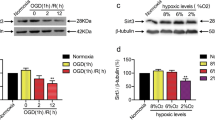
Abstract
Ischemic stroke (IS) poses a heavy burden on the healthcare system, and revascularization is the most effective treatment. However, ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, one main cause of revascularization complications, significantly hinders IS recovery. Unfortunately, none of the neuroprotectants tested to date has been successfully translated clinically for post-revascularization I/R injury therapy. In multiple pathophysiological processes, apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor (AATF) serves as a cell protector, but its role in neuronal I/R injury is unknown. Therefore, we firstly demonstrated the expression profiles of AATF in a distal middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (dMCAO/R) model and found that AATF expression was increased in cortical neuron after dMCAO/R. Over-expressing AATF reduced infarct volume, alleviated neuronal death, and promoted neurological functions. Next, we used an oxygen–glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) model to investigate the mechanism of AATF. Results indicated that AATF alleviated OGD/R-induced large-scale DNA fragmentation, which suggested that the protective effect of AATF may be attributed to parthanatos inhibition. After that, we examined the regulatory mechanism of AATF. We found that AATF did not affect poly (ADP-ribose) accumulation and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) nucleus translocation. AATF competitively interacted with nuclear AIF, which inhibited AIF from binding DNA. At last, we verified the effect and mechanism of AATF in dMCAO/R model. The present study, for the first time, demonstrates the expression, function, and mechanism of AATF in the context of neuronal I/R injury via dMCAO/R and OGD/R model, which provides new evidence in this area and may facilitate exploring new therapeutic targets.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacalini MG, Di Lonardo D, Catizone A, Ciccarone F, Bruno T, Zampieri M et al (2011) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation affects stabilization of Che-1 protein in response to DNA damage. DNA Repair (amst) 10:380–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.01.002
Bacalini MG, Tavolaro S, Peragine N, Marinelli M, Santangelo S, Del Giudice I et al (2012) A subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients display reduced levels of PARP1 expression coupled with a defective irradiation-induced apoptosis. Exp Hematol 40(197–206):e191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2011.11.005
Bruno T, De Nicola F, Iezzi S, Lecis D, D’Angelo C, Di Padova M et al (2006) Che-1 phosphorylation by ATM/ATR and Chk2 kinases activates p53 transcription and the G2/M checkpoint. Cancer Cell 10:473–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.012
Bruno T, Desantis A, Bossi G, Di Agostino S, Sorino C, De Nicola F et al (2010) Che-1 promotes tumor cell survival by sustaining mutant p53 transcription and inhibiting DNA damage response activation. Cancer Cell 18:122–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.027
Bruno T, Iezzi S, De Nicola F, Di Padova M, Desantis A, Scarsella M et al (2008) Che-1 activates XIAP expression in response to DNA damage. Cell Death Differ 15:515–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402284
Chen G, Li C, Zhang L, Yang J, Meng H, Wan H et al (2022) Hydroxysafflor yellow A and anhydrosafflor yellow B alleviate ferroptosis and parthanatos in PC12 cells injured by OGD/R. Free Radic Biol Med 179:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.12.262
Chiu LY, Ho FM, Shiah SG, Chang Y, Lin WW (2011) Oxidative stress initiates DNA damager MNNG-induced poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1-dependent parthanatos cell death. Biochem Pharmacol 81:459–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2010.10.016
Dhir N, Medhi B, Prakash A, Goyal MK, Modi M, Mohindra S (2020) Pre-clinical to clinical translational failures and current status of clinical trials in stroke therapy: a brief review. Curr Neuropharmacol 18:596–612. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X18666200114160844
Feigin VL, Brainin M, Norrving B, Martins S, Sacco RL, Hacke W et al (2022) World Stroke Organization (WSO): global stroke fact sheet 2022. Int J Stroke 17:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/17474930211065917
Guo S, Chen R, Chen X, Xie Z, Huo F, Wu Z (2018) Che-1 inhibits oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal apoptosis associated with inhibition of the p53-mediated proapoptotic signaling pathway. NeuroReport 29:1193–1200. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000001095
Jang KH, Jang T, Son E, Choi S, Kim E (2018) Kinase-independent role of nuclear RIPK1 in regulating parthanatos through physical interaction with PARP1 upon oxidative stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1865:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.10.004
Jelinek M, Jurajda M, and Duris K (2021) Oxidative stress in the brain: basic concepts and treatment strategies in stroke. Antioxidants (Basel) 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10121886
Jones PA, May GR, McLuckie JA, Iwashita A, Sharkey J (2004) Apoptosis is not an invariable component of in vitro models of cortical cerebral ischaemia. Cell Res 14:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7290225
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Arshad MI, Piquet-Pellorce C, Martin-Chouly C, Le Moigne-Muller G, Van Herreweghe F et al (2012) TRAIL induces necroptosis involving RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent PARP-1 activation. Cell Death Differ 19:2003–2014. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.90
Kaiser RWJ, Erber J, Hopker K, Fabretti F, Muller RU (2020) AATF/Che-1-An RNA binding protein at the nexus of DNA damage response and ribosome biogenesis. Front Oncol 10:919. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00919
Kim Y, Kim YS, Kim HY, Noh MY, Kim JY, Lee YJ et al (2018) Early treatment with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor (JPI-289) reduces infarct volume and improves long-term behavior in an animal model of ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 55:7153–7163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0910-6
Koehler RC, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2021) Targeting parthanatos in ischemic stroke. Front Neurol 12:662034. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.662034
Li P, Stetler RA, Leak RK, Shi Y, Li Y, Yu W et al (2018) Oxidative stress and DNA damage after cerebral ischemia: potential therapeutic targets to repair the genome and improve stroke recovery. Neuropharmacology 134:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.11.011
Li WH, Yang YL, Cheng X, Liu M, Zhang SS, Wang YH et al (2020) Baicalein attenuates caspase-independent cells death via inhibiting PARP-1 activation and AIF nuclear translocation in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Apoptosis 25:354–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-020-01600-w
Ling XX, Liu JX, Yun L, Du YJ, Chen SQ, Chen JL et al (2016) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor involved in hydroquinone-induced DNA damage response. Biomed Environ Sci 29:80–84. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2016.008
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K et al (2019) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 50:e344–e418. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
Srinivas AN, Suresh D, Mirshahi F, Santhekadur PK, Sanyal AJ, Kumar DP (2021) Emerging roles of AATF: checkpoint signaling and beyond. J Cell Physiol 236:3383–3395. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30141
Sun MS, Jin H, Sun X, Huang S, Zhang FL, Guo ZN et al (2018) Free radical damage in ischemia-reperfusion injury: an obstacle in acute ischemic stroke after revascularization therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:3804979. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3804979
Wang D, Chen TY, Liu FJ (2018) Che-1 attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by upregulation of Nrf2 signaling. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:1084–1093. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201802_14395
Wang Y, An R, Umanah GK, Park H, Nambiar K, Eacker SM et al (2016) A nuclease that mediates cell death induced by DNA damage and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Science 354. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad6872
Wang YJ, Li ZX, Gu HQ, Zhai Y, Jiang Y, Zhao XQ et al (2020) China Stroke Statistics 2019: a report from the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in Neurological Diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, the Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and Institute for Global Neuroscience and Stroke Collaborations. Stroke Vasc Neurol 5:211–239. https://doi.org/10.1136/svn-2020-000457
Wu S, Wu B, Liu M, Chen Z, Wang W, Anderson CS et al (2019) Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol 18:394–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30500-3
Xie J, Guo Q (2004) AATF protects neural cells against oxidative damage induced by amyloid beta-peptide. Neurobiol Dis 16:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2004.02.003
Xie J, Guo Q (2006) Apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor protects renal tubule cells against oxidative damage and apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:3336–3346. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006040311
Xu JC, Fan J, Wang X, Eacker SM, Kam TI, Chen L et al (2016) Cultured networks of excitatory projection neurons and inhibitory interneurons for studying human cortical neurotoxicity. Sci Transl Med 8: 333ra348. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aad0623
Zhao H, Tang J, Chen H, Gu W, Geng H, Wang L et al (2021) 14,15-EET reduced brain injury from cerebral ischemia and reperfusion via suppressing neuronal parthanatos. Int J Mol Sci 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189660
Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, Yin P, Zhu J, Chen W et al (2019) Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 394:1145–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 81571277 and No. 81071061) and the Clinical Research Special Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (No. 20204Y0131).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WX and WJ: study design and manuscript writing. WX, ZH, and DY: experiments performing and data analysis. Y-EZ and X-XZ: data analysis. R-CC: manuscript writing. WJ: work supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, W., Hu, Z., Yin, D. et al. AATF Competitively Interacts with Nuclear AIF and Inhibits Parthanatos of Neurons in dMCAO/R and OGD/R Models. J Mol Neurosci 72, 2218–2232 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02064-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02064-0