Biological principles of microRNA-mediated regulation: shared themes amid diversity. Nat Rev Genet 9(11):831–842. doi:10.1038/nrg2455
Chang T-C, Mendell JT (2007) microRNAs in vertebrate physiology and human disease. In: Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics, vol 8. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. pp 215–239. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.8.080706.092351
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6(4):259–269. doi:10.1038/nrc1840
Hsu JB-K, Chiu C-M, Hsu S-D, Huang W-Y, Chien C-H, Lee T-Y, Huang H-D (2011) miRTar: an integrated system for identifying miRNA-target interactions in human. BMC Bioinformatics 12:300. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-300
Sempere LF, Freemantle S, Pitha-Rowe I, Moss E, Dmitrovsky E, Ambros V (2004) Expression profiling of mammalian microRNAs uncovers a subset of brain-expressed microRNAs with possible roles in murine and human neuronal differentiation. Genome Biol 5 (3). doi:2004/5/3/R13
Krichevsky AM, Sonntag K-C, Isacson O, Kosik KS (2006) Specific microRNAs modulate embryonic stem cell-derived neurogenesis. Stem Cells 24(4):857–864. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2005-0441
Packer AN, Xing Y, Harper SQ, Jones L, Davidson BL (2008) The bifunctional microRNA miR-9/miR-9*regulates REST and CoREST and is downregulated in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 28(53):14341–14346. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2390-08.2008
Cheng L-C, Pastrana E, Tavazoie M, Doetsch F (2009) miR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Nat Neurosci 12(4):399–408. doi:10.1038/nn.2294
Choi PS, Zakhary L, Choi W-Y, Caron S, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Miska EA, McManus M, Harfe B, Giraldez AJ, Horvitz RH, Schier AF, Dulac C (2008) Members of the miRNA-200 family regulate olfactory neurogenesis. Neuron 57(1):41–55. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.018
Ivey KN, Srivastava D (2010) MicroRNAs as regulators of differentiation and cell fate decisions. Cell Stem Cell 7(1):36–41. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.06.012
Li X, Jin P (2010) Roles of small regulatory RNAs in determining neuronal identity. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(5):329–338. doi:10.1038/nrn2739
Liu S-P, Fu R-H, Yu H-H, Li K-W, Tsai C-H, Shyu W-C, Lin S-Z (2009) MicroRNAs regulation modulated self-renewal and lineage differentiation of stem cells. Cell Transplant 18(9):1039–1045. doi:10.3727/096368909x471224
Olsen L, Klausen M, Helboe L, Nielsen FC, Werge T (2009) MicroRNAs show mutually exclusive expression patterns in the brain of adult male rats. PLoS One 4(10):e7225. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007225
Bersten DC, Wright JA, McCarthy PJ, Whitelaw ML (2014) Regulation of the neuronal transcription factor NPAS4 by REST and microRNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839(1):13–24. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.11.004
Hsu P-K, Xu B, Mukai J, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA (2015) The BDNF Val66Met variant affects gene expression through miR-146b. Neurobiol Dis 77:228–237. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2015.03.004
Ying Q-L, Stavridis M, Griffiths D, Li M, Smith A (2003) Conversion of embryonic stem cells into neuroectodermal precursors in adherent monoculture. Nat Biotechnol 21(2):183–186. doi:10.1038/nbt780
Rathjen J, Lake J-A, Bettess MD, Washington JM, Chapman G, Rathjen PD (1999) Formation of a primitive ectoderm like cell population, EPL cells, from ES cells in response to biologically derived factors. J Cell Sci 112(5):601–612
Ying Q-L, Smith AG (2003) Defined conditions for neural commitment and differentiation. Methods Enzymol 365:327–341. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(03)65023-8
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnetjourna 17:10–12
Griffiths-Jones S (2006) miRBase: the microRNA sequence database. In: MicroRNA Protocols. Springer, pp 129–138. doi:10.1385/1-59745-123-1:129
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25(14):1754–1760. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W (2015) HTSeq-a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31(2):166–169. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26(1):139–140. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Pool M, Thiemann J, Bar-Or A, Fournier AE (2008) NeuriteTracer: a novel ImageJ plugin for automated quantification of neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci Methods 168(1):134–139. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.08.029
Stappert L, Roese-Koerner B, Bruestle O (2015) The role of microRNAs in human neural stem cells, neuronal differentiation and subtype specification. Cell Tissue Res 359(1):47–64. doi:10.1007/s00441-014-1981-y
Van Ooyen A (2005) Competition in neurite outgrowth and the development of nerve connections. In: VanPelt J, Kamermans M, Levelt CN, VanOoyen A, Ramakers GJA, Roelfsema PR (eds) Development, Dynamics and Pathology of Neuronal Networks: From Molecules to Functional Circuits, vol 147. Progress in Brain Research. pp 81–99. doi:10.1016/s0079-6123(04)47007-1
Forrest AR, Kanamori-Katayama M, Tomaru Y, Lassmann T, Ninomiya N, Takahashi Y, de Hoon MJ, Kubosaki A, Kaiho A, Suzuki M (2010) Induction of microRNAs, mir-155, mir-222, mir-424 and mir-503, promotes monocytic differentiation through combinatorial regulation. Leukemia 24(2):460–466. doi:10.1038/leu.2009.246
Nachmani D, Lankry D, Wolf DG, Mandelboim O (2010) The human cytomegalovirus microRNA miR-UL112 acts synergistically with a cellular microRNA to escape immune elimination. Nat Immunol 11(9):806–813. doi:10.1038/ni.1916
Wu S, Huang S, Ding J, Zhao Y, Liang L, Liu T, Zhan R, He X (2010) Multiple microRNAs modulate p21Cip1/Waf1 expression by directly targeting its 3′ untranslated region. Oncogene 29(15):2302–2308. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.34
Yun J, Koike H, Ibi D, Toth E, Mizoguchi H, Nitta A, Yoneyama M, Ogita K, Yoneda Y, Nabeshima T, Nagai T, Yamada K (2010) Chronic restraint stress impairs neurogenesis and hippocampus-dependent fear memory in mice: possible involvement of a brain-specific transcription factor Npas4. J Neurochem 114(6):1840–1851. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06893.x
Klaric T, Lardelli M, Key B, Koblar S, Lewis M (2014) Activity-dependent expression of neuronal PAS domain-containing protein 4 (npas4a) in the develop zebrafish brain. Front Neuroanat 8:148. doi:10.3389/fnana.2014.00148
Gogolla N, LeBlanc JJ, Quast KB, Südhof TC, Fagiolini M, Hensch TK (2009) Common circuit defect of excitatory-inhibitory balance in mouse models of autism. J Neurodev Disord 1(2):172–181. doi:10.1007/s11689-009-9023-x
Meechan DW, Tucker ES, Maynard TM, LaMantia A-S (2009) Diminished dosage of 22q11 genes disrupts neurogenesis and cortical development in a mouse model of 22q11 deletion/DiGeorge syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(38):16434–16445. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905696106
Morrow EM, Yoo S-Y, Flavell SW, Kim T-K, Lin Y, Hill RS, Mukaddes NM, Balkhy S, Gascon G, Hashmi A (2008) Identifying autism loci and genes by tracing recent shared ancestry. Science 321(5886):218–223. doi:10.1126/science.1157657
Jessberger S, Gage FH (2014) Adult neurogenesis: bridging the gap between mice and humans. Trends Cell Biol 24(10):558–563. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2014.07.003
Yun J, Nagai T, Furukawa-Hibi Y, Kuroda K, Kaibuchi K, Greenberg ME, Yamada K (2013) Neuronal Per Arnt Sim (PAS) domain protein 4 (NPAS4) regulates neurite outgrowth and phosphorylation of synapsin I. J Biol Chem 288(4):2655–2664. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.413310
S-i Y, Takahashi H, Nishimura N, Kinoshita M, Asahina R, Kitsuki M, Tatsumi K, Furukawa-Hibi Y, Hirai H, Nagai T, Yamada K, Tsuboi A (2014) Npas4 regulates Mdm2 and thus Dcx in experience-dependent dendritic spine development of newborn olfactory bulb interneurons. Cell Rep 8(3):843–857. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.056
Roberts RC (2007) Schizophrenia in translation: disrupted in schizophrenia (DISC1): integrating clinical and basic findings. Schizophr Bull 33(1):11. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbl063
Bersten DC, Bruning JB, Peet DJ, Whitelaw ML (2014) Human variants in the neuronal basic Helix-Loop-Helix/Per-Arnt-Sim (bHLH/PAS) transcription factor complex NPAS4/ARNT2 disrupt function. PLoS One 9(1):768. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085768
Coutellier L, Beraki S, Ardestani PM, Saw NL, Shamloo M (2012) Npas4: a neuronal transcription factor with a key role in social and cognitive functions relevant to developmental disorders. PLoS One 7(9):6604. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046604
Beveridge NJ, Cairns MJ (2012) MicroRNA dysregulation in schizophrenia. Neurobiol Dis 46(2):263–271. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.029
Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, Lee KW (2011) MicroRNA expression profiling in neurogenesis of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. J Genet 90(1):81–93. doi:10.1007/s12041-011-0041-6
Knelangen JM, van der Hoek MB, Kong W-C, Owens JA, Fischer B, Santos AN (2011) MicroRNA expression profile during adipogenic differentiation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Physiol Genomics 43(10):611–620. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00116.2010
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2002) Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med 8(9):963–970. doi:10.1038/nm747
Lee S-T, Chu K, Jung K-H, Yoon H-J, Jeon D, Kang K-M, Park K-H, Bae E-K, Kim M, Lee SK (2010) MicroRNAs induced during ischemic preconditioning. Stroke 41(8):1646–1651. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.579649
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M (2005) Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37(5):495–500. doi:10.1038/ng1536
Gribaudo S, Bovetti S, Friard O, Denorme M, Oboti L, Fasolo A, De Marchis S (2012) Transitory and activity‐dependent expression of neurogranin in olfactory bulb tufted cells during mouse postnatal development. J Comp Neurol 520(14):3055–3069. doi:10.1002/cne.23150
Ule J, Ule A, Spencer J, Williams A, Hu J-S, Cline M, Wang H, Clark T, Fraser C, Ruggiu M (2005) Nova regulates brain-specific splicing to shape the synapse. Nat Genet 37(8):844–852. doi:10.1038/ng1610
Blaesse P, Airaksinen MS, Rivera C, Kaila K (2009) Cation-chloride cotransporters and neuronal function. Neuron 61(6):820–838. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.003
Xu B, Hsu P-K, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA (2012) MicroRNA dysregulation in neuropsychiatric disorders and cognitive dysfunction. Neurobiol Dis 46(2):291–301. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2012.02.016
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank David Lawrence for his preliminary work on RNA-seq data analysis. F.C.C was supported by the Adelaide Graduate Research Scholarship from the University of Adelaide.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 228 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choy, F.C., Klarić, T.S., Koblar, S.A. et al. miR-744 and miR-224 Downregulate Npas4 and Affect Lineage Differentiation Potential and Neurite Development During Neural Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Mol Neurobiol 54, 3528–3541 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9912-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9912-4