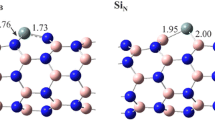
Abstract
The Fe-doped nanotubes can be considered as novel catalysts to SiO oxidation. The information of SiO oxidation on nano-catalysts is not clear. In this study, the SiO oxidation on Fe-carbon nanotube (CNT) and Fe-boron nitride nanotube (BNNT) is examined through Langmuir-Hinshelwood (LH) and Eley-Rideal (ER) paths. The SiO joins in the Fe atom of Fe-surface-\(\hbox {O}_{\mathrm {2}}\)* and Fe-surface-O* to create important structures with minor barrier energy. Cis-Fe-surface-OSiOO* in the ER is more stable than structures in LH pathway. In the LH and ER mechanisms the one and two \(\hbox {SiO}_{\mathrm {2}}\) are released at normal temperature, respectively. The abilities of Fe-CNT and Fe-BNNT to oxidation of SiO is investigated, and Fe-CNT and Fe-BNNT as novel metal-doped catalysts are proposed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganster P 2010 Phys. Chem. B81 5315
Kim B H 2011 J. Appl. Chem.110 513
Kajihara K 2015 J. Chem. Phys.98 29
Bongiorno A 2014 Phys. Rev. B70 195312
Itoh M 2008 J. Appl. Phys.103 026101
Takahashi Y 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett.84 876
Robinson J A 2016 Nano Lett.11 61747
Cho K 2013 Nano Lett.2 3513
Snow E 2015 Science3 71942
Peng S 2014 Chem. Phys. Lett.12 387271
Yeung C S 2018 J. Phys. Chem. C11 27401
Yoosefian M 2014 Struct. Chem.3 259
Star A 2006 J. Phys. Chem. B6 11021014
Haruta M 2013 Chem. Rec.4 375
Anderson W 2008 Nano Lett.3 8195
Zhou X 2007 J. Mol. Struct.11 82265
Castellino P 2006 Chem. Select1 40
Wei M 2010 Chem. Phys.41 96
Arnaldsson N 2014 J. Phys. Chem.1 57
Kishimoto T 2017 Chem. Lett.17 581
Munoz J 2016 Phys. Chem.14 28
Yang Q 2016 Catal. Chem.98 22
Artyushkova K 2013 Chem. Catal.18 41
Gao M 2016 Nano Lett.5 321
Tan Z and Li H 2019 J. Mater. Chem. A7 1607
Sun M and Zhang G 2015 Sci. China Mater.58 683
Liu B and Wei L 2015 J. Cryst. Growth277 293
Sharghi H and Aboonajmi J 2018 Adv. Organomet. Chem.3 4124
Kizuka T and Miyazawa K 2017 J. Nanotechnol.3 613746
Chen Y 2019 Chem. Phys.152 894
Li D 2007 Nano Scale19 118
Jaifi F 2003 J. Chem. Phys.8 28
Broda M A 2011 J. Mol. Phys.67 209
Kupka T 2012 J. Mol. Phys.38 241
Kupka T and Kaminsky J 2012 Vibr. Spectrosc.63 432
Taylor M 2006 Chem. Spect.24 636
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, W., Yan, L., Li, Y. et al. A DFT investigation of performance of metal-doped nanotubes as acceptable catalysts to SiO oxidation. Bull Mater Sci 43, 127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02099-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02099-2