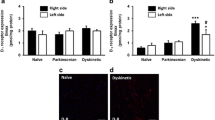
Abstract
Dopamine receptors in striatum are important for healthy brain functioning and are the target of levodopa-based therapy in Parkinson’s disease. Lateralization of dopaminergic neurotransmission in striata from different hemispheres occurs in patients, but also in healthy individuals. Our data show that the affinity of dopamine binding to dopamine D1 receptors is significantly higher in left than in right striatum. Analysis of data from radioligand binding to striatal samples from naïve, 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned, levodopa-treated and levodopa-induced dyskinetic rats shows differential receptor structure and gives hints on the causes of right/left lateralization of dopamine binding to striatal D1 receptors. Moreover, binding data showed loss of lateralization in levodopa (L-DOPA)-induced dyskinetic rats.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frasnelli E (2013) Brain and behavioural lateralization in invertebrates. Front Psychol 4:939
Heinsen H, Henn R, Eisenmenger W, Gotz M, Bohl J, Bethke B, Lockemann U, Puschel K (1994) Quantitative investigations on the human entorhinal area: left-right asymmetry and age-related changes. Anat Embryol (Berl) 190(2):181–194
Glick SD, Lyon RA, Hinds PA, Sowek C, Titeler M (1988) Correlated asymmetries in striatal D1 and D2 binding: relationship to apomorphine-induced rotation. Brain Res 455(1):43–48
Pandey P, Mersha MD, Dhillon HS (2013) A synergistic approach towards understanding the functional significance of dopamine receptor interactions. J Mol Signal 8(1):13
Navarro G, Ferré S, Cordomi A, Moreno E, Mallol J, Casadó V, Cortés A, Hoffmann H et al (2010) Interactions between intracellular domains as key determinants of the Quaternary structure and function of receptor heteromers. J Biol Chem 285(35):27346–27359
Orru M, Bakešová J, Brugarolas M, Quiroz C, Beaumont V, Goldberg SR, Lluís C, Cortés A et al (2011) Striatal pre- and postsynaptic profile of adenosine A(2A) receptor antagonists. PLoS One 6(1):e16088
Glick SD, Ross DA, Hough LB (1982) Lateral asymmetry of neurotransmitters in human brain. Brain Res 234(1):53–63
Thiel CM, Schwarting RKW (2001) Dopaminergic lateralisation in the forebrain: relations to behavioural asymmetries and anxiety in male Wistar rats. Neuropsychobiology 43(3):192–199
Schwarting RKW, Borta A (2005) Analysis of behavioral asymmetries in the elevated plus-maze and in the T-maze. J Neurosci Methods 141(2):251–260
Nikkhah G, Falkenstein G, Rosenthal C (2001) Restorative plasticity of dopamine neuronal transplants depends on the degree of hemispheric dominance. J Neurosci 21(16):6252–6263
Martin-Soelch C, Szczepanik J, Nugent A, Barhaghi K, Rallis D, Herscovitch P, Carson RE, Drevets WC (2011) Lateralization and gender differences in the dopaminergic response to unpredictable reward in the human ventral striatum. Eur J Neurosci 33(9):1706–1715
Larisch R, Meyer W, Klimke A, Kehren F, Vosberg H, Muller-Gartner HW (1998) Left-right asymmetry of striatal dopamine D2 receptors. Nucl Med Commun 19(8):781–787
Cho SS, Yoon EJ, Kim SE (2015) Asymmetry of dopamine D2/3 receptor availability in dorsal putamen and body mass index in non-obese healthy males. Exp Neurobiol 24(1):90–94
Tomer R, Slagter HA, Christian BT, Fox AS, King CR, Murali D, Gluck MA, Davidson RJ (2013) Love to win or hate to lose? Asymmetry of dopamine D2 receptor binding predicts sensitivity to reward versus punishment. J Cogn Neurosci 26(5):1039–1048
Tomer R, Goldstein RZ, Wang G-J, Wong C, Volkow ND (2008) Incentive motivation is associated with striatal dopamine asymmetry. Biol Psychol 77(1):98–101
Marin C, Bonastre M, Mengod G, Cortés R, Rodríguez-Oroz MC (2015) From unilateral to bilateral parkinsonism: Effects of lateralization on dyskinesias and associated molecular mechanisms. Neuropharmacology 97:365–375
Farré D, Muñoz A, Moreno E, Reyes-Resina I, Canet-Pons J, Dopeso-Reyes IG, Rico AJ, Lluis C et al (2015) Stronger dopamine D1 receptor-mediated neurotransmission in dyskinesia. Mol Neurobiol 52:1408–1420. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8936-x
Cenci MA, Lee CS, Björklund A (1998) L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the rat is associated with striatal overexpression of prodynorphin- and glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA. Eur J Neurosci 10(8):2694–2706
Casadó V, Ferrada C, Bonaventura J, Gracia E, Mallol J, Canela EI, Lluís C, Cortés A et al (2009) Useful pharmacological parameters for G-protein-coupled receptor homodimers obtained from competition experiments. Agonist–antagonist binding modulation. Biochem Pharmacol 78(12):1456–1463
Casadó V, Cortés A, Ciruela F, Mallol J, Ferré S, Lluis C, Canela EI, Franco R (2007) Old and new ways to calculate the affinity of agonists and antagonists interacting with G-protein-coupled monomeric and dimeric receptors: the receptor–dimer cooperativity index. Pharmacol Ther 116(3):343–354
Franco R, Casadó V, Mallol J, Ferrada C, Ferré S, Fuxe K, Cortés A, Ciruela F et al (2006) The two-state dimer receptor model: a general model for receptor dimers. Mol Pharmacol 69(6):1905–1912
Casadó V, Canti C, Mallol J, Canela EI, Lluis C, Franco R (1990) Solubilization of A1 adenosine receptor from pig brain: characterization and evidence of the role of the cell membrane on the coexistence of high- and low-affinity states. J Neurosci Res 26(4):461–473
Lee SP, So CH, Rashid AJ, Varghese G, Cheng R, Lança AJ, O'Dowd BF, George SR (2004) Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor co-activation generates a novel phospholipase C-mediated calcium signal. J Biol Chem 279(34):35671–35678
Rashid AJ, So CH, Kong MMC, Furtak T, El-Ghundi M, Cheng R, O'Dowd BF, George SR (2007) D1–D2 dopamine receptor heterooligomers with unique pharmacology are coupled to rapid activation of Gq/11 in the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(2):654–659
Chun LS, Free RB, Doyle TB, Huang X-P, Rankin ML, Sibley DR (2013) D1-D2 dopamine receptor synergy promotes calcium signaling via multiple mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol 84(2):190–200
Jin L-Q, Wang H-Y, Friedman E (2001) Stimulated D1 dopamine receptors couple to multiple Gα proteins in different brain regions. J Neurochem 78(5):981–990
Mannoury-la-Cour C, Vidal S, Pasteau V, Cussac D, Millan MJ (2007) Dopamine D1 receptor coupling to Gs/olf and Gq in rat striatum and cortex: a scintillation proximity assay (SPA)/antibody-capture characterization of benzazepine agonists. Neuropharmacology 52(3):1003–1014
May LT, Bridge LJ, Stoddart LA, Briddon SJ, Hill SJ (2011) Allosteric interactions across native adenosine-A3 receptor homodimers: quantification using single-cell ligand-binding kinetics. FASEB J 25(10):3465–3476
Yamamoto BK, Lane RF, Freed CR (1982) Normal rats trained to circle show asymmetric caudate dopamine release. Life Sci 30(25):2155–2162
Cannon DM, Klaver JM, Peck SA, Rallis-Voak D, Erickson K, Drevets WC (2008) Dopamine type-1 receptor binding in major depressive disorder assessed using positron emission tomography and [lsqb]11C[rsqb]NNC-112. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(5):1277–1287
Ryoo HL, Pierrotti D, Joyce JN (1998) Dopamine D3 receptor is decreased and D2 receptor is elevated in the striatum of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 13(5):788–797
Hurley MJ, Mash DC, Jenner P (2001) Dopamine D1 receptor expression in human basal ganglia and changes in Parkinson’s disease1. Mol Brain Res 87(2):271–279
Boileau I, Guttman M, Rusjan P, Adams JR, Houle S, Tong J, Hornykiewicz O, Furukawa Y et al (2009) Decreased binding of the D3 dopamine receptor-preferring ligand [11C]-(+)-PHNO in drug-naïve Parkinson’s disease. Brain 132:1366–1375
Morin N, Jourdain VA, Morissette M, Grégoire L, Di Paolo T (2014) Long-term treatment with L-DOPA and an mGlu5 receptor antagonist prevents changes in brain basal ganglia dopamine receptors, their associated signaling proteins and neuropeptides in parkinsonian monkeys. Neuropharmacology 79:688–706
Ginés S, Hillion J, Torvinen M, Le Crom S, Casadó V, Canela EI, Rondin S, Lew JY et al (2000) Dopamine D1 and adenosine A1 receptors form functionally interacting heteromeric complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(15):8606–8611
Ferre S, Baler R, Bouvier M, Caron MG, Devi LA, Durroux T, Fuxe K, George SR et al (2009) Building a new conceptual framework for receptor heteromers. Nat Chem Biol 5(3):131–134
El-Asmar L, Springael J-Y, Ballet S, Andrieu EU, Vassart G, Parmentier M (2005) Evidence for negative binding cooperativity within CCR5-CCR2b heterodimers. Mol Pharmacol 67(2):460–469
Sohy D, Parmentier M, Springael J-Y (2007) Allosteric transinhibition by specific antagonists in CCR2/CXCR4 heterodimers. J Biol Chem 282(41):30062–30069
Ferré S, Navarro G, Casadó V, Cortés A, Mallol J, Canela EI, Lluís C, Franco R (2010) Chapter 2—G protein-coupled receptor heteromers as new targets for drug development. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 91:41–52. doi:10.1016/S1877-1173(10)91002-8
Maggio R, Scarselli M, Capannolo M, Millan MJ (2015) Novel dimensions of D3 receptor function: focus on heterodimerisation, transactivation and allosteric modulation. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 25:1470
Borroto-Escuela D, Brito I, Romero-Fernandez W, Di Palma M, Oflijan J, Skieterska K, Duchou J, Van Craenenbroeck K et al (2014) The G protein-coupled receptor heterodimer network (GPCR-HetNet) and its hub components. Int J Mol Sci 15(5):8570
Lee FJS, Xue S, Pei L, Vukusic B, Chéry N, Wang Y, Wang YT, Niznik HB et al (2002) Dual regulation of NMDA receptor functions by direct protein-protein interactions with the dopamine D1 receptor. Cell 111(2):219–230
Fiorentini C, Gardoni F, Spano P, Di Luca M, Missale C (2003) Regulation of dopamine D1 receptor trafficking and desensitization by oligomerization with glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Biol Chem 278(22):20196–20202
Ladepeche L, Yang L, Bouchet D, Groc L (2013) Regulation of dopamine D1 receptor dynamics within the postsynaptic density of hippocampal glutamate synapses. PLoS One 8(9):e74512
Zheng Q, Liu Z, Wei C, Han J, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ren W (2014) Activation of the D1 receptors inhibits the long-term potentiation in vivo induced by acute morphine administration through a D1-GluN2A interaction in the nucleus accumbens. Neuroreport 25(15):1191–1197
Kisilevsky AE, Mulligan SJ, Altier C, Iftinca MC, Varela D, Tai C, Chen L, Hameed S et al (2008) D1 receptors physically interact with N-type calcium channels to regulate channel distribution and dendritic calcium entry. Neuron 58(4):557–570
Koh P, Bergson C, Undie AS, Goldman-Rakic PS, Lidow MS (2003) Up-regulation of the d1 dopamine receptor–interacting protein, calcyon, in patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60(3):311–319
Lidow MS, Roberts A, Zhang L, Koh P-O, Lezcano N, Bergson C (2001) Receptor crosstalk protein, calcyon, regulates affinity state of dopamine D1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 427(3):187–193
Joyce JN, Lexow N, Bird E, Winokur A (1988) Organization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in human striatum: receptor autoradiographic studies in Huntington’s disease and schizophrenia. Synapse 2(5):546–557
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (SAF2009-07276, SAF2011-23813, and SAF2012-39875-C02-01) and from Spanish Ministerio de Salud (PI09/01756). MMP is supported by Marie Curie CIG PCIG11-GA-2012-322013.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franco, R., Casadó-Anguera, V., Muñoz, A. et al. Hints on the Lateralization of Dopamine Binding to D1 Receptors in Rat Striatum. Mol Neurobiol 53, 5436–5445 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9468-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9468-8