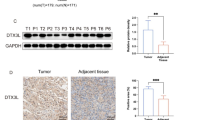
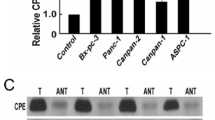
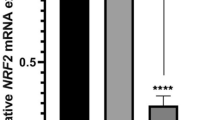
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer is the most lethal digestive cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer death in the US. IL-39, a heterodimer of p19 and EBI3, is a newly found cytokine and its role in the pathogenesis of neoplasia has not been studied yet. This study was designed to investigate the direct role of IL-39 in the growth of pancreatic cancer. Clonogenic survival assay, cell proliferation, and caspase-3 activity kits were used to evaluate the direct effects of IL-39 on cell survival, proliferation and apoptosis of the widely studied pancreatic cancer cell line MiaPaCa-2. We further investigated the possible molecular mechanisms by using RT-PCR and IHC. The percentage of colonies of pancreatic cancer cells increased significantly in the presence of IL-39. This was paralleled with the increase in the OD value of cancer cells in the presence of IL-39. Interestingly, the relative caspase-3 activity in cancer cells decreased significantly in the presence of IL-39. Furthermore, the pro-tumor effect of IL-39 on pancreatic cancer cells correlated with decreased anti-proliferative molecule p21.The anti-apoptotic effect of IL-39 correlated with decreased pro-apoptotic molecule TRAILR1. These results suggest that IL-39 favors growth of pancreatic cancer by promoting growth and inhibiting apoptosis of cancer cells. This suggests that IL-39 acts as a friend to pancreatic cancer. Thus, inhibition of effect of IL-39 on cells might be a promising strategy to treat pancreatic cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 January 2019
The original version of this article unfortunately contained a mistake in the text of the entire article. The word “IL-39” should read as “meteorin-like protein”. This has been corrected with this correction.
References
Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(17):1605.
Saif MW. Pancreatic neoplasm in 2011: an update. JOP. 2011;12(4):316–21.
Wolfgang CL, Herman JM, Laheru DA, Klein AP, Erdek MA, Fishman EK, et al. Recent progress in pancreatic cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(5):318–48. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21190.
Raimondi S, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: an overview. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6(12):699–708. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2009.177.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2017;67(1):7–30.
Ying H, Dey P, Yao W, Kimmelman AC, Draetta GF, Maitra A, et al. Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 2016;30(4):355–85. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.275776.115.
Conroy T, Bachet JB, Ayav A, Huguet F, Lambert A, Caramella C, et al. Current standards and new innovative approaches for treatment of pancreatic cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2016;57:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2015.12.026.
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74(11):2913–21. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155.
Amedei A, Niccolai E, Prisco D. Pancreatic cancer: role of the immune system in cancer progression and vaccine-based immunotherapy. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3354–68. https://doi.org/10.4161/hv.34392.
Porta C, Paglino C, Imarisio I, Bonomi L. Cytokine-based immunotherapy for advanced kidney cancer: past results and future perspectives in the era of molecularly targeted agents. Sci World J. 2007;7:837–49. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2007.154.
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH, Goggins M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2011;378(9791):607–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62307-0.
Wang X, Wei Y, Xiao H, Liu X, Zhang Y, Han G, et al. A novel IL-23p19/Ebi3 (IL-39) cytokine mediates inflammation in lupus-like mice. Eur J Immunol 2016;46(6):1343–50.
Li Z-y, Fan M-b, Zhang S-l, Qu Y, Zheng S-l, Song J, et al. Intestinal Metrnl released into the gut lumen acts as a local regulator for gut antimicrobial peptides. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2016;37(11):1458.
Li Z-Y, Song J, Zheng S-L, Fan M-B, Guan Y-F, Qu Y, et al. Adipocyte Metrnl antagonizes insulin resistance through PPARγ signaling. Diabetes 2015. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-0274.
Ushach I, Burkhardt AM, Martinez C, Hevezi PA, Gerber PA, Buhren BA, et al. METEORIN-LIKE is a cytokine associated with barrier tissues and alternatively activated macrophages. Clin Immunol 2015;156(2):119–27.
Zheng SL, Li ZY, Song J, Liu JM, Miao CY. Metrnl: a secreted protein with new emerging functions. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016;37(5):571–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.9.
Ding VA, Zhu Z, Steele TA, Wakefield MR, Xiao H, Balabanov D, et al. The novel role of IL-37 in prostate cancer: evidence as a promising radiosensitizer. Med Oncol 2018;35(1):6.
Fang Y, Chen X, Bai Q, Qin C, Mohamud AO, Zhu Z, et al. IL-9 inhibits HTB-72 melanoma cell growth through upregulation of p21 and TRAIL. J Surg Oncol. 2015;111(8):969–74.
Fang Y, Zhao L, Xiao H, Cook KM, Bai Q, Herrick EJ, et al. IL-33 acts as a foe to MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer. Med Oncol. 2017;34(2):23.
Zhu Z, Davidson KT, Brittingham A, Wakefield MR, Bai Q, Xiao H, et al. Trichomonas vaginalis: a possible foe to prostate cancer. Med Oncol. 2016;33(10):115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-016-0832-y.
Vainer N, Dehlendorff C, Johansen JSJO. Systematic literature review of IL-6 as a biomarker or treatment target in patients with gastric, bile duct, pancreatic and colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018;9(51):29820.
Wang X, Liu X, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Zhu G, Han G, et al. Interleukin (IL)-39 [IL-23p19/Epstein–Barr virus-induced 3 (Ebi3)] induces differentiation/expansion of neutrophils in lupus-prone mice. Clin Exp Immunol 2016;186(2):144–56.
Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Liu X, Zhu G, Han G, et al. Anti-IL-39 (IL-23p19/Ebi3) polyclonal antibodies ameliorate autoimmune symptoms in lupus-like mice. Mol Med Rep 2018;17(1):1660–6.
Johnson DG, Walker CL. Cyclins and cell cycle checkpoints. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1999;39:295–312. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.39.1.295.
Nicholl MB, Ledgewood CL, Chen X, Bai Q, Qin C, Cook KM, et al. IL-35 promotes pancreas cancer growth through enhancement of proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis: evidence for a role as an autocrine growth factor. Cytokine. 2014;70(2):126–33.
Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995;267(5203):1456–62.
Fang Y, Yu S, Braley-Mullen H. TGF-β promotes proliferation of thyroid epithelial cells in IFN-γ–/– mice by down-regulation of p21 and p27 via AKT pathway. Am J Pathol. 2012;180(2):650–60.
Sherr CJ. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994;79(4):551–5.
Zhang D, Li X, Chen C, Li Y, Zhao L, Jing Y, et al. Attenuation of p38-mediated miR-1/133 expression facilitates myoblast proliferation during the early stage of muscle regeneration. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(7):e41478. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041478.
Zhu Z, Zhang D, Lee H, Menon AA, Wu J, Hu K, et al. Macrophage-derived apoptotic bodies promote the proliferation of the recipient cells via shuttling microRNA-221/222. J Leukoc Biol. 2017;101(6):1349–59. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.3A1116-483R.
Griffith TS, Brunner T, Fletcher SM, Green DR, Ferguson TA. Fas ligand-induced apoptosis as a mechanism of immune privilege. Science. 1995;270(5239):1189–92.
Schumacher TN, Schreiber RD. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science. 2015;348(6230):69–74. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa4971.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Grant IOER 112-3749 for Yujiang Fang and we thank Mr. Joseph Schmidt, Mr. Nick Caruso, Mr. Benjamin G. Tlapec and Mr.Aldo dominguez for their contributes to this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants for Yujiang Fang (Iowa Science Foundation Grant ISF 16-8, IOER 05-14-01, IOER 112-3749 and IOER 112-3104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manning, A.A., Zhao, L., Zhu, Z. et al. IL-39 acts as a friend to pancreatic cancer. Med Oncol 36, 12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-018-1236-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-018-1236-y