Abstract
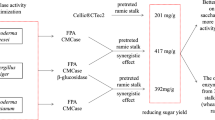
Enzymatic hydrolysis is considered an efficient and environmental strategy for the degradation of organic waste materials. Compared to mesophilic cellulases, thermostable cellulases with considerable activity are more advantageous in waste paper hydrolysis, particularly in terms of their participation in synergistic action. In this study, the synergistic effect of two different types of thermostable Chaetomium thermophilum cellulases, the endoglucanase CTendo45 and the cellobiohydrolase CtCel6, on five common kinds of waste papers was investigated. CtCel6 significantly enhanced the bioconversion process, and CTendo45 synergistically increased the degradation, with a maximum degree of synergistic effect of 1.67 when the mass ratio of CTendo45/CtCel6 was 5:3. The synergistic degradation products of each paper material were also determined. Additionally, the activities of CTendo45 and CtCel6 were found to be insensitive to various metals at 2 mM and 10 mM ion concentrations. This study gives an initial insight into a satisfactory synergistic effect of C. thermophilum thermostable cellulases for the hydrolysis of different paper materials, which provides a potential combination of enzymes for industrial applications, including environmentally friendly waste management and cellulosic ethanol production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, D. Y., Zhang, R. F., Yang, X. M., Wu, H. S., Xu, D. B., et al. (2011). Thermostable cellulase production of Aspergillus fumigatus Z5 under solid-state fermentation and its application in degradation of agricultural wastes. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 65, 717–725.
Eisted, R., & Christensen, T. H. (2011). Characterization of household waste in Greenland. Waste Management, 31, 1461–1466.
Elliston, A., Collins, S. R. A., Faulds, C. B., Roberts, I. N., & Waldron, K. W. (2014). Biorefining of waste paper biomass: increasing the concentration of glucose by optimising enzymatic hydrolysis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 172, 3621.
Ervasti, I., Miranda, R., & Kauranen, I. (2016). A global, comprehensive review of literature related to paper recycling: A pressing need for a uniform system of terms and definitions. Waste Management, 48, 64–71.
Pivnenko, K., Eriksson, E., & Astrup, T. F. (2015). Waste paper for recycling: Overview and identification of potentially critical substances. Waste Management, 45, 134–142.
Biedermann, M., Ingenhoff, J. E., Zurfluh, M., Richter, L., Simat, T., et al. (2013). Migration of mineral oil, photoinitiators and plasticisers from recycled paperboard into dry foods: A study under controlled conditions. Food Additives & Contaminants Part A Chemistry Analysis Control Exposure & Risk Assessment, 30, 885–898.
Lorenzini, R., Biedermann, M., Grob, K., Garbini, D., Barbanera, M., et al. (2013). Migration kinetics of mineral oil hydrocarbons from recycled paperboard to dry food: monitoring of two real cases. Food Additives & Contaminants Part A Chemistry Analysis Control Exposure & Risk Assessment, 30, 760–770.
Rojo, E. S., Ramos, M., Yates, M., Ma, M. L., Serrano, A. M. M., et al. (2014). Preparation, characterization and in vitro osteoblast growth of waste-derived biomaterials. RSC Advances, 4, 12630–12639.
Wang, L., Sharifzadeh, M., Templer, R., & Murphy, R. J. (2013). Bioethanol production from various waste papers: Economic feasibility and sensitivity analysis. Applied Energy, 111, 1172–1182.
Shi, A. Z., Koh, L. P., & Tan, H. T. W. (2009). The biofuel potential of municipal solid waste. Global Change Biology Bioenergy, 1, 317–320.
Manente, S., Micheluz, A., Ganzerla, R., Ravagnan, G., & Gambaro, A. (2012). Chemical and biological characterization of paper: A case study using a proposed methodological approach. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 74, 99–108.
Huy, N. D., Nguyen, C. L., Park, H. S., Loc, N. H., Choi, M. S., et al. (2016). Characterization of a novel manganese dependent endoglucanase belongs in GH family 5 from Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 121, 154–159.
Akimkulova, A., Zhou, Y., Zhao, X., & Liu, D. (2016). Improving the enzymatic hydrolysis of dilute acid pretreated wheat straw by metal ion blocking of non-productive cellulase adsorption on lignin. Bioresource Technology, 208, 110–116.
Liang, F. B., Song, Y. L., Huang, C. P., Li, Y. X., & Chen, B. H. (2013). Synthesis of novel lignin-based ion-exchange resin and its utilization in heavy metals removal. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 52, 1267–1274.
Zhou, Q. Z., Ji, P., Zhang, J. Y., & Han, C. (2017). Characterization of a novel thermostable GH45 endoglucanase from Chaetomium thermophilum and its biodegradation of pectin. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 124, 271–276.
Zhou, Q. Z., Jia, J. C., Ji, P., & Han, C. (2017). A novel application potential of GH6 cellobiohydrolase CtCel6 from thermophilic Chaetomium thermophilum for gene cloning, heterologous expression and biological characterization. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 19, 355–362.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Meleiro, L. P., Zimbardi, A. L., Souza, F. H., Masui, D. C., Silva, T. M., et al. (2014). A novel β-glucosidase from Humicola insolens with high potential for untreated waste paper conversion to sugars. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 173, 391–408.
Zhang, X. Z., Sathitsuksanoh, N., & Zhang, Y. H. (2010). Glycoside hydrolase family 9 processive endoglucanase from Clostridium phytofermentans: heterologous expression, characterization, and synergy with family 48 cellobiohydrolase. Bioresource Technology, 101, 5534–5538.
Karnaouri, A. C., Topakas, E., & Christakopoulos, P. (2014). Cloning, expression, and characterization of a thermostable GH7 endoglucanase from Myceliophthora thermophila capable of high-consistency enzymatic liquefaction. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 98, 231–242.
Ragauskas, A. J., Williams, C. K., Davison, B. H., Britovsek, G., Cairney, J., et al. (2006). The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science, 311, 484–489.
Chen, H., Han, Q., Venditti, R. A., & Jameel, H. (2015). Enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated newspaper having high lignin content for bioethanol production. BioResources, 10, 4077–4098.
Matkar, K., Chapla, D., Divecha, J., Nighojkar, A., & Madamwar, D. (2013). Production of cellulase by a newly isolated strain of Aspergillus sydowii and its optimization under submerged fermentation. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 78, 24–33.
Xin, F., Geng, A., Chen, M. L., & Gum, M. J. (2010). Enzymatic hydrolysis of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS)-pretreated newspaper for cellulosic ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 1052–1064.
van Wyk, J. P., & Mohulatsi, M. (2003). Biodegradation of wastepaper by cellulase from Trichoderma viride. Bioresource Technology, 86, 21–23.
Lee, R. L., Paul, J. W., Willem, H. Z., & Isak, S. P. (2002). Microbial cellulose utilization: Fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 66, 506–577.
Singhania, R. R., Patel, A. K., Pandey, A., & Ganansounou, E. (2017). Genetic modification: A tool for enhancing beta-glucosidase production for biofuel application. Bioresource Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.126.
da Silva, V. M., Sato, J. A. P., Araujo, J. N., Squina, F. M., Muniz, J. R. C., et al. (2017). Systematic studies of the interactions between a model polyphenol compound and microbial β-glucosidases. PLoS ONE, 12, e0181629.
Singhania, R. R., Patel, A. K., Sukumaran, R. K., Larroche, C., & Pandey, A. (2013). Role and significance of beta-glucosidases in the hydrolysis of cellulose for bioethanol production. Bioresource Technology, 127, 500–507.
Chu, K. H., & Feng, X. (2013). Enzymatic conversion of newspaper and office paper to fermentable sugars. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 91, 123–130.
Wang, L., Templer, R., & Murphy, R. J. (2012). High-solids loading enzymatic hydrolysis of waste papers for biofuel production. Applied Energy, 99, 23–31.
Lee, D. H., Cho, E. Y., Kim, C. J., & Kim, S. B. (2010). Pretreatment of waste newspaper using ethylene glycol for bioethanol production. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 15, 1094–1101.
Shi, H., Zhang, Y., Xu, B., Tu, M., & Wang, F. (2014). Characterization of a novel GH2 family α-L-arabinofuranosidase from hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga thermarum. Biotechnology Letters, 36, 1321–1328.
Verma, D., & Satyanarayana, T. (2012). Cloning, expression and applicability of thermo-alkali-stable xylanase of Geobacillus thermoleovorans in generating xylooligosaccharides from agro-residues. Bioresource Technology, 107, 333–338.
Pinzari, L., Zotti, Z. M., Mico, A. D., & Calvini, P. (2010). Biodegradation of inorganic components in paper documents: Formation of calcium oxalate crystals as a consequence of Aspergillus terreus Thom growth. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 64, 499–505.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Prof. Duochuan Li from Shandong Agricultural University for technical assistance. This research was supported by National Key Technology R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2015BAD15B05) and Funds of Shandong Double Tops Program (Grant No. SYL2017XTTD11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Ji, P., Zhou, Q. et al. Insights into the Synergistic Biodegradation of Waste Papers Using a Combination of Thermostable Endoglucanase and Cellobiohydrolase from Chaetomium thermophilum . Mol Biotechnol 60, 49–54 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-017-0043-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-017-0043-6