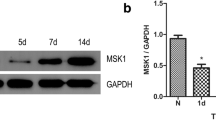
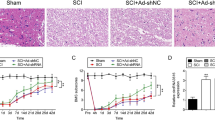
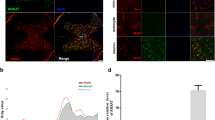
Abstract
The aim of our research is to investigate the regulatory role of TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis- fibroblast growth factor–inducible 14 (TWEAK-Fn14) pathway in nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) expression and neurogenesis status after spinal cord injury (SCI). We constructed a mice model of spinal cord injury and injected different lentiviral vectors which were transfected with TWEAK, TWEAK small interfering RNA (siRNA) and Fn14 siRNA into different groups of mice. Locomotor functional recovery status of the hind limb in mice was assessed using the Basso, Beattie and Bresnahan (BBB) test. Apoptosis status in the injured area was examined via TDT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end-labeling (TUNEL) staining, the expression of GAP-43 in injured spinal cord was quantified by immunohistochemistry and expressions of TWEAK, Fn14, NF-κB, TNF-α, and IL-1β were evaluated by either western blot or ELISA. The expressions of TWEAK, Fn14, and NF-κB in the model group were significantly higher compared with those in the control group. Furthermore, the TWEAK group in which TWEAK was overexpressed exhibited significantly higher expressions of TWEAK, Fn14, and NF-κB, TNF-α and IL-1β in relation to those in the model group (P < 0.05 for all). Moreover, the transfection of Fn14 siRNA antagonized the above effect of TWEAK transfection on injured mice. On the other hand, the TWEAK siRNA group in which the expression of TWEAK was inhibited exhibited significantly lower expressions of TWEAK, Fn14, NF-κB, TNF-α, and IL-1β (P < 0.05 for all). Moreover, the transfection of TWEAK siRNA enhanced the locomotor functional recovery status in injured mice and suppressed the apoptosis of injured areas (P < 0.05 for all). In conclusion, stimulating the TWEAK-Fn14 pathway may elevate the expression of NF-κB, thereby slow the function recovery of SCI mice whereas inhibiting the TWEAK-Fn14 pathway may improve the neurogenesis status in mice with spinal cord injuries.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 May 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02424-8
Abbreviations
- SCI:
-
Spinal cord injury
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin 1β
- TWEAK:
-
TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis
- Fn14:
-
Fibroblast growth factor–inducible 14
- SPF:
-
Specific pathogen free
- RT-PCR:
-
Real time-PCR
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene fluoride
- TBS-T:
-
Tris-buffered saline with Tween
- DPI:
-
Day post injury
References
Maegele M, Riess P, Sauerland S, Bouillon B, Hess S, McIntosh TK, Mautes A, Brockmann M et al (2005) Characterization of a new rat model of experimental combined neurotrauma. Shock 23(5):476–481
Beattie MS, Li Q, Bresnahan JC (2000) Cell death and plasticity after experimental spinal cord injury. Prog Brain Res 128:9–21. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(00)28003-5
Hausmann ON (2003) Post-traumatic inflammation following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 41(7):369–378. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3101483
Wei HY, Ma X (2014) Tamoxifen reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells, apoptosis and inhibits IKK/NF-kB pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurol Sci 35(11):1763–1768. doi:10.1007/s10072-014-1828-z
Han X, Lu M, Wang S, Lv D, Liu H (2012) Targeting IKK/NF-kappaB pathway reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells and apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett 511(1):28–32. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.01.030
Okamoto K, Martin DP, Schmelzer JD, Mitsui Y, Low PA (2001) Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in rat sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol 169(2):386–391. doi:10.1006/exnr.2001.7677
Liu G, Fan G, Guo G, Kang W, Wang D, Xu B, Zhao J (2016) FK506 attenuates the inflammation in rat spinal cord injury by inhibiting the activation of NF-kappaB in microglia cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s10571-016-0422-8
Xie W, Liu X, Xuan H, Luo S, Zhao X, Zhou Z, Xu J (2006) Effect of betamethasone on neuropathic pain and cerebral expression of NF-kappaB and cytokines. Neurosci Lett 393(2–3):255–259. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.09.077
Wiley SR, Winkles JA (2003) TWEAK, a member of the TNF superfamily, is a multifunctional cytokine that binds the TweakR/Fn14 receptor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14(3–4):241–249
Tirnitz-Parker JE, Viebahn CS, Jakubowski A, Klopcic BR, Olynyk JK, Yeoh GC, Knight B (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis is a mitogen for liver progenitor cells. Hepatology 52(1):291–302. doi:10.1002/hep.23663
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3(3):221–227. doi:10.1038/ni0302-221
Chen HN, Wang DJ, Ren MY, Wang QL, Sui SJ (2012) TWEAK/Fn14 promotes the proliferation and collagen synthesis of rat cardiac fibroblasts via the NF-small ka, CyrillicB pathway. Mol Biol Rep 39(8):8231–8241. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-1671-3
Ensign SP, Roos A, Mathews IT, Dhruv HD, Tuncali S, Sarkaria JN, Symons MH, Loftus JC et al (2016) SGEF is regulated via TWEAK/Fn14/NF-kappaB signaling and promotes survival by modulation of the DNA repair response to temozolomide. Mol Cancer Res 14(3):302–312. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0183
Lee JY, Kim HS, Choi HY, Oh TH, Yune TY (2012) Fluoxetine inhibits matrix metalloprotease activation and prevents disruption of blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury. Brain 135(Pt 8):2375–2389. doi:10.1093/brain/aws171
Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC (1995) A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma 12(1):1–21. doi:10.1089/neu.1995.12.1
Sasaki M, Hains BC, Lankford KL, Waxman SG, Kocsis JD (2006) Protection of corticospinal tract neurons after dorsal spinal cord transection and engraftment of olfactory ensheathing cells. Glia 53(4):352–359. doi:10.1002/glia.20285
Liu D, Huang Y, Li B, Jia C, Liang F, Fu Q (2015) Carvedilol promotes neurological function, reduces bone loss and attenuates cell damage after acute spinal cord injury in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 42(2):202–212. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.12345
Lee JY, Na WH, Choi HY, Lee KH, Ju BG, Yune TY (2016) Jmjd3 mediates blood-spinal cord barrier disruption after spinal cord injury by regulating MMP-3 and MMP-9 expressions. Neurobiol Dis 95:66–81. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2016.07.015
Kaplin AI, Deshpande DM, Scott E, Krishnan C, Carmen JS, Shats I, Martinez T, Drummond J et al (2005) IL-6 induces regionally selective spinal cord injury in patients with the neuroinflammatory disorder transverse myelitis. J Clin Invest 115(10):2731–2741. doi:10.1172/JCI25141
Kim S, Steelman AJ, Koito H, Li J (2011) Astrocytes promote TNF-mediated toxicity to oligodendrocyte precursors. J Neurochem 116(1):53–66. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07084.x
Hanada T, Yoshimura A (2002) Regulation of cytokine signaling and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13(4–5):413–421
Yamana J, Morand EF, Manabu T, Sunahori K, Takasugi K, Makino H, Yamamura M (2012) Inhibition of TNF-induced IL-6 by the TWEAK-Fn14 interaction in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast like synoviocytes. Cell Immunol 272(2):293–298. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.09.004
Burkly LC, Michaelson JS, Hahm K, Jakubowski A, Zheng TS (2007) TWEAKing tissue remodeling by a multifunctional cytokine: role of TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in health and disease. Cytokine 40(1):1–16. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2007.09.007
Yepes M (2007) TWEAK and the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 35(3):255–265
Wen X, Peng Z, Li Y, Wang H, Bishop JV, Chedwick LR, Singbartl K, Kellum JA (2012) One dose of cyclosporine A is protective at initiation of folic acid-induced acute kidney injury in mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27(8):3100–3109. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfr766
Sanz AB, Sanchez-Nino MD, Ortiz A (2011) TWEAK, a multifunctional cytokine in kidney injury. Kidney Int 80(7):708–718. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.180
Hung CC, Lin CH, Chang H, Wang CY, Lin SH, Hsu PC, Sun YY, Lin TN et al (2016) Astrocytic GAP43 induced by the TLR4/NF-kappaB/STAT3 axis attenuates astrogliosis-mediated microglial activation and neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 36(6):2027–2043. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3457-15.2016
Whitsett TG, Mathews IT, Cardone MH, Lena RJ, Pierceall WE, Bittner M, Sima C, LoBello J et al (2014) Mcl-1 mediates TWEAK/Fn14-induced non-small cell lung cancer survival and therapeutic response. Mol Cancer Res 12(4):550–559. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0458
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (81201740) and the program sponsored by the Science and Technology Department of Hunan, China (2012FJ6075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., He, J., He, H. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: TWEAK-Fn14 Influences Neurogenesis Status via Modulating NF-κB in Mice with Spinal Cord Injury. Mol Neurobiol 54, 7497–7506 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0248-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0248-x