Abstract
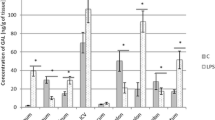
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS), also known as lipoglycans or endotoxins, form part of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Previous studies have described the various harmful impacts of LPS on humans and animals. Nevertheless, many aspects of these effects are still not fully explained. One of them is the influence of endotoxins on the neurochemical characterization of neurons within the enteric nervous system (ENS), which is found in the intestinal wall and plays important adaptive roles during pathological processes and exposures. In this study, the impact of a low single dose of Salmonella Enteritidis LPS on the duodenal enteric neurons immunoreactive to substance P (SP), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), pituitary adenylate cyclase activating peptide (PACAP-27), and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) was studied using a double immunofluorescence technique. During the study, it was shown that even a low dose of LPS affects the number of enteric neurons containing the neuropeptides studied, and these changes were dependent on the type of the enteric plexus. The most visible changes concerned the SP-like immunoreactive (LI) neurons in the outer submucous plexus (LPS caused an increase in the percentage of these neurons from15.74 ± 0.61 to 21.72 ± 0.79%). Furthermore, the VIP-LI neurons in the inner submucous plexus were seen to decrease from 12.64 ± 0.83 to 5.96 ± 0.58%. The mechanisms behind these noted fluctuations are not clear, but it may be connected with the pro-inflammatory and neurotoxic activity of LPS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad C, Tan YV, Cheung-Lau G, Nobuta H, Waschek JA (2012) VIP deficient mice exhibit resistance to lipopolysaccharide induced endotoxemia with an intrinsic defect in proinflammatory cellular responses. PLoS One 7:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036922
Askar B, Ibrahim H, Barrow P, Foster N (2015) Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) differentially affects inflammatory immune responses in human monocytes infected with viable Salmonella or stimulated with LPS. Peptides 71:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2015.06.009
Avetisyan M, Schill EM, Heuckeroth RO (2015) Building a second brain in the bowel. J Clin Invest 125:899–907
Benson S, Kattoor J, Wegner A, Hammes F, Reidick D, Grigoleit JS, Engler H, Oberbeck R, Schedlowski M, Elsenbruch S (2012) Acute experimental endotoxemia induces visceral hypersensitivity and altered pain evaluation in healthy humans. Pain 153:794–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2011.12.001
Brandenburg K, Wiese A (2004) Endotoxins: relationships between structure, function, and activity. Curr Top Med Chem 4:1127–1146
Brehmer A, Schrodl F, Neuhuber W (1999) Morphological classifications of enteric neurons--100 years after Dogiel. Anat Embryol (Berl) 200:125–135
Brehmer A, Croner R, Dimmler A, Papadopoulos T, Schrödl F, Neuhuber W (2004) Immunohistochemical characterization of putative primary afferent (sensory) myenteric neurons in human small intestine. Auton Neurosci 112:49–59
Brenneman DE, Phillips TM, Hauser J, Hill JM, Spong CY, Gozes I (2003) Complex array of cytokines released by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Neuropeptides 37:111–119
Brown DR, Timmermans JP (2004) Lessons from the porcine enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:50–54
Brunsson I, Fahrenkrug J, Jodal M, Sjöqvist A, Lundgren O (1995) Substance P effects on blood flow, fluid transport and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide release in the feline small intestine. J Physiol 483:727–734
Bulc M, Gonkowski S, Landowski P, Kamińska B, Całka J (2015) Immunohistochemical evidence of the co-localisation of cocaine and amphetamine regulatory peptide with neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase, vasoactive intestinal peptide and galanin within the circular muscle layer of the human caecum. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 74:176–182
Campos-Salinas J, Cavazzuti A, O’Valle F, Forte-Lago I, Caro M, Beverley SM, Delgado M, Gonzalez-Rey E (2014) Therapeutic efficacy of stable analogues of vasoactive intestinal peptide against pathogens. J Biol Chem 289:14583–14599. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.560573
Coquenlorge S, Duchalais E, Chevalier J, Cossais F, Rolli-Derkinderen M, Neunlist M (2014) Modulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced neuronal response by activation of the enteric nervous system. J Neuroinflammation 11:202. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0202-7
Cuesta MC, Quintero L, Pons H, Suarez-Roca H (2002) Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide increase IL-1 beta, IL-6 and TNF alpha secretion from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Neurochem Int 40:301–306
De Fontgalland D, Wattchow DA, Costa M, Brookes SJ (2008) Immunohistochemical characterization of the innervation of human colonic mesenteric and submucosal blood vessels. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:1212–1226. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2008.01150.x
Duty S, Jenner P (2011) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: a source of novel treatments and clues to the cause of the disease. Br J Pharmacol 164:1357–1391
Ekblad E (2006) CART in the enteric nervous system. Peptides 27:2024–2030
Freudenberg MA, Galanos C (1990) Bacterial lipopolysaccharides: structure, metabolism and mechanisms of action. Int Rev Immunol 6:207–221
Furness JB (2012) The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:286–294
Furness JB, Callaghan BP, Rivera LR, Cho HJ (2014) The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: integrated local and central control. Adv Exp Med Biol 817:39–71
Gonkowski S (2013) Substance P as a neuronal factor in the enteric nervous system of the porcine descending colon in physiological conditions and during selected pathogenic processes. Biofactors 39:542–551
Gonkowski S, Całka J (2012) Changes in pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide 27-like immunoreactive nervous structures in the porcine descending colon during selected pathological processes. J Mol Neurosci 48:777–787
Gonkowski S, Burlinski P, Calka J (2009) Proliferative enetropathy (PE) – induced changes in galanin – like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system of the porcine distal colon. Acta Vet Beograd 59:321–330
Gonkowski S, Makowska K, Calka J (2018) The influence of experimental inflammation and axotomy on leucine enkephalin (leuENK) distribution in intramural nervous structures of the porcine descending colon. BMC Vet Res 14:169. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-018-1496-y
Han P, Liang W, Baxter LC, Yin J, Tang Z, Beach TG, Caselli RJ, Reiman EM, Shi J (2014) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide is reduced in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 82:1724–1728
Hauser GJ, Dayao EK, Zukowska-Grojec Z (1995) Effect of neuropeptide Y on endotoxin-induced suppression of the response to various agonists in conscious rats. Life Sci 57:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(95)00266-9
Ibrahim H, Barrow P, Foster N (2012) VIP as a potential therapeutic agent in gram negative sepsis. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 12:308–315. https://doi.org/10.2174/187153012803832611
Kasparek MS, Fatima J, Iqbal CW, Duenes JA, Sarr MG (2007) Role of VIP and substance P in NANC innervation in the longitudinal smooth muscle of the rat jejunum - influence of extrinsic denervation. J Surg Res 141:22–30
Kowall NW, Quigley BJ Jr, Krause JE, Lu F, Kosofsky BE, Ferrante RJ (1993) Substance P and substance P receptor histochemistry in human neurodegenerative diseases. Regul Pept 46:174–185
Lake JI, Heuckeroth RO (2013) Enteric nervous system development: migration, differentiation, and disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 305:G1–G24. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00452.2012
Lopes Pires ME, Clarke SR, Marcondes S, Gibbins JM (2017) Lipopolysaccharide potentiates platelet responses via toll-like receptor 4-stimulated Akt-Erk-PLA2 signalling. PLoS One 12:e0186981. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186981
Maiti AK, Sharba S, Navabi N, Lindén SK (2018) Colonic levels of vasoactive intestinal peptide decrease during infection and exogenous VIP protects epithelial mitochondria against the negative effects of IFNγ and TNFα induced during Citrobacter rodentium infection. PLoS One 13:e0204567. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204567
Makowska K (2018) Chemically induced inflammation and nerve damage affect the distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactive (VIP-LI) nervous structures in the descending colon of the domestic pig. Neurogastroenterol Motil 30:e13439
Makowska K, Gonkowski S, Zielonka L, Dabrowski M, Calka J (2017) T2 toxin-induced changes in cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART)-like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system within selected fragments of the porcine digestive tract. Neurotox Res 31:136–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9675-8
Makowska K, Mikolajczyk A, Calka J, Gonkowski S (2018a) Neurochemical characterization of nerve fibers in the porcine gallbladder wall under physiological conditions and after the administration of Salmonella enteritidis lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Toxicol Res 7:73–83
Makowska K, Obremski K, Gonkowski S (2018b) The impact of T-2 toxin on vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactive (VIP-LI) nerve structures in the wall of the porcine stomach and duodenum. Toxins (Basel) 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10040138
Maldonado RF, Sá-Correia I, Valvano MA (2016) Lipopolysaccharide modification in Gram-negative bacteria during chronic infection. FEMS Microbiol Rev 40:480–493
Mao P, Meshul CK, Thuillier P, Reddy PH (2013) Neurotransmitter CART as a new therapeutic candidate for Parkinson’s disease. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 6:108–123
Meneses G, Bautista M, Florentino A, Díaz G, Acero G, Besedovsky H, Meneses D, Fleury A, Del Rey A, Gevorkian G, Fragoso G, Sciutto E (2016) Electric stimulation of the vagus nerve reduced mouse neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide. J Inflamm 13:1–11
Messenger JP, Furness JB (1990) Projections of chemically-specified neurons in the guinea-pig colon. Arch Histol Cytol 53:467–495
Mikawa S, Ohta Y, Kaji N, Islam MS, Murata T, Ozaki H, Hori M (2015) Time-dependent changes in inhibitory action of lipopolysaccharide on intestinal motility in rat. J Vet Med Sci 77:1443–1449. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.15-0198
Mikołajczyk A (2016) Safe and effective anaesthesiological protocols in domestic pigs. Ann Warsaw Univ Life Sci SGGW Anim Sci 55:219–227
Mikołajczyk A, Złotkowska D (2018) Neuroimmunological implications of subclinical lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella Enteritidis. Int J Mol Sci 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103274
Mikołajczyk A, Gonkowski S, Złotkowska D (2017) Modulation of the main porcine enteric neuropeptides by a single low-dose of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Salmonella Enteritidis. Gut Pathog 9:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13099-017-0225-6
Miura A, Hino H, Uchida K, Inoue S, Tateda T (2016) Peripheral nerve conduction abnormalities precede morphological alterations in an experimental rat model of sepsis. J Anesth 30:961–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-016-2247-5
Mohammadi Z (2011) Endotoxin in endodontic infections: a review. J Calif Dent Assoc 39(152–5):158–161
Nassar CF, Abdallah LE, Barada KA, Atweh SF, Saadé NE (1995) Effects of intravenous vasoactive intestinal peptide injection on jejunal alanine absorption and gastric acid secretion in rats. Regul Pept 55:261–267
Romero-Carbente JC, Guzmán-Mejía F, Cruz SL, López-Rubalcava C, González-Espinosa C (2014) Role of main neuroendocrine pathways activated by swim stress on mast cell-dependent peritoneal TNF production after LPS administration in mice. Inflamm Res 63:757–767
Shimizu Y, Matsuyama H, Shiina T, Takewaki T, Furness JB (2008) Tachykinins and their functions in the gastrointestinal tract. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:295–311
Silva RL, Lopes AH, Guimarães RM, Cunha TM (2017) CXCL1/CXCR2 signaling in pathological pain: role in peripheral and central sensitization. Neurobiol Dis 105:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2017.06.001
Steimle A, Autenrieth IB, Frick JS (2016) Structure and function: lipid A modifications in commensals and pathogens. Int J Med Microbiol 306:290–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2016.03.001
Szymanska K, Gonkowski S (2018) Bisphenol A-induced changes in the enteric nervous system of the porcine duodenum. Neurotoxicology 66:78–86
Temerozo JR, de Azevedo SSD, Insuela DBR, Vieira RC, Ferreira PLC, Carvalho VF, Bello G, Bou-Habib DC (2018) The neuropeptides vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide control HIV-1 infection in macrophages through activation of protein kinases A and C. Front Immunol 9:1336. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01336
Vasina V, Barbara G, Talamonti L, Stanghellini V, Corinaldesi R, Tonini M, De Ponti F, De Giorgio R (2006) Enteric neuroplasticity evoked by inflammation. Auton Neurosci 126-127:264–272
Verma N, Rettenmeier AW, Schmitz-Spanke S (2011) Recent advances in the use of Sus scrofa (pig) as a model system for proteomic studies. Proteomics 11:776–793
Wang YF, Mao YK, Xiao Q, Daniel EE, Borkowski KR, McDonald TJ (1997) The distribution of NPY-containing nerves and the catecholamine contents of canine enteric nerve plexuses. Peptides 18:221–234
Wojtkiewicz J, Równiak M, Crayton R, Majewski M, Gonkowski S (2012) Chemical coding of zinc-enriched neurons in the intramural ganglia of the porcine jejunum. Cell Tissue Res 350:215–223
Zhou JN, Hofman MA, Swaab DF (1995) VIP neurons in the human SCN in relation to sex, age, and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 16:571–576
Zizzo MG, Mulè F, Serio R (2004) Interplay between PACAP and NO in mouse ileum. Neuropharmacology 46:449–455
Funding
Publication was funded by KNOW (Leading National Research Centre) Scientific Consortium “Healthy Animal-Safe Food”, decision of Ministry of Science and Higher Education No. 05-1/KNOW2/2015 and statutory grant No. 25.610.001-300 from the Faculty of Medical Sciences, the University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn in Poland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rytel, L., Wojtkiewicz, J., Snarska, A. et al. Changes in the Neurochemical Characterization of Enteric Neurons in the Porcine Duodenum After Administration of Low-Dose Salmonella Enteritidis Lipopolysaccharides. J Mol Neurosci 71, 1556–1566 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01473-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01473-y