Abstract
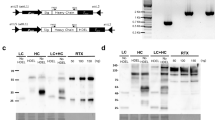
Production of monoclonal antibodies and pharmaceutical proteins in transgenic plants has been the focus of many research efforts for close to 30 years. Use of plants as bioreactors reduces large-scale production costs and minimizes risk for human pathogens contamination. Stable nuclear transformation of the plant genome offers a clear advantage in agricultural protein production platforms, limited only by the number of hectares that can be cultivated. We report here, for the first time, successful and stable expression of adalimumab in transgenic Nicotiana tabacum plants. The plant-derived adalimumab proved fully active and was shown to rescue L929 cells from the in vitro lethal effect of rhTNFα just as effectively as commercially available CHO-derived adalimumab (Humira). These results indicate that agricultural biopharming is an efficient alternative to mammalian cell-based expression platforms for the large-scale production of recombinant antibodies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stoger, E., Sack, M., Fischer, R., & Christou, P. (2002). Plantibodies: Applications, advantages and bottlenecks. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 13, 161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(02)00303-8.
Schillberg, S., Twyman, R. M., & Fischer, R. (2005). Opportunities for recombinant antigen and antibody expression in transgenic plants technology assessment. Vaccine, 23, 1764–1769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.11.002.
Fahad, S., Khan, F. A., Pandupuspitasari, N. S., et al. (2014). Recent developments in therapeutic protein expression technologies in plants. Biotechnology Letters, 37, 265–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1699-7.
Fischer, R., Stoger, E., Schillberg, S., et al. (2004). Plant-based production of biopharmaceuticals. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 7, 152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2004.01.007.
Hiatt, A., & Cafferkey, R. B. K. (1989). Production of antibodies in transgenic plants. Nature, 342, 76–78.
Gomord, V., Chamberlain, P., Jefferis, R., & Faye, L. (2005). Biopharmaceutical production in plants: Problems, solutions and opportunities. Trends in Biotechnology, 23, 559–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.09.003.
Goldstein, D. A., & Thomas, J. A. (2004). Biopharmaceuticals derived from genetically modified plants. QJM: Monthly Journal of the Association of Physicians, 97, 705–716. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hch121.
Huang, Z., Phoolcharoen, W., Lai, H., et al. (2010). High-level rapid production of full-size monoclonal antibodies in plants by a single-vector DNA replicon system, 106, 9–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22652.
Daniell, H., Streatfield, S. J., & Wycoff, K. (2001). Medical molecular farming: Production of antibodies, biopharmaceuticals and edible vaccines in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 6, 219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(01)01922-7.
Twyman, R. M., Stoger, E., Schillberg, S., et al. (2003). Molecular farming in plants: Host systems and expression technology. Trends in Biotechnology, 21, 570–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2003.10.002.
Sack, M., Hofbauer, A., Fischer, R., & Stoger, E. (2015). The increasing value of plant-made proteins. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 32, 163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.12.008.
Liénard, D., Sourrouille, C., Gomord, V., & Faye, L. (2007). Pharming and transgenic plants. Biotechnology Annual Review, 13, 115–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-2656(07)13006-4.
Yusibov, V., Kushnir, N., & Streatfield, S. J. (2016). Antibody production in plants and green algae. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 67, 669–701. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-111812.
Paul, M., Van, Dolleweerd C., Drake, P. M. W., et al. (2011). Future targets and aspirations. Molecular pharming. Human Vaccines. https://doi.org/10.4161/HV.7.3.14456.
Fischer, R., Twyman, R. M., & Schillberg, S. (2003). Production of antibodies in plants and their use for global health. Vaccine, 21, 820–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00607-2.
Twyman, R. M., Schillberg, S., & Fischer, R. (2008). Production of therapeutic antibodies in plants. Medicinal Plant Biotechnology: From Basic Research to Industrial Applications. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527619771.ch14.
Goldstein, D. A., & Thomas, J. A. (2004). Review Biopharmaceuticals derived from genetically modified plants. QJM, 97, 705–716. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hch121.
Fischer, R., & Emans, N. (2000). Molecular farming of pharmaceutical proteins. Transgenic Research, 9, 279–299. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008975123362.
Westerhof, L. B., Wilbers, R. H. P., van Raaij, D. R., et al. (2014). Monomeric IgA can be produced in planta as efficient as IgG, yet receives different N-glycans. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 12, 1333–1342. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12251.
Decker, T., & Gifford, G. E. (1987). Cell-associated tumor necrosis factor (TNF) as a killing mechanism of activated cytotoxic Information about subscribing to The Journal of Immunology is online at: Mechanism of activated cytotoxic macrophages. Journal of Immunology, 138, 957–962.
Mitoma, H., Horiuchi, T., Tsukamoto, H., et al. (2008). Mechanisms for cytotoxic effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents on transmembrane tumor necrosis factor α-expressing cells: Comparison among infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 58, 1248–1257. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23447.
Bazzoni, F., & Beutler, B. (1996). The tumor necrosis factor ligand and receptor families. The New England Journal Of Medicine, 334, 1717–1725.
Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products. (2004). Humira—European public assessment reports. Scientific discussion (pp. 1–25).
Shani, Z., Dekel, M., Tsabary, G., & Shoseyov, O. (1997). Cloning and characterization of elongation specific endo-1,4-β-glucanase (cel1) from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Molecular Biology, 34, 837–842.
Grohs, B., Niu, Y., Veldhuis, L., et al. (2010). Plant-produced trastuzumab inhibits the growth of HER2 positive cancer cells. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf102284f.
Ma, J. K. C., Drossard, J., Lewis, D., et al. (2015). Regulatory approval and a first-in-human phase I clinical trial of a monoclonal antibody produced in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 13, 1106–1120. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12416.
Wilken, L. R., & Nikolov, Z. L. (2012). Recovery and purification of plant-made recombinant proteins. Biotechnology Advances, 30, 419–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.07.020.
Bouquin, T., Thomsen, M., Nielsen, L. K., et al. (2002). Human anti-Rhesus D IgG1 antibody produced in transgenic plants. Transgenic Research, 11, 115–122. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015226418688.
Aalberse, R. C., Akkerdaas, J. H., & Van Ree, R. (2001). Cross-reactivity of IgE antibodies to allergens. Allergy, 56, 478–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(97)70245-8.
Bardor, M., Faveeuw, C., Fitchette, A.-C., et al. (2003). Immunoreactivity in mammals of two typical plant glyco-epitopes, core alpha(1,3)-fucose and core xylose. Glycobiology, 13, 427–434. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwg024.
Gomord, V. (2004). Production and glycosylation of plant-made pharmaceuticals: The antibodies as a challenge. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2, 83–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2004.00062.x.
Stein, H., Wilensky, M., Tsafrir, Y., et al. (2009). Production of bioactive, post-translationally modified, heterotrimeric, human recombinant type-I collagen in transgenic tobacco. Biomacromolecules, 3, 2640–2645.
Ausubel, F. M., Brent, R., Kingston, R. E., Moore, D. D., Seidman, J. G., Smith, J. A., et al. (1987). Protocols in molecular biology. New York, NY: Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience John Wiley and Sons.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Meirav Blanka for her help in the development of the quantitative ELISA and Dr. Yehudit Posen for critically reviewing this manuscript. This study was supported by the Minerva Center for bio-hybrid complex system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zvirin, T., Magrisso, L., Yaari, A. et al. Stable Expression of Adalimumab in Nicotiana tabacum. Mol Biotechnol 60, 387–395 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0075-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0075-6