Abstract
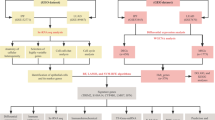
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a progressive status of acute lung injury (ALI), is primarily caused by an immune-mediated inflammatory disorder, which can be an acute pulmonary complication of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). As a chronic inflammatory disease regulated by the immune system, RA is closely associated with the occurrence and progression of respiratory diseases. However, it remains elusive whether there are shared genes between the molecular mechanisms underlying RA and ARDS. The objective of this study is to identify potential shared genes for further clinical drug discovery through integrated analysis of bulk RNA sequencing datasets obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, employing differentially expressed genes (DEGs) analysis and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). The hub genes were identified through the intersection of common DEGs and WGCNA-derived genes. The Random Forest (RF) and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithms were subsequently employed to identify key shared target genes associated with two diseases. Additionally, RA immune infiltration analysis and COVID-19 single-cell transcriptome analysis revealed the correlation between these key genes and immune cells. A total of 59 shared genes were identified from the intersection of DEGs and gene clusters obtained through WGCNA, which analyzed the integrated gene matrix of ALI/ARDS and RA. The RF and LASSO algorithms were employed to screen for target genes specific to ALI/ARDS and RA, respectively. The final set of overlapping genes (FCMR, ADAM28, HK3, GRB10, UBE2J1, HPSE, DDX24, BATF, and CST7) all exhibited a strong predictive effect with an area under the curve (AUC) value greater than 0.8. Then, the immune infiltration analysis revealed a strong correlation between UBE2J1 and plasma cells in RA. Furthermore, scRNA-seq analysis demonstrated differential expression of these nine target genes primarily in T cells and NK cells, with CST7 showing a significant positive correlation specifically with NK cells. Beyond that, transcriptome sequencing was conducted on lung tissue collected from ALI mice, confirming the substantial differential expression of FCMR, HK3, UBE2J1, and BATF. This study provides unprecedented evidence linking the pathophysiological mechanisms of ALI/ARDS and RA to immune regulation, which offers novel understanding for future clinical treatment and experimental research.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets involved in the study were all obtained from the GEO (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) database. The datasets generated from the study were included in the article and the core code of this study was available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ALI:
-
Acute lung injury
- ARDS:
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- BALF:
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- COVID-19:
-
Coronavirus Disease-2019
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- ECMO:
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- FAIM3:
-
Fas apoptotic inhibitory molecule 3
- GEO:
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- IFNs:
-
Type I interferons
- IRF1:
-
Interferon regulatory factor 1
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- LASSO:
-
Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- RF:
-
Random forest
- scRNA-seq:
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing
- TOM:
-
Topological overlap matrix
- WGCNA:
-
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis
References
Li, L., Huang, Q., Wang, D. C., Ingbar, D. H., & Wang, X. (2020). Acute lung injury in patients with COVID-19 infection. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 10(1), 20–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.16
Basil, M. C., & Levy, B. D. (2016). Specialized pro-resolving mediators: Endogenous regulators of infection and inflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology, 16(1), 51–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2015.4
Thompson, B. T., Chambers, R. C., & Liu, K. D. (2017). Acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine, 377(6), 562–572. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1608077
Meyer, N. J., Gattinoni, L., & Calfee, C. S. (2021). Acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Lancet, 398(10300), 622–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00439-6
Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D., & McInnes, I. B. (2016). Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (London, England), 388(10055), 2023–2038. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
Zhou, T. T., Sun, J. J., Tang, L. D., Yuan, Y., Wang, J. Y., & Zhang, L. (2023). Potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis with comorbid depression based on bioinformatics analysis. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, 1007624. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1007624
Yu, R., Zhang, J., Zhuo, Y., Hong, X., Ye, J., Tang, S., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Identification of diagnostic signatures and immune cell infiltration characteristics in rheumatoid arthritis by integrating bioinformatic analysis and machine-learning strategies. Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 724934. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.724934
Mueller, A.-L., Payandeh, Z., Mohammadkhani, N., Mubarak, S. M. H., Zakeri, A., Alagheband Bahrami, A., Brockmueller, A., & Shakibaei, M. (2021). Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: New treatment strategies. Cells, 10(11), 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113017
Zhao, J., Guo, S., Schrodi, S. J., & He, D. (2021). Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 790122. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.790122
McInnes, I. B., & Schett, G. (2017). Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (London, England), 389(10086), 2328–2337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31472-1
Köprülüoğlu, M., Naz, İ, Solmaz, D., & Akar, S. (2022). Hand functions and joint position sense in patients with psoriatic arthritis—A comparison with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy controls. Clinical Biomechanics (Bristol, Avon), 95, 105640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2022.105640
Zhuo, J., Lama, S., Knapp, K., Gutierrez, C., Lovett, K., Thai, S., & Craig, G. L. (2023). Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from the JointMan database. Science and Reports, 13(1), 11678. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-37452-y
Cao, Z., Li, Q., Wu, J., & Li, Y. (2023). Causal association of rheumatoid arthritis with obstructive lung disease: Evidence from Mendelian randomization study. Heart and Lung, 62, 35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrtlng.2023.05.020
Raiker, R., DeYoung, C., Pakhchanian, H., Ahmed, S., Kavadichanda, C., Gupta, L., & Kardes, S. (2021). Outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A multicenter research network study in the United States. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 51(5), 1057–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.08.010
Díaz Cuña, C., Consani, S., Rostan, S., Fernández, L., Moreira, E., & Sanmartí, R. (2022). Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra articular manifestations and comorbidities. Revista Colombiana de Reumatología (English Edition), 29(3), 196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcreue.2021.03.003
Mori, S., Cho, I., & Sugimoto, M. (2010). Acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with rapid aggravation of rheumatoid arthritis. Modern Rheumatology, 20(1), 77–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0228-3
Ritchie, M. E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., Hu, Y., Law, C. W., Shi, W., & Smyth, G. K. (2015). limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(7), e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Leek, J. T., Johnson, W. E., Parker, H. S., Jaffe, A. E., & Storey, J. D. (2012). The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 28(6), 882–883. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts034
Langfelder, P., & Horvath, S. (2008). WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 559. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Engebretsen, S., & Bohlin, J. (2019). Statistical predictions with glmnet. Clinical Epigenetics, 11(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-019-0730-1
Zhou, Q. M., Zhe, L., Brooke, R. J., Hudson, M. M., & Yuan, Y. (2021). A relationship between the incremental values of area under the ROC curve and of area under the precision-recall curve. Diagnostic and Prognostic Research, 5(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41512-021-00102-w
Chen, B., Khodadoust, M. S., Liu, C. L., Newman, A. M., & Alizadeh, A. A. (2018). Profiling tumor infiltrating immune cells with CIBERSORT. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1711, 243–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7493-1_12
Stuart, T., Butler, A., Hoffman, P., Hafemeister, C., Papalexi, E., Mauck, W. M., Hao, Y., Stoeckius, M., Smibert, P., & Satija, R. (2019). Comprehensive integration of single-cell data. Cell, 177(7), 1888-1902.e21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.031
Hu, C., Li, T., Xu, Y., Zhang, X., Li, F., Bai, J., Chen, J., Jiang, W., Yang, K., Ou, Q., Li, X., Wang, P., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Cell Marker 2.0: An updated database of manually curated cell markers in human/mouse and web tools based on scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), D870–D876. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac947
Liao, M., Liu, Y., Yuan, J., Wen, Y., Xu, G., Zhao, J., Cheng, L., Li, J., Wang, X., Wang, F., Liu, L., Amit, I., Zhang, S., & Zhang, Z. (2020). Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19. Nature Medicine, 26(6), 842–844. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0901-9
Love, M. I., Huber, W., & Anders, S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biology, 15(12), 550.
Robinson, M. D., McCarthy, D. J., & Smyth, G. K. (2010). edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 26(1), 139–140. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Grasselli, G., Tonetti, T., Protti, A., Langer, T., Girardis, M., Bellani, G., Laffey, J., Carrafiello, G., Carsana, L., Rizzuto, C., Zanella, A., Scaravilli, V., Pizzilli, G., Grieco, D. L., Di Meglio, L., de Pascale, G., Lanza, E., Monteduro, F., Zompatori, M., … collaborators. (2020). Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: A multicentre prospective observational study. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 8(12), 1201–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30370-2
Dang, W., Tao, Y., Xu, X., Zhao, H., Zou, L., & Li, Y. (2022). The role of lung macrophages in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflammation Research, 71(12), 1417–1432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01645-4
Chen, X., Tang, J., Shuai, W., Meng, J., Feng, J., & Han, Z. (2020). Macrophage polarization and its role in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflammation Research, 69(9), 883–895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01378-2
Sweeney, R. M., & McAuley, D. F. (2016). Acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Lancet, 388(10058), 2416–2430. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)00578-x
Claser, C., Nguee, S. Y. T., Balachander, A., Wu Howland, S., Becht, E., Gunasegaran, B., Hartimath, S. V., Lee, A. W. Q., Theng Theng Ho, J., Bing Ong, C., Newell, E. W., Goggi, J., Guan Ng, L., & Renia, L. (2019). Lung endothelial cell antigen cross-presentation to CD8(+)T cells drives malaria-associated lung injury. Nature Communications, 10(1), 4241. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12017-8
Qiu, Y., Liu, C., Shi, Y., Hao, N., Tan, W., & Wang, F. (2023). Integrating bioinformatic resources to identify characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis-related usual interstitial pneumonia. BMC Genomics, 24(1), 450. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09548-2
Chen, X., Qi, D., Fan, S., He, Y., Jing, H., & Wang, D. (2023). Interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) inhibits lung endothelial regeneration following inflammation-induced acute lung injury. Clinical Science (London, England: 1979), 137(5), 367–383. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20220876
Liu, Y., Jiang, H., Kang, T., Shi, X., Liu, X., Li, C., Hou, X., & Li, M. (2023). Platelets-related signature based diagnostic model in rheumatoid arthritis using WGCNA and machine learning. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, 1204652. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1204652
Li, X., He, A., Liu, Y., Huang, Y., & Zhang, X. (2023). Bioinformatics identification of ferroptosis-related genes and therapeutic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Frontiers in Medicine (Lausanne), 10, 1192153. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1192153
Shima, H., Takatsu, H., Fukuda, S., Ohmae, M., Hase, K., Kubagawa, H., Wang, J.-Y., & Ohno, H. (2010). Identification of TOSO/FAIM3 as an Fc receptor for IgM. International Immunology, 22(3), 149–156. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxp121
Zhang, Y.-R., Yu, Z., Xiong, W.-J., Liu, X.-X., Liu, H.-M., Cui, R., Wang, Q., Chen, W.-M., Qiu, L.-G., & Yi, S.-H. (2020). TOSO interacts with SYK and enhances BCR pathway activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Chinese Medical Journal (Engl), 133(17), 2090–2097. https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000000999
Huang, H.-H., & Liang, Y. (2022). Integrating molecular interactions and gene expression to identify biomarkers and network modules of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Technology and Health Care, 30(S1), 135–142. https://doi.org/10.3233/THC-228013
Bendavid, G., Hubeau, C., Perin, F., Gillard, A., Nokin, M.-J., Carnet, O., Gerard, C., Noel, A., Lefebvre, P., Rocks, N., & Cataldo, D. (2022). Role for the metalloproteinase ADAM28 in the control of airway inflammation, remodelling and responsiveness in asthma. Frontiers in Immunology, 13, 1067779. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1067779
Zhong, Y., Lin, H., Li, Q., Liu, C., & Shen, J. (2021). CircRNA_100565 contributes to cisplatin resistance of NSCLC cells by regulating proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy via miR-337-3p/ADAM28 axis. Cancer Biomarkers: Section A of Disease Markers, 30(2), 261–273. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-201705
Hubeau, C., Rocks, N., & Cataldo, D. (2020). ADAM28: Another ambivalent protease in cancer. Cancer Letters, 494, 18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.08.031
Xie, Y., Zheng, Z.-W., He, H.-T., & Chang, Z.-B. (2022). LncRNA NEAT1 induces autophagy through the miR-128-3p/ADAM28 axis to suppress apoptosis of nonsmall-cell lung cancer. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences, 38(10), 933–949. https://doi.org/10.1002/kjm2.12582
Li, T., Gu, Y., Xu, B., Kuca, K., Zhang, J., & Wu, W. (2023). CircZBTB44 promotes renal carcinoma progression by stabilizing HK3 mRNA structure. Molecular Cancer, 22(1), 77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01771-5
Shi, X., Pan, Z., Cai, W., Zhang, Y., Duo, J., Liu, R., & Cai, T. (2023). Identification and immunological characterization of cuproptosis-related molecular clusters in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, 1171445. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1171445
Tuo, Z., Zheng, X., Zong, Y., Li, J., Zou, C., Lv, Y., & Liu, J. (2020). HK3 is correlated with immune infiltrates and predicts response to immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 10(1), 319–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.6
O’Sullivan, I., Chopra, A., Carr, J., Kim, T. S., & Cohen, E. P. (2008). Immunity to growth factor receptor-bound protein 10, a signal transduction molecule, inhibits the growth of breast cancer in mice. Cancer Research, 68(7), 2463–2470. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5685
Deng, Y.-J., Ren, E.-H., Yuan, W.-H., Zhang, G.-Z., Wu, Z.-L., & Xie, Q.-Q. (2020). GRB10 and E2F3 as diagnostic markers of osteoarthritis and their correlation with immune infiltration. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland), 10(3), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10030171
Wang, Z., Meng, Z., & Chen, C. (2022). Screening of potential biomarkers in peripheral blood of patients with depression based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis and machine learning algorithms. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13, 1009911. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1009911
Warren, K. J., Fang, X., Gowda, N. M., Thompson, J. J., & Heller, N. M. (2016). The TORC1-activated proteins, p70S6K and GRB10, regulate IL-4 signaling and M2 macrophage polarization by modulating phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-2. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291(48), 24922–24930.
Morrow, J. D., Cho, M. H., Platig, J., Zhou, X., DeMeo, D. L., Qiu, W., Celli, B., Marchetti, N., Criner, G. J., Bueno, R., Washko, G. R., Glass, K., Quackenbush, J., Silverman, E. K., & Hersh, C. P. (2018). Ensemble genomic analysis in human lung tissue identifies novel genes for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Human Genomics, 12(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-018-0132-z
Wang, T., Jin, C., Yang, P., Chen, Z., Ji, J., Sun, Q., Yang, S., Feng, Y., Tang, J., & Sun, Y. (2023). UBE2J1 inhibits colorectal cancer progression by promoting ubiquitination and degradation of RPS3. Oncogene, 42(9), 651–664. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02581-7
Yang, D., Ma, X., Xu, J., Jia, K., Liu, X., & Zhang, P. (2021). Zfx-induced upregulation of UBE2J1 facilitates endometrial cancer progression via PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Biology and Therapy, 22(3), 238–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2021.1883186
Haeger, S. M., Yang, Y., & Schmidt, E. P. (2016). Heparan sulfate in the developing, healthy, and injured lung. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 55(1), 5–11. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2016-0043TR
Zhang, Y., Xu, F., Guan, L., Chen, M., Zhao, Y., Guo, L., Li, X., Zheng, Y., Gao, A., & Li, S. (2022). Histone H4 induces heparan sulfate degradation by activating heparanase in chlorine gas-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respiratory Research, 23(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-022-01932-y
Liu, T., Gan, H., He, S., Deng, J., Hu, X., Li, L., Cai, L., He, J., Long, H., Cai, J., Li, H., Zhang, Q., Wang, L., Chen, F., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Li, J., Yang, L., Liu, Y., … Shan, H. (2022). RNA helicase DDX24 stabilizes LAMB1 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Research, 82(17), 3074–3087. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-3748
Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Wang, W., Liu, F., Wang, W., Su, C., Zhu, H., Liao, Z., Zhang, B., & Chen, X. (2022). ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of lincRNA LINC02551 enhances the stability of DDX24 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis. Cell Death and Disease, 13(11), 926. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05386-4
Hu, X., Li, F., Zhou, Y., Gan, H., Wang, T., Li, L., Long, H., Li, B., & Pang, P. (2022). DDX24 promotes metastasis by regulating RPL5 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Medicine, 11(23), 4513–4525. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.4835
Khatun, A., Wu, X., Qi, F., Gai, K., Kharel, A., Kudek, M. R., Fraser, L., Ceicko, A., Kasmani, M. Y., Majnik, A., Burns, R., Chen, Y.-G., Salzman, N., Taparowsky, E. J., Fang, D., Williams, C. B., & Cui, W. (2023). BATF is required for Treg homeostasis and stability to prevent autoimmune pathology. Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany), 10, e2206692. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202206692
Pham, D., Silberger, D. J., Nguyen, K. N., Gao, M., Weaver, C. T., & Hatton, R. D. (2023). Batf stabilizes Th17 cell development via impaired Stat5 recruitment of Ets1-Runx1 complexes. The EMBO Journal, 42(8), e109803. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2021109803
Wu, X., Kasmani, M. Y., Zheng, S., Khatun, A., Chen, Y., Winkler, W., Zander, R., Burns, R., Taparowsky, E. J., Sun, J., & Cui, W. (2022). BATF promotes group 2 innate lymphoid cell-mediated lung tissue protection during acute respiratory virus infection. Science Immunology, 7(67), eabc9934. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abc9934
Bae, S., Kim, K., Kang, K., Kim, H., Lee, M., Oh, B., Kaneko, K., Ma, S., Choi, J. H., Kwak, H., Lee, E. Y., Park, S. H., & Park-Min, K.-H. (2023). RANKL-responsive epigenetic mechanism reprograms macrophages into bone-resorbing osteoclasts. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 20(1), 94–109. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-022-00959-x
Yan, Z., Lijuan, Y., Yinhang, W., Yin, J., Jiamin, X., Wei, W., Yuefen, P., & Shuwen, H. (2022). Screening and analysis of RNAs associated with activated memory CD4 and CD8 T cells in liver cancer. World Journal of Surgical Oncology, 20(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-021-02461-6
Jiang, Z., Luo, Y., Wei, L., Gu, R., Zhang, X., Zhou, Y., & Zhang, S. (2023). Bioinformatic analysis and machine learning methods in neonatal sepsis: Identification of biomarkers and immune infiltration. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071853
Moreira, T. G., Gauthier, C. D., Murphy, L., Lanser, T. B., Paul, A., Matos, K. T. F., Mangani, D., Izzy, S., Rezende, R. M., Healy, B. C., Baecher-Allan, C. M., Chitnis, T., Kuchroo, V., & Weiner, H. L. (2023). Nasal administration of anti-CD3 mAb (Foralumab) downregulates NKG7 and increases TGFB1 and GIMAP7 expression in T cells in subjects with COVID-19. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 120(11), e2220272120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2220272120
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the GEO database for providing their platforms and contributors for uploading their meaningful datasets (GSE2322, GSE76293, GSE55235, GSE55457, GSE77298, GSE145926) and Xiantao (www.xiantao.love) for partial data processing.
Funding
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (NO.7232169).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. JS, JT, and LL contributed equally to this work. Data collection and analysis: JS, JT, LL, CZ, WC, and MQ; Writing original draft preparation: JS, JT, LL, and XC; Experimental design and financial support: XC and ZH; Conception and design and final approval of the version to be published: XC and ZH; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors provided their consent to publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, J., Tang, J., Liu, L. et al. Integrative Analyses of Bulk and Single-Cell RNA Seq Identified the Shared Genes in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01141-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01141-6