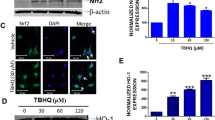
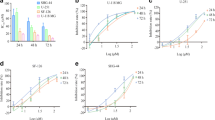
Abstract
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) grade IV glioma is the most frequent and deadly intracranial cancer. This tumor is determined by unrestrained progression, uncontroled angiogenesis, high infiltration and weak response to treatment, which is chiefly because of abnormal signaling pathways in the tumor. A member related to the Cap ‘n’ collar family of keypart-leucine zipper transcription agents—the transcription factor NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-regulates adaptive protection answers by organized upregulation of many genes that produce the cytoprotective factors. In reply to cellular pressures types such as stresses, Nrf2 escapes Kelch-like ECH-related protein 1 (Keap1)-facilitated suppression, moves from the cytoplasm towards the nucleus and performs upregulation of gene expression of antioxidant responsive element (ARE). Nrf2 function is related tocontrolling many types of diseases in the human specially GBM tumor.Thus, we will review the epigeneticalregulatory actions on the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway and potential therapeutic options in GBM by aiming the stimulation of Nrf2.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-related protein 1
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant responsive element
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- IDH-1:
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- RTK:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- MGMT:
-
O6-methylguanyl DNA methyltransferase
- RA:
-
Retinoic acid
- TEM:
-
Trans-mission electron microscopy
- TXNIP:
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein 1
- EGR1:
-
Early growth response 1
References
Wirsching H-G, Galanis E, Weller M. Glioblastoma. Handb Clin Neurol. 2016;134:381–97.
Ahmed S, Hasan MM, Aschner M, Mirzaei H, Alam W, Shah SMM, et al. Therapeutic potential of marine peptides in glioblastoma: Mechanistic insights. Cel Signal. 2021;87:110142.
Kourti M, Jiang WG, Cai J. Aspects of carbon monoxide in form of CO-releasing molecules used in cancer treatment: more light on the way. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:1–12.
Nakada M, Kita D, Watanabe T, Hayashi Y, Teng L, Pyko IV, et al. Aberrant signaling pathways in glioma. Cancers. 2011;3(3):3242–78.
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21(21):2683–710.
Tan AC, Ashley DM, López GY, Malinzak M, Friedman HS, Khasraw M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(4):299–312.
Tsai W-C, Hueng D-Y, Lin C-R, Yang TC, Gao H-W. Nrf2 expressions correlate with WHO grades in gliomas and meningiomas. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(5):722.
Ji X, Wang H, Zhu J, Zhu L, Pan H, Li W, et al. Knockdown of Nrf2 suppresses glioblastoma angiogenesis by inhibiting hypoxia-induced activation of HIF-1α. Int J Cancer. 2014;135(3):574–84.
Ahmad F, Dixit D, Sharma V, Kumar A, Joshi SD, Sarkar C, et al. Nrf2-driven TERT regulates pentose phosphate pathway in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(5):e2213-e.
Sarfraz I, Rasul A, Hussain G, Shah MA, Zahoor AF, Asrar M, et al. 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase fuels multiple aspects of cancer cells: From cancer initiation to metastasis and chemoresistance. BioFactors. 2020;46(4):550–62.
Adnan M, Rasul A, Hussain G, Shah MA, Sarfraz I, Nageen B, et al. Physcion and Physcion 8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside: Natural anthraquinones with potential anticancer activities. Curr Drug Targets. 2021;22(5):488–504.
Muscarella LA, Barbano R, D’Angelo V, Copetti M, Coco M, Balsamo T, et al. Regulation of KEAP1 expression by promoter methylation in malignant gliomas and association with patient’s outcome. Epigenetics. 2011;6(3):317–25.
Li W, Kong AN. Molecular mechanisms of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48(2):91–104.
Lee J-M, Johnson JA. An important role of Nrf2-ARE pathway in the cellular defense mechanism. BMB Rep. 2004;37(2):139–43.
Lau A, Villeneuve NF, Sun Z, Wong PK, Zhang DD. Dual roles of Nrf2 in cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2008;58(5–6):262–70.
Niture SK, Kaspar JW, Shen J, Jaiswal AK. Nrf2 signaling and cell survival. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;244(1):37–42.
Rangasamy T, Guo J, Mitzner WA, Roman J, Singh A, Fryer AD, et al. Disruption of Nrf2 enhances susceptibility to severe airway inflammation and asthma in mice. J Exp Med. 2005;202(1):47–59.
Chen X-L, Kunsch C. Induction of cytoprotective genes through Nrf2/antioxidant response element pathway: a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(8):879–91.
Niture SK, Jaiswal AK. Nrf2 protein up-regulates antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and prevents cellular apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(13):9873–86.
Reddy N, Kleeberger S, Bream J, Fallon P, Kensler T, Yamamoto M, et al. Genetic disruption of the Nrf2 compromises cell-cycle progression by impairing GSH-induced redox signaling. Oncogene. 2008;27(44):5821–32.
Zhao F, Wu T, Lau A, Jiang T, Huang Z, Wang X-J, et al. Nrf2 promotes neuronal cell differentiation. Free Radical Biol Med. 2009;47(6):867–79.
Cho H-Y, Reddy SP, Yamamoto M, Kleeberger SR. The transcription factor NRF2 protects against pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J. 2004;18(11):1258–60.
Sporn MB, Liby KT. NRF2 and cancer: the good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(8):564–71.
Shah ZA, Li R-C, Thimmulappa RK, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Biswal S, et al. Role of reactive oxygen species in modulation of Nrf2 following ischemic reperfusion injury. Neuroscience. 2007;147(1):53–9.
Cho H-Y, Jedlicka AE, Reddy SP, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Zhang L-Y, et al. Role of NRF2 in protection against hyperoxic lung injury in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002;26(2):175–82.
Calkins MJ, Johnson DA, Townsend JA, Vargas MR, Dowell JA, Williamson TP, et al. The Nrf2/ARE pathway as a potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11(3):497–508.
Kanamori M, Higa T, Sonoda Y, Murakami S, Dodo M, Kitamura H, et al. Activation of the NRF2 pathway and its impact on the prognosis of anaplastic glioma patients. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17(4):555–65.
Shibata T, Kokubu A, Saito S, Narisawa-Saito M, Sasaki H, Aoyagi K, et al. NRF2 mutation confers malignant potential and resistance to chemoradiation therapy in advanced esophageal squamous cancer. Neoplasia. 2011;13(9):864-IN26.
Panieri E, Saso L. Potential applications of NRF2 inhibitors in cancer therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:1–34.
Gañán-Gómez I, Wei Y, Yang H, Boyano-Adánez MC, García-Manero G. Oncogenic functions of the transcription factor Nrf2. Free Radical Biol Med. 2013;65:750–64.
Zhu J, Wang H, Chen F, Fu J, Xu Y, Hou Y, et al. An overview of chemical inhibitors of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway and their potential applications in cancer therapy. Free Radical Biol Med. 2016;99:544–56.
Wang Z, Li Z, Xu H, Liao Y, Sun C, Chen Y, et al. PSMD12 promotes glioma progression by upregulating the expression of Nrf2. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(8):700.
Zhu J, Wang H, Ji X, Zhu L, Sun Q, Cong Z, et al. Differential Nrf2 expression between glioma stem cells and non-stem-like cells in glioblastoma. Oncol Lett. 2014;7(3):693–8.
Seng S, Avraham H, Birrane G, Jiang S, Li H, Katz G, et al. NRP/B mutations impair Nrf2-dependent NQO1 induction in human primary brain tumors. Oncogene. 2009;28(3):378–89.
Pan H, Wang H, Zhu L, Wang X, Cong Z, Sun K, et al. The involvement of Nrf2–ARE pathway in regulation of apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell U251. Neurol Res. 2013;35(1):71–8.
Bu X, Qu X, Guo K, Meng X, Yang X, Huang Q, et al. CD147 confers temozolomide resistance of glioma cells via the regulation of β-TrCP/Nrf2 pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(12):3013.
Zhu J, Wang H, Fan Y, Hu Y, Ji X, Sun Q, et al. Knockdown of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 by lentivirus induces differentiation of glioma stem-like cells. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(3):1170–8.
Zhao M, Xu H, Zhang B, Hong B, Yan W, Zhang J. Impact of nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2–like 2 and p62/sequestosome expression on prognosis of patients with gliomas. Hum Pathol. 2015;46(6):843–9.
Youn P, Chen Y, Furgeson DY. Cytoprotection against beta-amyloid (Aβ) peptide-mediated oxidative damage and autophagy by Keap1 RNAi in human glioma U87mg cells. Neurosci Res. 2015;94:70–8.
Bhattacharjee S, Dashwood RH. Epigenetic regulation of NRF2/KEAP1 by phytochemicals. Antioxidants. 2020;9(9):865.
Zimta A-A, Cenariu D, Irimie A, Magdo L, Nabavi SM, Atanasov AG, et al. The role of Nrf2 activity in cancer development and progression. Cancers. 2019;11(11):1755.
Sun W, Zhang W, Yu J, Lu Z, Yu J. Inhibition of Nrf2 might enhance the anti-tumor effect of temozolomide in glioma cells via inhibition of Ras/Raf/MEK signaling pathway. Int J Neurosci. 2021;131(10):975–83.
Liu J, Qin X, Ma W, Jia S, Zhang X, Yang X, et al. Corilagin induces apoptosis and autophagy in NRF2-addicted U251 glioma cell line. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):1–10.
Zhou Y, Wang H-D, Zhu L, Cong Z-X, Li N, Ji X-J, et al. Knockdown of Nrf2 enhances autophagy induced by temozolomide in U251 human glioma cell line. Oncol Rep. 2013;29(1):394–400.
Li K, Ouyang L, He M, Luo M, Cai W, Tu Y, et al. IDH1 R132H mutation regulates glioma chemosensitivity through Nrf2 pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(17):28865.
Mimura J, Kosaka K, Maruyama A, Satoh T, Harada N, Yoshida H, et al. Nrf2 regulates NGF mRNA induction by carnosic acid in T98G glioblastoma cells and normal human astrocytes. J Biochem. 2011;150(2):209–17.
Gao X, Guo N, Xu H, Pan T, Yan A, Mi Y, et al. Ibuprofen induces ferroptosis of glioblastoma cells via downregulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling pathway. Anticancer Drugs. 2020;31(1):27–34.
Jia Y, Wang H-D, Wang Q, Ding H, Wu H-M, Pan H. GSH depletion and consequent AKT inhibition contribute to the Nrf2 knockdown-induced decrease in proliferation in glioblastoma U251 cells. Oncol Rep. 2017;37(4):2252–60.
Zhang L, Wang H. FTY720 inhibits the Nrf2/ARE pathway in human glioblastoma cell lines and sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide. Pharmacol Rep. 2017;69(6):1186–93.
Choi E-O, Jeong J-W, Park C, Hong SH, Kim G-Y, Hwang H-J, et al. Baicalein protects C6 glial cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis through regulation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(3):798–806.
Wang G, Yang Q, Zheng C, Li D, Li J, Zhang F. Physiological Concentration of H 2 O 2 supports dopamine neuronal survival via activation of Nrf2 signaling in glial cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41(1):163–71.
Pan H, Wang Q, Niu W, Wu Q, Jia Y, Sun K, et al. Mel Aggravates Pyroptosis Induced by Temozolomide Through Inhibiting NRF2-are Pathway in Glioblastoma. 2020.
Hu Z, Mi Y, Qian H, Guo N, Yan A, Zhang Y, et al. A Potential Mechanism of Temozolomide Resistance in Glioma-Ferroptosis. Front Oncol. 2020;10:897.
Jumnongprakhon P, Govitrapong P, Tocharus C, Pinkaew D, Tocharus J. Melatonin protects methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation through NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways in glioma cell line. Neurochem Res. 2015;40(7):1448–56.
Pan H, Wang H, Jia Y, Wang Q, Li L, Wu Q, et al. VPA and MEL induce apoptosis by inhibiting the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway in TMZ-resistant U251 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(1):908–14.
Zhang H, He J, Dai Z, Wang Z, Liang X, He F, et al. PDIA5 is Correlated with immune infiltration and predicts poor prognosis in gliomas. Front Immunol. 2021;12:19.
Kyani A, Tamura S, Yang S, Shergalis A, Samanta S, Kuang Y, et al. Discovery and Mechanistic Elucidation of a Class of PDI Inhibitors for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. ChemMedChem. 2018;13(2):164.
Shi L, Li H, Zhan Y. All-trans retinoic acid enhances temozolomide-induced autophagy in human glioma cells U251 via targeting Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(3):2709–14.
Qin X, Liu J, Pan D, Ma W, Cheng P, Jin F. Corilagin induces human glioblastoma U251 cell apoptosis by impeding activity of (immuno) proteasome. Oncol Rep. 2021;45(4):1–11.
Guo Y, Wang C, Jiang M, Zhu H, Weng M, Sun L, et al. Baohuoside I via mTOR apoptotic signaling to inhibit glioma cell growth. Cancer Management and Research. 2020;12:11435.
Amin AG, Jeong SW, Gillick JL, Sursal T, Murali R, Gandhi CD, et al. Targeting the mTOR pathway using novel ATP-competitive inhibitors, Torin1, Torin2 and XL388, in the treatment of glioblastoma. Int J Oncol. 2021;59(4):1–9.
Nawaz J, Rasul A, Shah MA, Hussain G, Riaz A, Sarfraz I, et al. Cardamonin: A new player to fight cancer via multiple cancer signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2020;250:117591.
Sukumari-Ramesh S, Prasad N, Alleyne CH, Vender JR, Dhandapani KM. Overexpression of Nrf2 attenuates Carmustine-induced cytotoxicity in U87MG human glioma cells. BMC Cancer. 2015;15(1):1–10.
Guo X-D, Ji J, Xue T-F, Sun Y-Q, Guo R-B, Cheng H, et al. FTY720 exerts anti-glioma effects by regulating the glioma microenvironment through increased CXCR4 internalization by glioma-associated microglia. Front Immunol. 2020;11:178.
Takasaki T, Hagihara K, Satoh R, Sugiura R. More than just an immunosuppressant: the emerging role of FTY720 as a novel inducer of ROS and apoptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:1–13.
Wruck C, Claussen M, Fuhrmann G, Römer L, Schulz A, Pufe T, et al. Luteolin protects rat PC 12 and C6 cells against MPP+ induced toxicity via an ERK dependent Keapl-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Neuropsychiatric disorders an integrative approach: Springer; 2007. p. 57–67.
Sajadimajd S, Khazaei M. Oxidative stress and cancer: the role of Nrf2. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018;18(6):538–57.
Escoll M, Lastra D, Robledinos-Antón N, Wandosell F, Antón IM, Cuadrado A. WIP modulates oxidative stress through NRF2/KEAP1 in glioblastoma cells. Antioxidants. 2020;9(9):773.
Kumari S, Badana AK, Malla R. Reactive oxygen species: a key constituent in cancer survival. Biomarker insights. 2018;13:1177271918755391.
Wang J, Liu P, Xin S, Wang Z, Li J. Nrf2 suppresses the function of dendritic cells to facilitate the immune escape of glioma cells. Exp Cell Res. 2017;360(2):66–73.
Ohue Y, Nishikawa H. Regulatory T (Treg) cells in cancer: Can Treg cells be a new therapeutic target? Cancer Sci. 2019;110(7):2080–9.
Godoy PR, Pour Khavari A, Rizzo M, Sakamoto-Hojo ET, Haghdoost S. Targeting NRF2, regulator of antioxidant system, to sensitize glioblastoma neurosphere cells to radiation-induced oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:1–17.
Zhou J, Zhang F, Chen J, Zhang S, Wang H. Chlorogenic acid inhibits human glioma U373 cell progression via regulating the SRC/MAPKs signal pathway: based on network pharmacology analysis. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2021;15:1369.
Cong Z-X, Wang H-D, Wang J-W, Zhou Y, Pan H, Zhang D-D, et al. ERK and PI3K signaling cascades induce Nrf2 activation and regulate cell viability partly through Nrf2 in human glioblastoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2013;30(2):715–22.
Haas B, Klinger V, Keksel C, Bonigut V, Kiefer D, Caspers J, et al. Inhibition of the PI3K but not the MEK/ERK pathway sensitizes human glioma cells to alkylating drugs. Cancer Cell Int. 2018;18(1):1–14.
Escoll M, Lastra D, Pajares M, Robledinos-Antón N, Rojo AI, Fernández-Ginés R, et al. Transcription factor NRF2 uses the Hippo pathway effector TAZ to induce tumorigenesis in glioblastomas. Redox Biol. 2020;30:101425.
Ma L, Liu J, Zhang X, Qi J, Yu W, Gu Y. p38 MAPK-dependent Nrf2 induction enhances the resistance of glioma cells against TMZ. Med Oncol. 2015;32(3):69.
Jia Y, Wang H, Wang Q, Ding H, Wu H, Pan H. Silencing Nrf2 impairs glioma cell proliferation via AMPK-activated mTOR inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;469(3):665–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict on interest
The authors of this article declear no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahcheraghi, S.H., Salemi, F., Alam, W. et al. The Role of NRF2/KEAP1 Pathway in Glioblastoma: Pharmacological Implications. Med Oncol 39, 91 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01693-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01693-0