Abstract
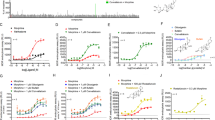
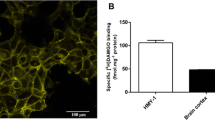
Imidazoline receptor antisera-selected (IRAS) protein, the mouse homologue named Nischarin, was found to target to early endosomes with properties of sorting nexins in vitro. Recently, we generated IRAS knockout mice and found IRAS deficiency exacerbated the analgesic tolerance and physical dependence caused by opioids, suggesting that IRAS plays a role in regulating μ opioid receptor (MOR) functions. In the present study, we found that IRAS interacts with MOR and regulates MOR trafficking in vitro. In the CHO or HEK293 cells co-expressing MOR and IRAS, IRAS, through its PX domain, interacted with MOR. The interaction facilitated the recycling of internalized MOR and prevented MOR downregulation induced by DAMGO, the MOR agonist. Functionally, IRAS accelerated MOR resensitization and attenuated DAMGO-induced MOR desensitization, which is believed as one of mechanisms mediating opioid tolerance and dependence. Taken together, we propose that IRAS is a new MOR interacting protein and regulates agonist-induced trafficking of MOR via sorting internalized MOR to the recycling pathway, which may be a molecular mechanism underlying IRAS modulating opioid tolerance and dependence.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
von Zastrow M, Svingos A, Haberstock-Debic H, Evans C (2003) Regulated endocytosis of opioid receptors: cellular mechanisms and proposed roles in physiological adaptation to opiate drugs. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13(3):348–353
Kuijl C, Pilli M, Alahari SK, Janssen H, Khoo PS, Ervin KE, Calero M, Jonnalagadda S et al (2013) Rac and Rab GTPases dual effector Nischarin regulates vesicle maturation to facilitate survival of intracellular bacteria. EMBO J 32(5):713–727. doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.10
Whistler JL, Enquist J, Marley A, Fong J, Gladher F, Tsuruda P, Murray SR, Von Zastrow M (2002) Modulation of postendocytic sorting of G protein-coupled receptors. Science 297(5581):615–620. doi:10.1126/science.1073308
Piletz JE, Ivanov TR, Sharp JD, Ernsberger P, Chang CH, Pickard RT, Gold G, Roth B et al (2000) Imidazoline receptor antisera-selected (IRAS) cDNA: Cloning and characterization. DNA Cell Biol 19(6):319–329. doi:10.1089/10445490050043290
Li F, Wu N, Su R, Chen Y, Lu X, Liu Y, Li J (2012) Imidazoline receptor antisera-selected/Nischarin regulates the effect of agmatine on the development of morphine dependence. Addict Biol 17(2):392–408. doi:10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00373.x
Wu N, Su RB, Xu B, Lu XQ, Liu Y, Zheng JQ, Piletz JE, Li J et al (2005) IRAS, a candidate for I1-imidazoline receptor, mediates inhibitory effect of agmatine on cellular morphine dependence. Biochem Pharmacol 70(7):1079–1087. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2005.07.006
Zhang L, Zhao TY, Hou N, Teng Y, Cheng X, Wang B, Chen Y, Jiang L et al (2013) Generation and primary phenotypes of imidazoline receptor antisera-selected (IRAS) knockout mice. CNS Neuroscience Therapeutics 19(12):978–981. doi:10.1111/cns.12192
Lim KP, Hong WJ (2004) Human nischarin/imidazoline receptor antisera-selected protein is targeted to the endosomes by a combined action of a PX domain and a coiled-coil region. J Biol Chem 279(52):54770–54782. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411315200
Alahari SK, Lee JW, Juliano RL (2000) Nischarin, a novel protein that interacts with the integrin alpha 5 subunit and inhibits cell migration. J Cell Biol 151(6):1141–1154. doi:10.1083/jcb.151.6.1141
Liang YJ, Wu DF, Yang LQ, Hoellt V, Koch T (2007) Interaction of the mu-opioid receptor with synaptophysin influences receptor trafficking and signaling. Mol Pharmacol 71(1):123–131. doi:10.1124/mol.106.026062
Pfeiffer M, Koch T, Schroder H, Laugsch M, Hollt V, Schulz S (2002) Heterodimerization of somatostatin and opioid receptors cross-modulates phosphorylation, internalization, and desensitization. J Biol Chem 277(22):19762–19772. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110373200
Hanyaloglu AC, von Zastrow M (2007) A novel sorting sequence in the beta2-adrenergic receptor switches recycling from default to the Hrs-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 282(5):3095–3104. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605398200
Wang B, Liu Y, Shan Y, Yao Z, Liu X, Su R, Sun Q, Cong Y et al (2009) Generation and characterization of novel human IRAS monoclonal antibodies. J Biomed Biotechnol 2009:973754. doi:10.1155/2009/973754
Li J, Huang P, Chen C, de Riel JK, Weinstein H, Liu-Chen LY (2001) Constitutive activation of the mu opioid receptor by mutation of D3.49(164), but not D3.32(147): D3.49(164) is critical for stabilization of the inactive form of the receptor and for its expression. Biochemistry 40(40):12039–12050
Xia ZP, Liu YH (2001) Reliable and global measurement of fluorescence resonance energy transfer using fluorescence microscopes. Biophy J 81(4):2395–2402
Wang DX, Sun XC, Bohn LM, Sadee W (2005) Opioid receptor homo- and heterodimerization in living cells by quantitative bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. Mol Pharmacol 67(6):2173–2184. doi:10.1124/mol.104.010272
Zerial M, McBride H (2001) Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(2):107–117. doi:10.1038/35052055
Teasdale RD, Collins BM (2012) Insights into the PX (phox-homology) domain and SNX (sorting nexin) protein families: structures, functions and roles in disease. Biochem J 441:39–59. doi:10.1042/Bj20111226
Jang IH, Lee S, Park JB, Kim JH, Lee CS, Hur EM, Kim IS, Kim KT et al (2003) The direct interaction of phospholipase C-gamma 1 with phospholipase D2 is important for epidermal growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem 278(20):18184–18190. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208438200
Lee CS, Kim IS, Park JB, Lee MN, Lee HY, Suh PG, Ryu SH (2006) The phox homology domain of phospholipase D activates dynamin GTPase activity and accelerates EGFR endocytosis. Nat Cell Biol 8(5):477–U101. doi:10.1038/Ncb1401
Parks WT, Frank DB, Huff C, Renfrew Haft C, Martin J, Meng X, de Caestecker MP, McNally JG et al (2001) Sorting nexin 6, a novel SNX, interacts with the transforming growth factor-beta family of receptor serine-threonine kinases. J Biol Chem 276(22):19332–19339. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100606200
Odley A, Hahn HS, Lynch RA, Marreez Y, Osinska H, Robbins J, Dorn GW 2nd (2004) Regulation of cardiac contractility by Rab4-modulated beta2-adrenergic receptor recycling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(18):7082–7087. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308335101
Garland AM, Grady EF, Lovett M, Vigna SR, Frucht MM, Krause JE, Bunnett NW (1996) Mechanisms of desensitization and resensitization of G protein-coupled neurokinin1 and neurokinin2 receptors. Mol Pharmacol 49(3):438–446
Henry AG, White IJ, Marsh M, von Zastrow M, Hislop JN (2011) The role of ubiquitination in lysosomal trafficking of delta-opioid receptors. Traffic 12(2):170–184. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01145.x
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Szabo K, Haft CR, Trejo J (2002) Down-regulation of protease-activated receptor-1 is regulated by sorting nexin 1. Mol Biol Cell 13(6):1965–1976. doi:10.1091/mbc.E01-11-0131
Martini L, Whistler JL (2007) The role of mu opioid receptor desensitization and endocytosis in morphine tolerance and dependence. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17(5):556–564. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2007.10.004
Grady EF, Bohm SK, Bunnett NW (1997) Turning off the signal: mechanisms that attenuate signaling by G protein-coupled receptors. Am J Physiol 273(3 Pt 1):G586–601
Williams JT, Ingram SL, Henderson G, Chavkin C, von Zastrow M, Schulz S, Koch T, Evans CJ et al (2013) Regulation of mu-opioid receptors: desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance. Pharmacol Rev 65(1):223–254. doi:10.1124/pr.112.005942
Christie MJ (2008) Cellular neuroadaptations to chronic opioids: tolerance, withdrawal and addiction. Br J Pharmacol 154(2):384–396. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.100
Sim-Selley LJ, Selley DE, Vogt LJ, Childers SR, Martin TJ (2000) Chronic heroin self-administration desensitizes mu opioid receptor-activated G-proteins in specific regions of rat brain. J Neuroscience 20(12):4555–4562
Stone LS, German JP, Kitto KF, Fairbanks CA, Wilcox GL (2014) Morphine and clonidine combination therapy improves therapeutic window in mice: synergy in antinociceptive but not in sedative or cardiovascular effects. PLoS One 9(10):e109903. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109903
Su RB, Li J, Gao K, Pei G, Qin BY (2000) Influence of idazoxan on analgesia, tolerance, and physical dependence of morphine in mice and rats in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin 21(11):1011–1015
Cong M, Perry SJ, Hu LA, Hanson PI, Claing A, Lefkowitz RJ (2001) Binding of the beta2 adrenergic receptor to N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor regulates receptor recycling. J Biol Chem 276(48):45145–45152. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106087200
Huang P, Steplock D, Weinman EJ, Hall RA, Ding Z, Li J, Wang Y, Liu-Chen LY (2004) kappa Opioid receptor interacts with Na(+)/H(+)-exchanger regulatory factor-1/Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50 (NHERF-1/EBP50) to stimulate Na(+)/H(+) exchange independent of G(i)/G(o) proteins. J Biol Chem 279(24):25002–25009. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313366200
Martini L, Thompson D, Kharazia V, Whistler JL (2010) Differential regulation of behavioral tolerance to WIN55,212-2 by GASP1. Neuropsychopharmacol 35(6):1363–1373. doi:10.1038/npp.2010.6
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Dr. Lee-Yuan Liu-Chen (School of Medicine, Temple University, USA) for giving the advice and revising this manuscript. This work was supported by the Key Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30930040), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2009CB522008 and No. 2015CB553504), and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 7122137).
Conflict of Interest
We declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Ma, H., Wu, N. et al. IRAS Modulates Opioid Tolerance and Dependence by Regulating μ Opioid Receptor Trafficking. Mol Neurobiol 53, 4918–4930 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9417-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9417-6