Abstract
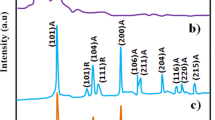
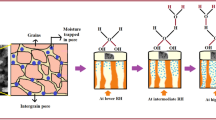
This paper presents the humidity sensing properties of surface-modified polyaniline (PAni). In this study, the impedance response and dielectric properties of pure- and doped-PAni have been investigated as a function of relative humidity (RH%) and frequency. PAni and PAni/Mn composite samples are synthesized by one-step interfacial polymerization process. The structural properties and surface morphologies of the prepared materials have been characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), respectively. XRD confirms the formation of PAni and it shows semi-crystalline behaviour. FESEM shows granular, porous and well-distributed structure. It has been observed that the porosity and nanogranular structure increased with increasing doping percentage. Here, we observe that porous and granular structure of Mn-doped PAni shows better response and recovery time (\({\sim }28\hbox { s}\)) and decreases in electrical impedance. Dielectric constants, dielectric loss and AC conductivity have also been discussed with variations in frequency and relative humidity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malenahalli H N, Nanjanagudu G G and Yoon-Bo S 2017 Appl. Mater. Today 9 419
Stefan C, Anna M and Marian Z 2018 Polym. Test. 67 342
Toshiaki O 2012 Int. J. Corros., Article ID 915090 7
Deshpande N G, Gudage Y G, Ramphal S, Vyas J C, Kim J B and Lee Y P 2009 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 138 76
Sikarwar S and Yadav B C 2015 Sens. Actuators A Phys. 233 54
Blank T A, Eksperiandova L P and Belikov K N 2016 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 228 416
Alwis L, Sun T and Grattan K T V 2013 Measurement 46 4052
Garcia L R and Lunadei L 2011 Comput. Electron. Agr. 79 42
Swanson A J, Raymond S G, Janssens S, Breukers R D, Bhuiyan M D H, Lovell-Smith J W et al 2016 Sens. Actuators A Phys. 249 217
Das R, Pattanayak A J and Sarat K S 2018 Polym. Nanocomposit. Energy Environ. Appl. p 205, chap 7. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102262-7.00007-6
Nambiar S and Yeow John T W 2011 Biosens. Bioelectron. 26 1825
Jong M M, Neeta T, Khalil K H, Rajendra N G and Yoon B S 2018 Biosens. Bioelectron. 102 540
Ramya R, Sivasubramanian R and Sangaranarayanan M V 2013 Electrochim. Acta 101 109
Kuilla T, Bhadra S, Yao D, Kim N H, Bose S and Lee J H 2010 Prog. Polym. Sci. 35 1350
Yang L and Mujie Y 2012 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 161 967
Milind V K, Sanjay K A, Sonali D N, Jalindar D A and Bharat B K 2013 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 178 140
Ilaria F, Iole V, Cesare C and Maria V R 2015 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 220 534
Mehrnaz J, Amir H N and Mehdi N 2014 Adv. Polym. Tech. 33 1
Ramaprasad A T and Vijayalakshmi R 2010 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 148 117
Song E and Choi J-W 2013 Nanomaterials 3 498
Liming W, Qin Y, Hui B, Fuqiang H, Qun W and Lidong C 2015 J. Mater. Chem. A 15 7086
Vineet K S, Poonam Y, Raghvendra S Y, Priya M and Avinash C P 2012 Nanoscale 4 3886
Benson J, Kovalenko I, Boukhalfa S, Lashmore D, Sanghadasa M and Yushin G 2013 Adv. Mater. 25 6625
Qingqing C, Meixiang N and Ying G 2018 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 254 30
Rachna R, Sheetal C, Nidhi C, Tulika D and Pundir C S 2012 Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 50 112
Nanjundan A K, Hyun J C, Yeon R S, Dong W C, Liming D and Jong B B 2012 ACS Nano 6 1715
Jain S, Chakane S, Samui A B, Krishnamurthy V N and Bhoraskar S V 2003 Sens. Actuators B96 124
Parvatikar N, Jain S, Khasim S, Revansiddappa M, Bhoraskar S V and Ambika Prasad M V N 2006 Sens. Actuators B114 599
Pandey S 2016 J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices1 431
McGovern S T, Spinks G M and Wallace G G 2005 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 107 657
Aussawasathien D, Dong J H and Dai L 2005 Synth. Met. 154 37
Pouget J P 1991 Macromolecules 24 779
Borah R, Banerjee S and Kumar A 2014 Synth. Met. 197 225
Gupta K, Jana P C and Meikap A K 2010 Synth. Met. 160 1566
Xingbin Y, Zhixin T, Jiangtao C and Qunji X 2011 Nanoscale 3 212
Chiou N R and Epstein A J 2005 Adv. Mater. 17 1679
Jozefowicz M E, Laversanne R, Javadi H H S, Epstein A J, Pouget J P, Tang X et al 1989 Phys. Rev. B 39 12958
Cosmin L, Zujovic Z D and Travas-Sejdic J 2009 Macromol. Rapid Commun. 30 1663
Jiaxing Huang and Richard B Kaner 2004 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126 851
Shishov M A, Moshnikov V A and Sapurina I Y 2013 Chem. Pap. 67 909
Zhou Y K, He B L, Zhou W J, Huang J, Li X H, Wu B et al 2004 Electrochim. Acta 49 257
Jaroslav S, Irina S, Miroslava T and Elena N K 2008 Macromolecules 41 3530
Jain S, Chakane S, Samui A B, Krishnamurthy V N and Bhoraskar S V 2003 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 96 124
Fuke M V, Kanitkar P, Kulkarni M, Kale B B and Aiyer R C 2010 Talanta 81 320
Tuccimei P, Moroni M and Norcia D 2006 Appl. Radiat. Isot. 64 254
Khalil J H 2014 Appl. Modern Sci. 8 124
Sui G, Jana S, Zhong W H, Fuqua M A and Ulven C A 2008 Acta Mater. 56 2381
Prem Nazeer K, Jacob S A, Thamilselvan M, Mangalaraj D, Narayandass S K and Junsin Yi 2004 Polym. Int. 53 898
Choudhury A 2009 Sens. Actuators B Chem. 138 318
Jain A, Sagar P and Mehra R M 2007 Mater. Sci.—Poland 25 237
Imene B A 2015 J. Nanomater. Article ID 516902
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to UP state government through the Centre of Excellence Scheme for providing XRD facility at the Department of Physics, University of Lucknow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, D., Shukla, R.K. Impedance variation with different relative humidities of PAni/Mn nanofibres. Bull Mater Sci 43, 95 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-2063-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-2063-2