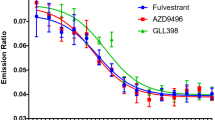
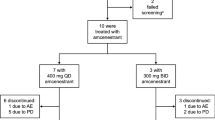
Abstract
Elacestrant (RAD-1901), a selective estrogen receptor degrader, was approved by USFDA on January 27, 2023, for the treatment of breast cancer. It has been developed by Menarini Group under the brand name Orserdu®. Elacestrant showed anticancer activity both in vitro and in vivo in ER+ HER2-positive breast cancer models. The present review delebrates the development stages of Elacestrant, with its medicinal chemistry, synthesis, mechanism of action, and pharmacokinetic studies. Clinical data and safety profile has also been discussed, including data from randomized trials.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Saber A, Sakr M, Abo-Seida OM, Keshk A, Chen H. A novel deep-learning model for automatic detection and classification of breast cancer using the transfer-learning technique. IEEE Access. 2021;9:71194–209.
Lee H-R, Kim T-H, Choi K-C. Functions and physiological roles of two types of estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ, identified by estrogen receptor knockout mouse. Lab Anim Res. 2012;28(2):71–6.
Ogino Y, Ansai S, Watanabe E, Yasugi M, Katayama Y, Sakamoto H, Okamoto K, Okubo K, Yamamoto Y, Hara I. Evolutionary differentiation of androgen receptor is responsible for sexual characteristic development in a teleost fish. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):1428.
McInerney EM, Tsai M-J, O’Malley BW, Katzenellenbogen BS. Analysis of estrogen receptor transcriptional enhancement by a nuclear hormone receptor coactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1996;93(19):10069–73.
Manna P, Molehin D, Ahmed A. Dysregulation of aromatase in breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancers: An overview of therapeutic strategies. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2016;144:487–537.
Boersma C, Mosselman S. Estrogen receptors alpha and beeta two receptors of a kind. Curr Med Chem. 2000;7(5):561–76.
Marino M, Galluzzo P, Ascenzi P. Estrogen signaling multiple pathways to impact gene transcription. Curr Genom. 2006;7(8):497–508.
FDA FDA approves elacestrant for ER-positive, HER2-negative, ESR1-mutated advanced or metastatic breast cancer. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-elacestrant-er-positive-her2-negative-esr1-mutated-advanced-or-metastatic-breast-cancer#:~:text=On%20January%2027%2C%202023%2C%20the,one%20line%20of%20endocrine%20therapy.
OncLive, T.; Exchange, P., SERMS, SERDS, and PROTEC are poised to shake up treatments for ER+ breast cancer.
Group M. Stemline Therapeutics, a subsidiary of Menarini Group, Receives U.S. FDA Approval for ORSERDU™ (elacestrant) as the First and Only Treatment Specifically Indicated for Patients with ESR1 Mutations in ER+, HER2− Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer. (2023)
Chen Y-C, Yu J, Metcalfe C, De Bruyn T, Gelzleichter T, Malhi V, Perez-Moreno PD, Wang X. Latest generation estrogen receptor degraders for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022;31(6):515–29.
Li Y, Orahoske CM, Urmetz SM, Zhang W, Huang Y, Gan C, Su B. Identification of estrogen receptor down-regulators for endocrine resistant breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2022;224: 106162.
Ciruelos E, Pascual T, Vozmediano MLA, Blanco M, Manso L, Parrilla L, Muñoz C, Vega E, Calderón MJ, Sancho B. The therapeutic role of fulvestrant in the management of patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast. 2014;23(3):201–8.
Wang Y, Tang S-C. The race to develop oral SERDs and other novel estrogen receptor inhibitors: recent clinical trial results and impact on treatment options. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022;41(4):975–90.
de Vries E, Venema C, Glaudemans A, Jager A, Menke-vanderHouvenvanOordt C, Neven P, Jiang H, Wang D, O’Neill A, Patki A. Abstract P1-10-04: Elacestrant, a novel oral selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), decreases tumoral 18F-FES uptake in a phase 1 study of ER+, HER2−, advanced breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2018;78(4):P1-10-04-P1-10–04.
Pancholi S, Simigdala N, Ribas R, Schuster E, Leal MF, Nikitorowicz-Buniak J, Rega C, Bihani T, Patel H, Johnston SR. Elacestrant demonstrates strong anti-estrogenic activity in PDX models of estrogen-receptor positive endocrine-resistant and fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022;8(1):125.
Zhou J, Shen R, Liu J, Deng X, Xin L, Zhou H-B, Huang J. A novel selective estrogen receptor degrader induces cell cycle arrest in breast cancer via ERα degradation and the autophagy-lysosome pathway. Bioorg Med Chem. 2023;82:117235.
Bidard F-C, Kaklamani VG, Neven P, Streich G, Montero AJ, Forget F, Mouret-Reynier M-A, Sohn JH, Taylor D, Harnden KK. Elacestrant (oral selective estrogen receptor degrader) versus standard endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: results from the randomized phase III EMERALD trial. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(28):3246–56.
Froelich W. Elacestrant provides greater PFS for breast cancer patients. LWW. 2022;44:28.
Ferraro E, Walsh EM, Tao JJ, Chandarlapaty S, Jhaveri K. Accelerating drug development in breast cancer: new frontiers for ER inhibition. Cancer Treat Rev. 2022;109:102432.
Jacobson A. Elacestrant improves progression-free survival after endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist. 2022;27:S7–8.
Sanchez KG, Nangia JR, Schiff R, Rimawi MF. Elacestrant and the promise of Oral SERDs. Wolters Kluwer Health. 2022;40:3227–9.
Varella L, Cristofanilli M. Evaluating elacestrant in the management of ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: evidence to date. OncoTargets Therapy. 2023;16:189–96.
Weaver, C., Elacestrant hormone therapy for advanced breast cancer.
Muchmore DB. Raloxifene: a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with multiple target system effects. Oncologist. 2000;5(5):388–92.
Das S, Kulkarni S, Singh Y, Kumar P, Thareja S. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) for the treatment of ER+ breast cancer: an overview. J Mol Struct. 2022;1270:133853.
Wu Y-L, Yang X, Ren Z, McDonnell DP, Norris JD, Willson TM, Greene GL. Structural basis for an unexpected mode of SERM-mediated ER antagonism. Mol Cell. 2005;18(4):413–24.
Chinnasamy K, Saravanan M, Poomani K. Investigation of binding mechanism and downregulation of elacestrant for wild and L536S mutant estrogen receptor-α through molecular dynamics simulation and binding free energy analysis. J Comput Chem. 2020;41(2):97–109.
Lu Y, Liu W. Selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs): a promising strategy for estrogen receptor positive endocrine-resistant breast cancer. J Med Chem. 2020;63(24):15094–114.
Bhatia N, Hazra S, Thareja S. Selective Estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) for the treatment of breast cancer: An overview. Eur J Med Chem. 2023;256:115422.
Shomali M, Cheng J, Sun F, Koundinya M, Guo Z, Hebert AT, McManus J, Levit MN, Hoffmann D, Courjaud A. SAR439859, a novel selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), demonstrates effective and broad antitumor activity in wild-type and mutant ER-positive breast cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021;20(2):250–62.
Donahue K, Xu W. Therapeutic strategies to target activating estrogen receptor α mutations. Nucl Recept. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78315-0_15.
Kudera J., Elacestrant on course to gain FDA approval. Living Beyond Breast Cancer. (2022)
Chemical S-S. Elacestrant dihydrochloride. (2022)
FDA. Highlights of prescribing information. (2023)
Bafna D, Ban F, Rennie PS, Singh K, Cherkasov A. Computer-aided ligand discovery for estrogen receptor alpha. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4193.
Fanning SW, Greene G, Conlan MG. X-ray crystal structure analysis of elacestrant (RAD1901), a novel selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), bound to estrogen receptor alpha ligand binding domain. Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2020;38:e15647.
Markey M. Useful processes of preparation and intermediates useful for the preparation of Compound 1, a selective estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) modulator/degrader (SERM/SERD), having utility for the treatment of ER+ cancers including breast cancer are described. (2020)
Conlan MG, de Vries EF, Glaudemans A, Wang Y, Troy S. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of elacestrant, a novel oral selective estrogen receptor degrader, in healthy post-menopausal women. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020;45:675–89.
Jager A, de Vries EG, der Houven van Oordt C, Neven P, Venema CM, Glaudemans AW, Wang Y, Bagley RG, Conlan MG, Aftimos P. A phase 1b study evaluating the effect of elacestrant treatment on estrogen receptor availability and estradiol binding to the estrogen receptor in metastatic breast cancer lesions using 18F-FES PET/CT imaging. Breast Cancer Res. 2020;22(1):1–11.
Rebecca G, Conlan MG, Aftimos P. A phase 1b study evaluating the effect of elacestrant treatment on estrogen receptor availability and estradiol binding to the estrogen receptor in metastatic breast cancer lesions using 18F-FES PET/CT imaging Jager, Agnes; de Vries, Elisabeth GE; der Houven van Oordt, C Willemien Menke-van; Neven, Patrick; Venema, Clasina M; Glaudemans, Andor WJM; Wang, Yamei; Bagley. (2020)
May NS, Glioblastoma T. Leading oral SERD shows prolonged activity.
Bardia A, Neven P, Streich G, Montero AJ, Forget F, Mouret-Reynier M-A, Sohn JH, Vuylsteke P, Harnden KK, Khong H. Abstract GS2-02: Elacestrant, an oral selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), vs investigator’s choice of endocrine monotherapy for ER+/HER2-advanced/metastatic breast cancer (mBC) following progression on prior endocrine and CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy: results of EMERALD phase 3 trial. Cancer Res. 2022;82(4_Supplement):GS2-02-GS2-02.
Martin L, Pancholi S, Simigdala N, Nikitorowicz-Buniak J, Ribas R, Garner F, Bihani T, Dowsett M. Abstract P4-04-09: new oral SERD elacestrant (RAD1901) shows efficacy in breast cancer models harbouring ESR1 mutations and enhances the antiproliferative activity of mTORC1 and CDK4/6 inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2018;78(4_Supplement):P4-04-09-P4-04–9.
Gombos A. Selective oestrogen receptor degraders in breast cancer: a review and perspectives. Curr Opin Oncol. 2019;31(5):424–9.
Patel H, Tao N, Arlt H, Bihani T. Abstract P4-13-03: Elacestrant (RAD1901) demonstrates anti-tumor activity in models resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2019;79(4_Supplement):P4-13-03-P4-13–03.
De Santo I, McCartney A, Migliaccio I, Di Leo A, Malorni L. The emerging role of ESR1 mutations in luminal breast cancer as a prognostic and predictive biomarker of response to endocrine therapy. Cancers. 2019;11(12):1894.
Bihani T, Patel HK, Arlt H, Tao N, Jiang H, Brown JL, Purandare DM, Hattersley G, Garner F. Elacestrant (RAD1901), a selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), has antitumor activity in multiple ER þ breast cancer patient-derived xenograft models.
Patel H, Tao N, Arlt H, Bihani T. Abstract P6-20-08: anti-tumor activity of elacestrant (RAD1901) in models harboring ESR1 mutations resistant to standard of care therapies. Cancer Res. 2019;79(4_Supplement):P6-20-08-P6-20–08.
Arlt H, Garner F, Bihani T. Abstract P4-04-17: Elacestrant (RAD1901) demonstrates anti-tumor activity in a fulvestrant-resistant PDX model. Cancer Res. 2018;78(4_Supplement):P4-04-17-P4-04–17.
Rugo H, Bardia A, Cortés J, Curigliano G, Hamilton E, Hurvitz S, Loibl S, Scartoni S, Sahmoud T, Grzegorzewski K. Abstract OT2-01-03: ELEVATE: A phase 1b/2, open-label, umbrella study evaluating elacestrant in various combinations in women and men with metastatic breast cancer (mBC). Cancer Res. 2023;83(5_Supplement):OT2-01-03-OT2-01–3.
Robertson J, Harrison M. Fulvestrant: pharmacokinetics and pharmacology. Br J Cancer. 2004;90(1):S7–10.
Aftimos P, Cortés J, Bidard F, Kaklamani V, Bardia A, Neven P, Streich G, Montero A, Forget F, Reynier MM. 220P Elacestrant vs fulvestrant or aromatase inhibitor (AI) in phase III trial evaluating elacestrant, an oral selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), vs standard of care (SOC) endocrine monotherapy for ER+/HER2-advanced/metastatic breast cancer (mBC): Subgroup analysis from EMERALD. Ann Oncol. 2022;33:S638.
Hamilton E, Pusztai L, Soliman HH, Hurvitz S, Grzegorzewski K, Habboubi N, Marreddy P, Sahmoud T, Ibrahim N. Abstract OT2-01-04: ELONA: An open-label, phase 1b–2 study of elacestrant, in combination with onapristone in patients with estrogen receptor-positive, progesterone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2023;83(5_Supplement):OT2-01-04-OT2-01–4.
Kaklamani VG, Bardia A, Aftimos PG, Cortes J, Lu JM, Neven P, Streich G, Montero AJ, Forget F, Mouret-Reynier MA, Sohn J. Subgroup analysis of patients with no prior chemotherapy in EMERALD: A phase 3 trial evaluating elacestrant, an oral selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), versus investigator’s choice of endocrine monotherapy for ER+/HER2-advanced/metastatic breast cancer (mBC). Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2022)
Downton T, Zhou F, Segara D, Jeselsohn R, Lim E. Oral selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) in breast cancer: advances, challenges, and current status. Drug Design Dev Therapy. 2022;16:2933–48.
Patel HK, Tao N, Lee K-M, Huerta M, Arlt H, Mullarkey T, Troy S, Arteaga CL, Bihani T. Elacestrant (RAD1901) exhibits anti-tumor activity in multiple ER+ breast cancer models resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2019;21(1):1–17.
Medthority, The Menarini Group announced that the FDA has approved Orserdu for the treatment of postmenopausal women or adult men, with ER+, HER2-, ESR1-mutated advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following at least one line of endocrine therapy. 31st Jan 2023 ed.; Medthority (2023)
Rugo HS, Bardia A, Cortes J, Curigliano G, Hamilton E, Hurvitz S, Loibl S, Scartoni S, Sahmoud T, Grzegorzewski KJ, Habboubi N. ELEVATE: A Phase 1b/2, Open-Label, Umbrella Study Evaluating Elacestrant in Various Combinations in Women and Men With Metastatic Breast Cancer (mBC). (2022)
John P. Cunha, D., FACOEP, ORSERDU. 2/2/2023 ed.; RxList. (2023)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology (DST) for providing the Departmental DST-FIST Grant (SR/FST/LSI-656/2016) to the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Natural Products, Central University of Punjab, India.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST designed the study and checked and reviewed the manuscript. NB collected the data and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. ST revised and wrote the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, N., Thareja, S. Elacestrant: a new FDA-approved SERD for the treatment of breast cancer. Med Oncol 40, 180 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02045-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02045-2