Abstract
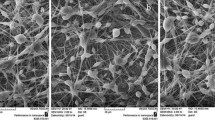
Nanofibrous membranes used for burn treatment have become widely popular due to their large surface area and high porous structure. In this study, electrospinning was used to fabricate a blended nanofibrous membrane of polyvinylidene pyrolidone (PVP) and gelatin, to use as wound dressing. The physical and mechanical properties of this novel membrane were investigated using SEM, FTIR and tensile tests. Results showed that poor mechanical properties of gelatin, which are preferred in medical applications for curing burns as they allow for antigen activity and skin repair, can be enhanced by adding PVP in the solution. Silver sulfadiazine (AgSD), an antibacterial agent, was also impregnated into the PVP/gelatin nanofibrous structure during electrospinning. The membrane thus fabricated showed antibacterial activities against both the Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus. AgSD release behaviour of fabricated samples indicated short-term drug delivery. It was concluded that the proposed drug-loaded membrane can be used as wound dressing, specifically, in treating skin burns.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pillay V, Dott C, Choonara Y E, Tyagi C, Tomar L, Kumar P et al 2013 Nanomaterials 2013 1
Ma Z, He W, Yong T and Ramakrishna 2005 Tissue Eng. 11 1149
Kong H and Jang J 2008 Am. Chem. Soc. 24 2051
Zhu, L, Liu, X, Du, L and Jin Y 2016 Biomed. Pharmacol. 83 33
Jorge S A and Dantas S R P E 2003 Abordagem multiprofissional do tratamento de feridas (Sao Paulo: Atheneu)
Cho Y S, Choi Y H, Yoon C and You J S 2014 Burns 41 1
Latarjet J 1995 Burns 21 221
Pereira T, Dos Santos D, Lima-Ribeiro M H M, de Pontes-Filho N T, Carneiro-Leão A M D A and Correia M T D S 2012 BioMed. Res. Inter. 2012 1
Rangel M F and Pereira A P J T 2007 Bras. Med. 92 20
Kumar P M and Ghosh A 2017 Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 96 243
Cribbs R K, Luqutte M H and Besner G E 1998 Surg. Res. 80 69
Nam G, Rangasamy S, Purushothaman B and Song J M 2015 Nanomater. Nanotech. 5 1
Cherylann M, Gail Land Joel E 2004 Cont. Educ. Top. 74
Mayhall C G 2003 Clin. Infect. Dis. 37 543
Benjamin A and Lipsky Christopher H 2009 Clin. Pract. 49 1541
Heo D N, Yang D H, Lee J B, Bae M S, Kim J H, Moon S H et al 2013 Biomed. Nanotech. 9 511
May S R 1991 Clin. Mater. 8 243
Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Kumar P T S, Nair S V and Tamura H 2011 Biotech. Adv. 29 322
Valizadeh M, Hosseini Ravandi S A and Ramakrishna S 2013 Tex. Polym. 1 70
Baker B M, Handorf A M, Ionescu L C, Li W J and Mauck R L 2009 Expert Rev. Med. Dev. 6 515
Shao W, Liu H, Liu X, Wang Sh, Wu J and Zhang R 2015 Carbohydr. Polym. 132 351
Boateng J, Burgos-Amador R, Okeke O and Pawar H 2015 Biol. Macromol. 79 63
Saarai A, Kasparkova V, Sedlacek A T and Saha P 2013 Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 18 152
Zhan J and Lan P 2012 Res. Upd. Polym. Sci. 1 59
Mobarake L G, Prabhakaran M P, Morshed M, Esfahani M H N and Ramakrishna S 2008 Biomaterials 29 4532
Kuijpers A J, Engbers G H M, Krijgsveld J, Zaat S A J, Dankert J and Feijen J 2000 Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 11 225
Ratanavaraporn J, Rangkupan R, Jeeratawatchai H, Kanokpanont S and Damrongsakkul S 2010 Biologic. Macromol. 47 431
Giri N, Natarajan R K, Gunasekaran S and Shreemathi S 2011 Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 3 624
Wang H, Qiao X and Chen J 2005 Mater. Chem. Phys. 94 449
Zhang X, Sun N, Wu B and Lu Y 2008 Powder Technol. 182 480
Li P, Wu L and Li B 2016 Mater. Sci. Eng. 60 54
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Emad Darman Drug Company for providing silver sufadiazine during the research, which is free of charge. Also, we pay special thanks to Research Institute for Biotechnology and Bioengineering of Isfahan University of Technology for antimicrobial tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semnani, D., Poursharifi, N., Banitaba, N. et al. Electrospun polyvinylidene pyrolidone/gelatin membrane impregnated with silver sulfadiazine as wound dressing for burn treatment. Bull Mater Sci 41, 72 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-018-1601-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-018-1601-7