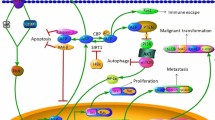
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the primary malignancy of hepatocytes and the second most common cause of cancer-related mortality across the globe. Despite significant advancements in screening, diagnosis, and treatment modalities for HCC, the mortality-to-incidence ratio remain unacceptably high. A recent study indicates that a minor population of HCCs are AFP negative or express the normal range of AFP levels. Although it is a gold standard and a more reliable biomarker in the advanced stage of HCC and poorly differentiated tumors, it does not serve as a suitable means for screening HCC. AFP plays a significant role in the development and progression of HCC and understanding its role is crucial. By examining the molecular mechanisms involved in AFP-mediated tumorigenesis, we can better understand HCC pathogenesis and identify potential therapeutic targets. This article details the role of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the carcinogenic transformation of hepatocytes. The article also focuses on information about the structure, biosynthesis, and regulation of AFP at the gene level. Additionally, it discusses the immune evasion, metastasis, and control of gene expression that AFP mediates during HCC.
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Abbreviations
- AFP:
-
Alpha-fetoprotein
- AFPR:
-
Alpha-fetoprotein receptor
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- AP-1:
-
Activator protein-1
- ATRA:
-
All-trans retinoic acid
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- C/EBP:
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein
- CBP:
-
CREB-binding protein
- CTLs:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- CXCL2:
-
CXC motif chemokine ligand 2
- CXCR4:
-
CXC motif chemokine receptor 4
- DC:
-
Dendritic cells
- DCP:
-
Des carboxy prothrombin
- E-cadherin:
-
Epithelial cadherin
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- EpCAM:
-
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule
- Fam 20CKinase:
-
Family with sequence similarity 20, member C kinase
- Fn14:
-
Fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14
- Fox A:
-
Forkhead box A
- FTF:
-
Four and a half LIM domain protein
- GADD153:
-
Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 153
- GADD45a:
-
Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 45 alpha
- GRC:
-
Glucocorticoid receptor complex
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HBx:
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha
- HNF:
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor
- IL-12:
-
Interleukin-12
- K19:
-
Keratin 19
- LCA:
-
Lens culinaris agglutinin
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
- MMP2/9:
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase 2/9
- MPTP:
-
Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- Mtor:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- N-cadherin:
-
Neural cadherin
- NF-1:
-
Nuclear factor 1
- NK cells:
-
Natural killer cells
- N-ras:
-
Neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog
- P21:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1
- P53:
-
Tumor protein 53
- PD-1:
-
Programmed cell death protein-1
- PDL1:
-
Programmed Cell death-ligand 1
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PIP3:
-
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- PTM:
-
Post-translational modification
- RAR:
-
Retinoic acid receptor
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- siRNA:
-
Silencing RNA
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtuin 1
- Sp-1:
-
Specificity protein
- TILs:
-
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
- TNFRSF12A:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor super family12A
- TNM:
-
Tumor, node, metastasis staging system
- TWEAK:
-
TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis
- US:
-
Ultra sound
- ZBTB20:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 20
- Zhx2:
-
Zinc finger and homeoboxes protein 2
References
Galle, P. R., Foerster, F., Kudo, M., Chan, S. L., Llovet, J. M., Qin, S., Schelman, W. R., Chintharlapalli, S., Abada, P. B., Sherman, M., & Zhu, A. X. (2019). Biology and significance of alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver International, 12, 2214–2229.
Adigun OO, Yarrarapu SNS, Khetarpal S. (2022). Alpha Fetoprotein. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing
Suresh, D., Srinivas, A. N., & Kumar, D. P. (2020). Etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Special focus on fatty liver disease. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 601710.
Manuc, D., Preda, C. M., Sandra, I., Baicus, C., Cerban, R., Constantinescu, I., Olteanu, A. O., Ciora, C. A., Manuc, T., Chiriac, D. E., & Chifulescu, A. E. (2020). Signification of serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in cases of compensated cirrhosis and hepatitis C virus without hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Medicine and Life, 1, 68–74.
Di Carlo, I., Mannino, M., Toro, A., Ardiri, A., Galia, A., Cappello, G., & Bertino, G. (2012). Persistent increase in alpha-fetoprotein level in a patient without underlying liver disease who underwent curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. A case report and review of the literature. World Journal of Surgical Oncology, 10, 1–6.
Charrière, B., Maulat, C., Suc, B., & Muscari, F. (2016). Contribution of alpha-fetoprotein in liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. World Journal of Hepatology, 21, 881–890.
Huang, J., Liu, F. C., Li, L., Zhou, W. P., Jiang, B. G., & Pan, Z. Y. (2020). Nomograms to predict the long-time prognosis in patients with alpha-fetoprotein negative hepatocellular carcinoma following radical resection. Cancer Medicine, 8, 2791–2802.
Hadziyannis, E., Sialevris, K., Georgiou, A., & Koskinas, J. (2013). Analysis of serum alpha fetoprotein-L3% and des- gamma carboxyprothrombin markers in cases with misleading hepatocellular carcinoma total alpha fetoprotein levels. Oncology Reports, 29, 835–839.
Abduljabbar, A. H. (2023). Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound and alpha-fetoprotein measurement for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance: A retrospective comparative study. Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, 54, 31.
Yen, Y. H., Liu, Y. W., Li, W. F., Wang, C. C., Yong, C. C., Lin, C. C., & Lin, C. Y. (2023). Alpha-fetoprotein combined with radiographic tumor burden score to predict overall survival after liver resection in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel), 15(4), 1203.
Arrieta, O., Cacho, B., Morales-Espinosa, D., Ruelas-Villavicencio, A., Flores-Estrada, D., & Hernández-Pedro, N. (2007). The progressive elevation of alpha fetoprotein for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis. BMC Cancer, 7(1), 1–9.
Głowska-Ciemny, J., Szymański, M., Kuszerska, A., Malewski, Z., von Kaisenberg, C., & Kocyłowski, R. (2023). The role of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in contemporary oncology: The path from a diagnostic biomarker to an anticancer drug. International Journal of Molecular Sciences., 24(3), 2539.
Lee, C. W., Tsai, H. I., Lee, W. C., Huang, S. W., Lin, C. Y., Hsieh, Y. C., Kuo, T., Chen, C. W., & Yu, M. C. (2019). Normal alpha-fetoprotein hepatocellular carcinoma: Are they really normal? Journal of Clinical Medicine., 8(10), 1736.
Carr, B. I., Akkiz, H., Üsküdar, O., Yalçın, K., Guerra, V., Kuran, S., Karaoğullarından, Ü., Altıntaş, E., Özakyol, A., Tokmak, S., & Ballı, T. (2018). HCC with low-and normal-serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. Clinical Practice (London, England), 15(1), 453.
Galle, P. R., Foerster, F., Kudo, M., Chan, S. L., Llovet, J. M., Qin, S., Schelman, W. R., Chintharlapalli, S., Abada, P. B., Sherman, M., & Zhu, A. X. (2019). Biology and significance of alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver International, 39(12), 2214–2229.
Hu, X., Chen, R., Wei, Q., & Xu, X. (2022). The Landscape of alpha fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma: Where are we? International Journal of Biological Sciences., 18(2), 536.
Muscari, F., & Maulat, C. (2020). Preoperative alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is this 50-year biomarker still up-to-date. Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.21037/tgh.2019.12.09
Jasirwan, C. O., Fahira, A., Siregar, L., & Loho, I. (2020). The alpha-fetoprotein serum is still reliable as a biomarker for the surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in Indonesia. BMC Gastroenterology., 20(1), 1–8.
Chan, S. L., Mo, F. K., Johnson, P. J., Hui, E. P., Ma, B. B., Ho, W. M., Lam, K. C., Chan, A. T., Mok, T. S., & Yeo, W. (2009). New utility of an old marker: Serial alpha-fetoprotein measurement in predicting radiologic response and survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing systemic chemotherapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(3), 446–452.
Lai, Q., Avolio, A. W., Manzia, T. M., Sorge, R., Agnes, S., Tisone, G., Berloco, P. B., & Rossi, M. (2012). Combination of biological and morphological parameters for the selection of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma waiting for liver transplantation. Clinical Transplantation, 26(2), E125–E131.
Kawaoka, T., Aikata, H., Murakami, E., Nakahara, T., Naeshiro, N., Tanaka, M., Honda, Y., Miyaki, D., Nagaoki, Y., Takaki, S., Hiramatsu, A., Waki, K., Takahashi, S., & Chayama, K. (2012). Evaluation of the mRECIST and α-fetoprotein ratio for stratification of the prognosis of advanced-hepatocellular-carcinoma patients treated with sorafenib. Oncology, 83(4), 192–200.
Liu, L., Zhao, Y., Jia, J., Chen, H., Bai, W., Yang, M., Yin, Z., He, C., Zhang, L., Guo, W., Niu, J., Yuan, J., Cai, H., Xia, J., Fan, D., & Han, G. (2016). The prognostic value of alpha-fetoprotein response for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization. Scientific Reports, 6, 19851.
Paul, S. B., Sahu, P., Sreenivas, V., Nadda, N., Gamanagatti, S. R., Nayak, B., Shalimar, S., & Acharya, S. K. (2019). Prognostic role of serial alpha-fetoprotein levels in hepatocellular carcinoma treated with locoregional therapy. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 54(9), 1132–1137.
Kelley, R. K., Meyer, T., Rimassa, L., Merle, P., Park, J. W., Yau, T., Chan, S. L., Blanc, J. F., Tam, V. C., Tran, A., & Dadduzio, V. (2020). Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels and clinical outcomes in the phase III CELESTIAL Study of cabozantinib versus placebo in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 26(18), 4795–4804.
Jasirwan, C. O., Fahira, A., Siregar, L., & Loho, I. (2020). The alpha fetoprotein serum is still reliable as a biomarker for the surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in Indonesia. BMC Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-020-01365-1
Trevisani, F., Garuti, F., & Neri, A. (2019). Alpha-fetoprotein for diagnosis, prognosis, and transplant selection. Seminars in Liver Disease, 39(02), 163–177.
Kandasamy, A., & Pottakkat, B. (2020). Alpha-fetoprotein: A molecular bootstrap for hepatocellular carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular and Immuno Oncology, 3, 92–95.
Wang, X., & Wang, Q. (2018). Alpha-fetoprotein and hepatocellular carcinoma immunity. Canadian Journal of Gastroenterol Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9049252
Zheng, Y., Zhu, M., & Li, M. (2020). Effects of alpha-fetoprotein on the occurrence and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 10, 2439–2446.
Zhang, H., Cao, D., Zhou, L., Zhang, Y., Guo, X., Li, H., Chen, Y., Spear, B. T., Wu, J. W., Xie, Z., & Zhang, W. J. (2015). ZBTB20 is a sequence-specific transcriptional repressor of alpha-fetoprotein gene. Science and Reports, 5, 11979.
Chaudhari, P., Tian, L., Deshmukh, A., & Jang, Y. Y. (2016). Expression kinetics of hepatic progenitor markers in cellular models of human liver development recapitulating hepatocyte and biliary cell fate commitment. Experimental Biology and Medicine (Maywood), 15, 1653–1662.
Chen, Y., Zhao, Y., Feng, L., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., & Feng, G. (2016). Association between alpha-fetoprotein and metabolic syndrome in a Chinese asymptomatic population: A cross-sectional study. Lipids in Health and Disease, 15, 85.
Lazarevich NL. (2013). AFP (alpha-fetoprotein). Retrieved January 11, 2013, from http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org
Lazarevich, N. L. (2000). Molecular mechanisms of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression. Biochemistry (Moscow), 1, 117–133.
Shen, S., Feng, H., Liu, L., Su, W., Yu, L., & Wu, J. (2020). TCP10L negatively regulates alpha-fetoprotein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMB Reports, 8, 431–436.
Chen, W., Peng, J., Ye, J., Dai, W., Li, G., & He, Y. (2020). Aberrant AFP expression characterizes a subset of hepatocellular carcinoma with distinct gene expression patterns and inferior prognosis. Journal of Cancer, 2, 403–413.
Bois-Joyeux, B., Thomassin, H., Richard, F., Ikonomova, R., Denissenko, M., & Danan, J. L. (1995). Plusieurs facteurs de transcription participent au fonctionnement du promoteur du gene alpha-foetoproteine. Bulletin du Cancer, 82, 541–550.
Cui, R., Nguyen, T. T., Taube, J. H., Stratton, S. A., Feuerman, M. H., & Barton, M. C. (2005). Family members p53 and p73 act together in chromatin modification and direct repression of alpha-fetoprotein transcription. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 200(47), 39152–39160.
Nguyen, T. T., Cho, K., Stratton, S. A., & Barton, M. C. (2005). Transcription factor interactions and chromatin modifications associated with p53-mediated, developmental repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 6, 2147–2157.
Lee, K. C., Crowe, A. J., & Barton, M. C. (1999). p53-mediated repression of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression by specific DNA binding. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2, 1279–1288.
Jin, L., Morford, L., Peterson, M., & Spear, B. (2006). Alpha-fetoprotein regulator-1 posttranscriptionally represses alpha-fetoprotein expression. The FASEB Journal, 20, A1344–A1344.
Xue, J., Cao, Z., Cheng, Y., Wang, J., Liu, Y., Yang, R., Li, H., Jiang, W., Li, G., Zhao, W., & Zhang, X. (2020). Acetylation of alpha-fetoprotein promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Letters, 471, 12–26.
Mah, W. C., & Lee, C. G. D. N. A. (2014). methylation: Potential biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomarker Research, 1, 1–3.
Zhao, T., Jia, L., Li, J., Ma, C., Wu, J., Shen, J., Dang, L., Zhu, B., Li, P., Zhi, Y., Lan, R., Xu, Y., Hao, Z., Chai, Y., Li, Q., Hu, L., & Sun, S. (2020). Heterogeneities of site-specific N-glycosylation in HCC tumors with low and high AFP concentrations. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 496.
Verhelst, X., Dias, A. M., Colombel, J. F., Vermeire, S., Van Vlierberghe, H., Callewaert, N., & Pinho, S. S. (2020). Protein glycosylation as a diagnostic and prognostic marker of chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Gastroenterology, 1, 95–110.
Tagliabracci, V. S., Wiley, S. E., Guo, X., Kinch, L. N., Durrant, E., Wen, J., Xiao, J., Cui, J., Nguyen, K. B., Engel, J. L., Coon, J. J., Grishin, N., Pinna, L. A., Pagliarini, D. J., & Dixon, J. E. (2015). A single kinase generates the majority of the secreted phosphoproteome. Cell, 7, 1619–1632.
Mizejewski, G. J. (2019). Protein binding and interactions with alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): A review of multiple AFP cell surface receptors, intracytoplasmic binding, and inter-molecular complexing proteins. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology Forecast, 1, 1016.
Li, M., Li, H., Li, C., Wang, S., Jiang, W., Liu, Z., Zhou, S., Liu, X., McNutt, M. A., & Li, G. (2011). Alpha-fetoprotein: A new member of intracellular signal molecules in regulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling in human hepatoma cell lines. International Journal of Cancer, 3, 524–532.
Shi, X., Wang, J., Lei, Y., Cong, C., Tan, D., & Zhou, X. (2019). Research progress on the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in gynecological cancer (Review). Molecular Medicine Reports, 6, 4529–4535.
Yuan, T. L., & Cantley, L. C. (2008). PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: Variations on a theme. Oncogene, 41, 5497–5510.
Lu, Y., Zhu, M., Li, W., Lin, B., Dong, X., Chen, Y., Xie, X., Guo, J., & Li, M. (2016). Alpha fetoprotein plays a critical role in promoting metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 3, 549–558.
Qiao, M., Sheng, S., & Pardee, A. B. (2008). Metastasis and AKT activation. Cell Cycle, 19, 2991–2996.
Hung, C. M., Garcia-Haro, L., Sparks, C. A., & Guertin, D. A. (2012). mTOR-dependent cell survival mechanisms. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 12, a008771.
Chen, J., Zhao, J., Ma, R., Lin, H., Liang, X., & Cai, X. (2014). Prognostic significance of E-cadherin expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 8, e103952.
Scheau, C., Badarau, I. A., Costache, R., Caruntu, C., Mihai, G. L., Didilescu, A. C., Constantin, C., & Neagu, M. (2019). The role of matrix metalloproteinases in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma. Analytical Cellular Pathology (Amsterdam), 2019, 9423907.
Huang, F., & Geng, X. P. (2010). Chemokines and hepatocellular carcinoma. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 15, 1832–1836.
Dohi, T., & Burkly, L. C. (2012). The TWEAK/Fn14 pathway as an aggravating and perpetuating factor in inflammatory diseases: Focus on inflammatory bowel diseases. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 2, 265–279.
Feng, S. L., Guo, Y., Factor, V. M., Thorgeirsson, S. S., Bell, D. W., Testa, J. R., Peifley, K. A., & Winkles, J. A. (2000). The Fn14 immediate-early response gene is induced during liver regeneration and highly expressed in both human and murine hepatocellular carcinomas. American Journal of Pathology, 4, 1253–1261.
Li, M., Li, H., Li, C., Guo, L., Liu, H., Zhou, S., Liu, X., Chen, Z., Shi, S., Wei, J., McNutt, M. A., & Li, G. (2009). Cytoplasmic alpha-fetoprotein functions as a co-repressor in RA-RAR signaling to promote the growth of human hepatoma Bel 7402 cells. Cancer Letters, 2, 190–199.
Aronin, A., Amsili, S., Prigozhina, T. B., Tzdaka, K., Rachmilewitz, J., Shani, N., Tykocinski, M. L., & Dranitzki, E. M. (2013). Fn14•TRAIL effectively inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth. PLoS ONE, 10, e77050.
Hu, G., Zeng, W., & Xia, Y. (2017). TWEAK/Fn14 signaling in tumors. Tumour Biology, 6, 1010428317714624.
Wang, S., Jiang, W., Chen, X., Zhang, C., Li, H., Hou, W., Liu, Z., McNutt, M. A., Lu, F., & Li, G. (2012). Alpha-fetoprotein acts as a novel signal molecule and mediates transcription of Fn14 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Hepatology, 2, 322–329.
Li, M. S., Li, P. F., He, S. P., Du, G. G., & Li, G. (2002). The promoting molecular mechanism of alpha-fetoprotein on the growth of human hepatoma Bel7402 cell line. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 3, 469–475.
Tunissiolli, N. M., Castanhole-Nunes, M. M. U., Biselli-Chicote, P. M., Pavarino, E. C., da Silva, R. F., da Silva, R. C., & Goloni-Bertollo, E. M. (2017). Hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive review of biomarkers, clinical aspects, and therapy. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 4, 863–872.
Li, M. S., Ma, Q. L., Chen, Q., Liu, X. H., Li, P. F., Du, G. G., & Li, G. (2005). Alpha-fetoprotein triggers hepatoma cells escaping from immune surveillance through altering the expression of Fas/FasL and tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand and its receptor of lymphocytes and liver cancer cells. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 17, 2564–2569.
Yamamoto, M., Tatsumi, T., Miyagi, T., Tsunematsu, H., Aketa, H., Hosui, A., Kanto, T., Hiramatsu, N., Hayashi, N., & Takehara, T. (2011). α-Fetoprotein impairs activation of natural killer cells by inhibiting the function of dendritic cells. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 2, 211–219.
Gao, Q., Qiu, S. J., Fan, J., Zhou, J., Wang, X. Y., Xiao, Y. S., Xu, Y., Li, Y. W., & Tang, Z. Y. (2007). Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 18, 2586–2593.
Zhu, M., & Li, M. (2020). Inhibition of autophagy and immune response: Alpha-fetoprotein stimulates initiation of liver cancer. J Cancer Immunol, 3, 69–73.
Li, H., Liu, Y., Jiang, W., Xue, J., Cheng, Y., Wang, J., Yang, R., & Zhang, X. (2021). Icaritin promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation by down-regulating AFP gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer, 1, 318.
Collins, M., Ling, V., & Carreno, B. M. (2005). The B7 family of immune-regulatory ligands. Genome Biology, 6, 223.
Stansfield, W. E., Ranek, M., Pendse, A., Schisler, J. C., Wang, S., Pulinilkunnil, T., & Willis, M. S. (2014). The pathophysiology of cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Cellular and Molecular Pathobiology of Cardiovascular Disease. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-405206-2.00004-1
Cha, M. Y., Kim, C. M., Park, Y. M., & Ryu, W. S. (2004). Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential for the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in hepatoma cells. Hepatology, 6, 1683–1693.
Kline, C. L., Jackson, R., Engelman, R., Pledger, W. J., Yeatman, T. J., & Irby, R. B. (2008). Src kinase induces tumor formation in the c-SRC C57BL/6 mouse. International Journal of Cancer, 12, 2665–2673.
Hobert, O., & Westphal, H. (2000). Functions of LIM-homeobox genes. Trends in Genetics, 2, 75–83.
Dudich, E., Semenkova, L., Dudich, I., Gorbatova, E., Tochtamisheva, N., Tatulov, E., Nikolaeva, M., & Sukhikh, G. (1999). alpha-fetoprotein causes apoptosis in tumor cells via a pathway independent of CD95, TNFR1 and TNFR2 through activation of caspase-3-like proteases. European Journal of Biochemistry, 3, 750–761.
Chen, T., Dai, X., Dai, J., Ding, C., Zhang, Z., Lin, Z., Hu, J., Lu, M., Wang, Z., Qi, Y., Zhang, L., Pan, R., Zhao, Z., Lu, L., Liao, W., & Lu, X. (2020). AFP promotes HCC progression by suppressing the HuR-mediated Fas/FADD apoptotic pathway. Cell Death & Disease, 10, 822.
Li, M., Liu, X., Zhou, S., Li, P., & Li, G. (2005). Effects of alpha fetoprotein on escape of Bel 7402 cells from attack of lymphocytes. BMC Cancer, 5, 96.
Funding
We acknowledge the support of the Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham SEED grant [Project ID: K-PHAR-22-662] to LRN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LRN & VV designed and conceptualized the review, writing and revising, and proofreading of the manuscript. SS & AH wrote the first draft. BLN, ARK, BSM, and AV conducted a literature survey and data collection. BLN carried out the artwork.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Samban, S.S., Hari, A., Nair, B. et al. An Insight Into the Role of Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) in the Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol Biotechnol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00890-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00890-0