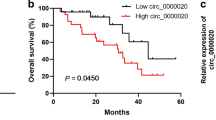
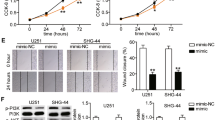
Abstract
Glioma is one of the most aggressive malignancies and has a poor survival rate. G protein subunit gamma 12 (GNG12), a member of G protein family, has been reported to participate in cancer disorders. However, the role and functional mechanism of GNG12 in glioma are not fully understood. The expression of GNG12 mRNA and miR-876-5p was measured by qRT-PCR. The level of GNG12 protein was measured by western blot. Cell proliferation and cell migration were monitored by CCK-8 assay and wound healing assay. The role of GNG12 on tumorigenicity in vivo was determined by animal models. The interaction between GNG12 and miR-876-5p was validated by dual-luciferase reporter experiment. The phosphorylation levels of PI3K and AKT were monitored by western blot. The upregulated expression of GNG12 was identified in tumor tissues and cells of glioma. GNG12 knockdown inhibited glioma cell growth and migration, and slowed tumor development in vivo. Besides, GNG12 knockdown weakened the phosphorylation levels of PI3K and AKT. GNG12 was verified to be a target of miR-876-5p whose enrichment suppressed the expression and function of GNG12. MiR-876-5p repressed glioma cell proliferation, migration, and the activity of PI3K/AKT signaling by targeting GNG12. MiR-876-5p-targeted GNG12 contributes to the malignant development of glioma by increasing the PI3K/AKT signaling activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Asano T, Morishita R, Matsuda T, Fukada Y, Yoshizawa T, Kato K (1993) Purification of four forms of the beta gamma subunit complex of G proteins containing different gamma subunits. J Biol Chem 268(27):20512–20519
Cai YD, Zhang S, Zhang YH, Pan X, Feng K, Chen L, Huang T, Kong X (2018) Identification of the gene expression rules that define the subtypes in glioma. J Clin Med 7(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100350
Chai C, Song LJ, Han SY, Li XQ, Li M (2018) MicroRNA-21 promotes glioma cell proliferation and inhibits senescence and apoptosis by targeting SPRY1 via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 24(5):369–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12785
Chen RQ, Xu XH, Liu F, Li CY, Li YJ, Li XR, Jiang GY, Hu F, Liu D, Pan F, Qiu XY, Chen XQ (2019) The binding of PD-L1 and Akt facilitates glioma cell invasion upon starvation via Akt/Autophagy/F-actin signaling. Front Oncol 9:1347. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01347
Chen S, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zeng YY, Li Z, Li ML, Li FF, You J, Zhang ZM, Tzeng CM (2018) WW domain-binding protein 2 acts as an oncogene by modulating the activity of the glycolytic enzyme ENO1 in glioma. Cell Death Dis 9(3):347. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0376-5
Chipman LB, Pasquinelli AE (2019) miRNA targeting: growing beyond the seed. Trends Genet 35(3):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2018.12.005
Cloughesy TF, Cavenee WK, Mischel PS (2014) Glioblastoma: from molecular pathology to targeted treatment. Annu Rev Pathol 9:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130324
Fennell LJ, Kane A, Liu C, McKeone D, Fernando W, Su C, Bond C, Jamieson S, Dumenil T, Patch AM, Kazakoff SH, Pearson JV, Waddell N, Leggett B, Whitehall VLJ (2020) APC Mutation Marks an Aggressive Subtype of BRAF Mutant Colorectal Cancers. Cancers (Basel) 12(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051171
Gao G, Yang M, Wang F, Dang G, Zhang X, Zhao J, Wang X, Jin B (2020) Coagulation factor 2 thrombin receptor promotes malignancy in glioma under SOX2 regulation. Aging (Albany NY) 12(11):10594–10613. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103281
Giunti L, Da Ros M, De Gregorio V, Magi A, Landini S, Mazzinghi B, Buccoliero AM, Genitori L, Giglio S, Sardi I (2019) A microRNA profile of pediatric glioblastoma: the role of NUCKS1 upregulation. Mol Clin Oncol 10(3):331–338. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2019.1795
Harrandah AM, Mora RA, Chan EKL (2018) Emerging microRNAs in cancer diagnosis, progression, and immune surveillance. Cancer Lett 438:126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.09.019
Jin X, Xie H, Liu X, Shen Q, Wang Z, Hao H, Gu Y (2020) RELL1, a novel oncogene, accelerates tumor progression and regulates immune infiltrates in glioma. Int Immunopharmacol 87:106707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106707
Khan IS, Ehtesham M (2014) Targeting glioblastoma cancer stem cells: the next great hope?. Neurosurg Focus 37(6):E7. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.9.focus14509
Larson KC, Lipko M, Dabrowski M, Draper MP (2010) Gng12 is a novel negative regulator of LPS-induced inflammation in the microglial cell line BV-2. Inflamm Res 59(1):15–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0062-2
Liao YX, Zhang ZP, Zhao J, Liu JP (2018) Effects of fibronectin 1 on cell proliferation, senescence and apoptosis of human glioma cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 48(3):1382–1396. https://doi.org/10.1159/000492096
Li J, Jin C, Zou C, Qiao X, Ma P, Hu D, Li W, Jin J, Jin X, Fan P (2020a) GNG12 regulates PD-L1 expression by activating NF-κB signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. FEBS Open Bio 10(2):278–287. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.12784
Li Z, Xie X, Fan X, Li X (2020b) Long Non-coding RNA MINCR Regulates miR-876-5p/GSPT1 Axis to Aggravate Glioma Progression. Neurochem Res 45(7):1690–1699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03029-8
Luo C, Zhao S, Dai W, Zheng N,Wang J (2018) Proteomic analyses reveal GNG12 regulates cell growth and casein synthesis by activating the Leu-mediated mTORC1 signaling pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 11:1092–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.08.013
Mehta S, Lo Cascio C (2018) Developmentally regulated signaling pathways in glioma invasion. Cell Mol Life Sci 75(3):385–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2608-8
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Mennel HD, Risau W (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor and glioma angiogenesis: coordinate induction of VEGF receptors, distribution of VEGF protein and possible in vivo regulatory mechanisms. Int J Cancer 59(4):520–529. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.2910590415
Pritchard CC, Kroh E, Wood B, Arroyo JD, Dougherty KJ, Miyaji MM, Tait JF, Tewari M (2012) Blood cell origin of circulating microRNAs: a cautionary note for cancer biomarker studies. Cancer Prev Res (phila) 5(3):492–497. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.Capr-11-0370
Ricard D, Idbaih A, Ducray F, Lahutte M, Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY (2012) Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 379(9830):1984–1996. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61346-9
Spangle JM, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ (2017) The emerging role of PI3K/AKT-mediated epigenetic regulation in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.03.002
Sun J, Zhang Y, Li B, Dong Y, Sun C, Zhang F, Jin L, Chen D, Wang W (2019) PITPNA-AS1 abrogates the inhibition of miR-876-5p on WNT5A to facilitate hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cell Death Dis 10(11):844. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2067-2
Sun S, Wang Y, Wu Y, Gao Y, Li Q, Abdulrahman AA, Liu XF, Ji GQ, Gao J, Li L, Wan FP, Li YQ, Gao DS (2018) Identification of COL1A1 as an invasion-related gene in malignant astrocytoma. Int J Oncol 53(6):2542–2554. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4568
Wang Y, Xie Y, Li X, Lin J, Zhang S, Li Z, Huo L, Gong R (2018) MiR-876-5p acts as an inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting DNMT3A. Pathol Res Pract 214(7):1024–1030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2018.04.012
Xia S, Lal B, Tung B, Wang S, Goodwin CR, Laterra J (2016) Tumor microenvironment tenascin-C promotes glioblastoma invasion and negatively regulates tumor proliferation. Neuro Oncol 18(4):507–517. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nov171
Xie Y, Shi X, Sheng K, Han G, Li W, Zhao Q, Jiang B, Feng J, Li J, Gu Y (2019) PI3K/Akt signaling transduction pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (Review). Mol Med Rep 19(2):783–791. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9713
Xu J, Zheng J, Wang J, Shao J (2019a) miR-876-5p suppresses breast cancer progression through targeting TFAP2A. Exp Ther Med 18(2):1458–1464. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7689
Xu Z, Yu Z, Tan Q, Wei C, Tang Q, Wang L, Hong Y (2019b) MiR-876-5p regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration through targeting WNT5A and MITF. Biosci Rep 39(6). https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20190066
Yasuda H, Lindorfer MA, Myung CS, Garrison JC (1998) Phosphorylation of the G protein gamma12 subunit regulates effector specificity. J Biol Chem 273(34):21958–21965. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.34.21958
Zhao R, Song Y, Wang Y, Huang Y, Li Z, Cui Y, Yi M, Xia L, Zhuang W, Wu X, Zhou Y (2019) PD-1/PD-L1 blockade rescue exhausted CD8+ T cells in gastrointestinal stromal tumours via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway. Cell Prolif 52(3):e12571. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12571
Zhao H, Zheng Y, You J, Xiong J, Ying S, Xie L, Song X, Yao Y, Jin Z, Zhang C (2020) Tumor suppressor role of miR-876-5p in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett 20(2):1281–1287. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11680
Funding
This work was supported by the 2019–2020 General Project of Health Commission of Hubei Province: Study on the Blocking Effect and Mechanism of Interleukin-33 on Tumor Immune Escape (grant number WJ2019M099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Ling Li; Methodology: Qiuying Zhang, Leyong Yuan; Formal analysis and investigation: Yanlong Yang; Writing — original draft preparation: Xiaobo Wang; Writing — review and editing: Ling Li, Fangfang Liu; Funding acquisition: Mingshui Xie; Resources: Yang Liu; Supervision: Ling Li, Xiaobo Wang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Suizhou Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine (Suizhou, China). The processing of clinical tissue samples is in strict compliance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to Participate
All patients signed written informed consent.
Consent for Publication
Consent for publication was obtained from the participants.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Zhang, Q., Yuan, L. et al. GNG12 Targeted by miR-876-5p Contributes to Glioma Progression Through the Activation of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. J Mol Neurosci 72, 441–450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01956-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01956-x