Abstract
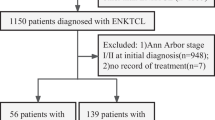
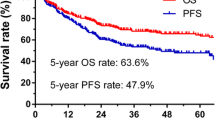
Extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type (ENKTL) is a clinically heterogeneous disease with poor prognosis and requires risk stratification in affected patients. Recent studies have shown that Ki-67 may serve as a prognostic marker in certain types of lymphoma. We analyzed Ki-67 expression and its correlation with prognosis in 182 patients with ENKTL from January 2002 to June 2013. The patients were classified into two groups through a median value: low (<60 %) versus high Ki-67 (≥60 %). High Ki-67 expression was more common in patients with B symptoms (p = 0.02), bulky disease (p = 0.001), and extraupper aerodigestive tract NK/T-cell lymphoma (p = 0.001). High Ki-67 expression was significantly associated with poor overall survival (p < 0.0001) and progression-free survival (p < 0.0001). For patients with low-risk IPI or KPI, Ki-67 at diagnosis could contribute to distinguish patients with favorable outcomes from those with poor outcomes. The results of multivariate analysis showed that the high Ki-67 expression is an independent prognostic factor for overall survival and progression-free survival. (OS, p = 0.001; PFS, p = 0.003). Our data showed that Ki-67 is an effective prognostic indicator of survival in ENKTL patients. This prognostic index may be helpful in identifying high-risk patients with ENKTL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee JH, et al. Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(4):612–8. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.1384.
Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(25):4124–30. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.4558.
Sabattini E, Bacci F, Sagramoso C, Pileri SA. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues in 2008: an overview. Pathologica. 2010;102(3):83–7.
Sun J, Yang Q, Lu Z, He M, Gao L, Zhu M, et al. Distribution of lymphoid neoplasms in China: analysis of 4,638 cases according to the World Health Organization classification. Am J Clin Pathol. 2012;138(3):429–34. doi:10.1309/AJCP7YLTQPUSDQ5C.
Kim TM, Park YH, Lee SY, Kim JH, Kim DW, Im SA, et al. Local tumor invasiveness is more predictive of survival than International Prognostic Index in stage I(E)/II(E) extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood. 2005;106(12):3785–90. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-05-2056.
Aviles A, Diaz NR, Neri N, Cleto S, Talavera A. Angiocentric nasal T/natural killer cell lymphoma: a single centre study of prognostic factors in 108 patients. Clin Lab Haematol. 2000;22(4):215–20. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2257.2000.00307.x.
Cheung MM, Chan JK, Lau WH, Ngan RK, Foo WW. Early stage nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma: clinical outcome, prognostic factors, and the effect of treatment modality. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;54(1):182–90. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(02)02916-4
Chim CS, Ma SY, Au WY, Choy C, Lie AK, Liang R, et al. Primary nasal natural killer cell lymphoma: long-term treatment outcome and relationship with the International Prognostic Index. Blood. 2004;103(1):216–21. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-05-1401.
Au WY, Weisenburger DD, Intragumtornchai T, Nakamura S, Kim WS, Sng I, et al. Clinical differences between nasal and extranasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a study of 136 cases from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood. 2009;113(17):3931–7. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-10-185256.
Velders GA, Kluin-Nelemans JC, De Boer CJ, Hermans J, Noordijk EM, Schuuring E, et al. Mantle-cell lymphoma: a population-based clinical study. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(4):1269–74.
Pastuszewski W, Dziegiel P, Krecicki T, Podhorska-Okolow M, Ciesielska U, Gorzynska E, et al. Prognostic significance of metallothionein, p53 protein and Ki-67 antigen expression in laryngeal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(1A):335–42.
Endl E, Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: fascinating forms and an unknown function. Exp Cell Res. 2000;257(2):231–7. doi:10.1006/excr.2000.4888.
Llanos M, Alvarez-Arguelles H, Aleman R, Oramas J, Diaz-Flores L, Batista N. Prognostic significance of Ki-67 nuclear proliferative antigen, bcl-2 protein, and p53 expression in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Med Oncol. 2001;18(1):15–22. doi:10.1385/MO:18:1:15.
He X, Chen Z, Fu T, Jin X, Yu T, Liang Y, et al. Ki-67 is a valuable prognostic predictor of lymphoma but its utility varies in lymphoma subtypes: evidence from a systematic meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:153. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-153.
Kim SJ, Kim BS, Choi CW, Choi J, Kim I, Lee YH, et al. Ki-67 expression is predictive of prognosis in patients with stage I/II extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(8):1382–7. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm183.
Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris N, Jaffe E, Pileri S, Stein H, et al., editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC; 2008.
Kim TM, Heo DS. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: new staging system and treatment strategies. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(12):2242–8. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01319.x.
Carbone PP, Kaplan HS, Musshoff K, Smithers DW, Tubiana M. Report of the committee on Hodgkin’s disease staging classification. Cancer Res. 1971;31(11):1860–1.
Shipp MA, Harrington DP, Anderson JR. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):987–94. doi:10.1056/NEJM199309303291402.
Wang L, Wang Zh, Chen Xq, Li Yj, Wang Kf, Xia Yf et al. First-line combination of gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and L-asparaginase (GELOX) followed by involved-field radiation therapy for patients with stage IE/IIE extranodal natural killer/T‐cell lymphoma. Cancer. 2013;119(2):348–55.
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(4):1244.
Grillo-Lopez AJ, Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Peterson BA, Carter WD, Varns CL, et al. Response criteria for NHL: importance of ‘normal’ lymph node size and correlations with response rates. Ann Oncol. 2000;11(4):399–408.
Schluter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C, Becker MH, Key G, Flad HD, et al. The cell proliferation-associated antigen of antibody Ki-67: a very large, ubiquitous nuclear protein with numerous repeated elements, representing a new kind of cell cycle-maintaining proteins. J Cell Biol. 1993;123(3):513–22.
Scholzen T, Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol. 2000;182(3):311–22. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(200003)182:3<311:AID-JCP1>3.0.CO;2-9.
Colomo L, Lopez-Guillermo A, Perales M, Rives S, Martinez A, Bosch F, et al. Clinical impact of the differentiation profile assessed by immunophenotyping in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2003;101(1):78–84. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-04-1286.
Jerkeman M, Anderson H, Dictor M, Kvaloy S, Akerman M, Cavallin-Stahl E. Assessment of biological prognostic factors provides clinically relevant information in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma—a Nordic Lymphoma Group study. Ann Hematol. 2004;83(7):414–9. doi:10.1007/s00277-004-0855-x.
Szczuraszek K, Mazur G, Jelen M, Dziegiel P, Surowiak P, Zabel M. Prognostic significance of Ki-67 antigen expression in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Anticancer Res. 2008;28(2A):1113–8.
Suzuki R, Suzumiya J, Yamaguchi M, Nakamura S, Kameoka J, Kojima H, et al. Prognostic factors for mature natural killer (NK) cell neoplasms: aggressive NK cell leukemia and extranodal NK cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(5):1032–40. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp418.
Huang JJ, Zhu YJ, Xia Y, Zhao W, Lin TY, Jiang WQ, et al. A novel prognostic model for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Med Oncol. 2012;29(3):2183–90. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-0030-x.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Li Jiang, Pengfei Li and Hua Wang have contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Li, P., Wang, H. et al. Prognostic significance of Ki-67 antigen expression in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Med Oncol 31, 218 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0218-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0218-y