Abstract
The serotonin 2C receptor (5-HT2CR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor implicated in emotion, feeding, reward, and cognition. 5-HT2CRs are pharmacological targets for mental disorders and metabolic and reward system abnormalities, as alterations in 5-HT2CR expression, RNA editing, and SNPs are involved in these disturbances. To date, 5-HT2CR activity has mainly been measured by quantifying inositol phosphate production and intracellular Ca2+ release, but these assays are not suitable for in vivo analysis. Here, we developed a 5-HT2CR-Tango assay system, a novel analysis tool of 5-HT2CR activity based on the G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-arrestin interaction. With desensitization of activated 5-HT2CR by arrestin, this system converts the 5-HT2CR-arrestin interaction into EGFP reporter gene signal via the LexA transcriptional activation system. For validation of our system, we measured activity of two 5-HT2CR RNA-editing isoforms (INI and VGV) in HEK293 cells transfected with EGFP reporter gene. The INI isoform displayed both higher basal- and 5-HT-stimulated activities than the VGV isoform. Moreover, an inhibitory effect of 5-HT2CR antagonist SB242084 was also detected by 5-HT2CR-Tango system. This novel tool is useful for in vitro high-throughput targeted 5-HT2CR drug screening and can be applied to future in vivo brain function studies associated with 5-HT2CRs in transgenic animal models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowski D, Staufenbiel M (1995) Identification of the 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor as a 60-kDa N-glycosylated protein in choroid plexus and hippocampus. J Neurochem 65(2):782–790
Atwood BK, Lopez J, Wager-Miller J, Mackie K, Straiker A (2011) Expression of G protein-coupled receptors and related proteins in HEK293, AtT20, BV2, and N18 cell lines as revealed by microarray analysis. BMC Genomics 12(14)
Barker EL, Westphal RS, Schmidt D, Sanders-Bush E (1994) Constitutively active 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptors reveal novel inverse agonist activity of receptor ligands. J Biol Chem 269(16):11687–11690
Barnea G, Strapps W, Herrada G, Berman Y, Ong J, Kloss B, Axel R, Lee KJ (2008) The genetic design of signaling cascades to record receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(1):64–69
Berg KA, Clarke WP, Cunningham KA, Spampinato U (2008) Fine-tuning serotonin2c receptor function in the brain: molecular and functional implications. Neuropharmacology 55(6):969–976
Burns CM, Chu H, Rueter SM, Hutchinson LK, Canton H, Sanders-Bush E, Emeson RB (1997) Regulation of serotonin-2C receptor G-protein coupling by RNA editing. Nature 387(6630):303–308
Canal CE, Mahautmr KC, Cao C, Sanders-Bush E, Airey DC (2009) RNA editing of the serotonin 2C receptor and expression of Galpha(q) protein: genetic mouse models do not support a role for regulation or compensation. J Neurochem 108(5):1136–1142
Fitzgerald LW, Iyer G, Conklin DS, Krause CM, Marshall A, Patterson JP, Tran DP, Jonak GJ, Hartig PR (1999) Messenger RNA editing of the human serotonin 5-HT2C receptor. Neuropsychopharmacology 21(2 Suppl):82S–90S
Gurevich I, Englander MT, Adlersberg M, Siegal NB, Schmauss C (2002a) Modulation of serotonin 2C receptor editing by sustained changes in serotonergic neurotransmission. J Neurosci 22(24):10529–10532
Gurevich I, Tamir H, Arango V, Dwork AJ, Mann JJ, Schmauss C (2002b) Altered editing of serotonin 2C receptor pre-mRNA in the prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide victims. Neuron 34(3):349–356
Hartman JL, Northup JK (1996) Functional reconstitution in situ of 5-hydroxytryptamine2c (5HT2c) receptors with alphaq and inverse agonism of 5HT2c receptor antagonists. J Biol Chem 271(37):22591–22597
Herrick-Davis K, Grinde E, Weaver BA (2007) Serotonin 5-HT(2C) receptor homodimerization is not regulated by agonist or inverse agonist treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 568(1–3):45–53
Inagaki HK, Ben-Tabou de-Leon S, Wong AM, Jagadish S, Ishimoto H, Barnea G, Kitamoto T, Axel R, Anderson DJ (2012) Visualizing neuromodulation in vivo: TANGO-mapping of dopamine signaling reveals appetite control of sugar sensing. Cell 148(3):583–595
Iwamoto K, Bundo M, Kato T (2009) Serotonin receptor 2C and mental disorders: genetic, expression and RNA editing studies. RNA Biol 6(3):248–253
Kono M, Tucker AE, Tran J, Bergner JB, Turner EM, Proia RL (2014) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 reporter mice reveal receptor activation sites in vivo. J Clin Invest 124(5):2076–2086
Labasque M, Reiter E, Becamel C, Bockaert J, Marin P (2008) Physical interaction of calmodulin with the 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor C-terminus is essential for G protein-independent, arrestin-dependent receptor signaling. Mol Biol Cell 19(11):4640–4650
Labasque M, Meffre J, Carrat G, Becamel C, Bockaert J, Marin P (2010) Constitutive activity of serotonin 2C receptors at G protein-independent signaling: modulation by RNA editing and antidepressants. Mol Pharmacol 78(5):818–826
Maas S, Kawahara Y, Tamburro KM, Nishikura K (2006) A-to-I RNA editing and human disease. RNA Biol 3(1):1–9
Marinissen MJ, Gutkind JS (2001) G-protein-coupled receptors and signaling networks: emerging paradigms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(7):368–376
Marion S, Weiner DM, Caron MG (2004) RNA editing induces variation in desensitization and trafficking of 5-hydroxytryptamine 2c receptor isoforms. J Biol Chem 279(4):2945–2954
McGrew L, Chang MS, Sanders-Bush E (2002) Phospholipase D activation by endogenous 5-hydroxytryptamine 2C receptors is mediated by Galpha13 and pertussis toxin-insensitive Gbetagamma subunits. Mol Pharmacol 62(6):1339–1343
Meltzer HY, Roth BL (2013) Lorcaserin and pimavanserin: emerging selectivity of serotonin receptor subtype-targeted drugs. J Clin Invest 123(12):4986–4991
Niswender CM, Copeland SC, Herrick-Davis K, Emeson RB, Sanders-Bush E (1999) RNA editing of the human serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine 2C receptor silences constitutive activity. J Biol Chem 274(14):9472–9478
Oakley RH, Laporte SA, Holt JA, Barak LS, Caron MG (1999) Association of beta-arrestin with G protein-coupled receptors during clathrin-mediated endocytosis dictates the profile of receptor resensitization. J Biol Chem 274(45):32248–32257
Pierce KL, Lefkowitz RJ (2001) Classical and new roles of beta-arrestins in the regulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(10):727–733
Porter RH, Benwell KR, Lamb H, Malcolm CS, Allen NH, Revell DF, Adams DR, Sheardown MJ (1999) Functional characterization of agonists at recombinant human 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors in CHO-K1 cells. Br J Pharmacol 128(1):13–20
Slotkin W, Nishikura K (2013) Adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing and human disease. Genome Med 5(11):105
Takakura H, Hattori M, Takeuchi M, Ozawa T (2012) Visualization and quantitative analysis of G protein-coupled receptor-beta-arrestin interaction in single cells and specific organs of living mice using split luciferase complementation. ACS Chem Biol 7(5):901–910
Van Oekelen D, Luyten WH, Leysen JE (2003) 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors and their atypical regulation properties. Life Sci 72(22):2429–2449
Wang Q, O'Brien PJ, Chen CX, Cho DS, Murray JM, Nishikura K (2000) Altered G protein-coupling functions of RNA editing isoform and splicing variant serotonin2C receptors. J Neurochem 74(3):1290–1300
Watanabe Y, Tanaka M (2011) p62/SQSTM1 in autophagic clearance of a non-ubiquitylated substrate. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 16):2692–2701
Watanabe Y, Ikegawa M, Naruse Y, Tanaka M (2009) A novel splicing variant form suppresses the activity of full-length signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A. FEBS J 276(21):6312–6323
Watanabe Y, Tatebe H, Taguchi K, Endo Y, Tokuda T, Mizuno T, Nakagawa M, Tanaka M (2012) p62/SQSTM1-dependent autophagy of Lewy body-like alpha-synuclein inclusions. PLoS One 7(12):e52868
Watanabe Y, Yoshimoto K, Tatebe H, Kita M, Nishikura K, Kimura M, Tanaka M (2014) Enhancement of alcohol drinking in mice depends on alterations in RNA editing of serotonin 2C receptors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17(5):739–751
Werry TD, Gregory KJ, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A (2005) Characterization of serotonin 5-HT2C receptor signaling to extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2. J Neurochem 93(6):1603–1615
Werry TD, Stewart GD, Crouch MF, Watts A, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A (2008) Pharmacology of 5HT(2C) receptor-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation: agonist-specific activation pathways and the impact of RNA editing. Biochem Pharmacol 76(10):1276–1287
Yoshimoto K, Watanabe Y, Tanaka M, Kimura M (2012) Serotonin2C receptors in the nucleus accumbens are involved in enhanced alcohol-drinking behavior. Eur J Neurosci 35(8):1368–1380
Zhang R, Xie X (2012) Tools for GPCR drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33(3):372–384
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. David J. Anderson (California Institute of Technology) for providing the Valium-TEVcs-LexA-HAtag-2A-arrestin1-TEVp plasmid vector. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Nos. 25290014 and 25640024 to MT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
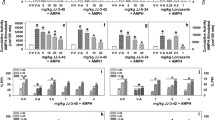
SB242084 had no effect on cell viability and the direct inhibition of the reporter gene expression. A. HEK293 cells stably transfected with reporter plasmid were cultured with 0–20 μg/mL SB242084 for 24 h, followed by a cell viability assay. Values (%) are shown relative to SB242084-untreated cells and are represented by mean ± S.D. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA (post hoc Tukey’s test). The experiment was repeated five times. B. The reporter gene expression of these cells was measured. Values (%) are shown relative to SB242084-untreated cells and are represented by mean ± S.D. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA (post hoc Tukey’s test). The experiment was repeated five times. (PPTX 57 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, Y., Tsujimura, A., Aoki, M. et al. Development of the 5-HT2CR-Tango System Combined with an EGFP Reporter Gene. J Mol Neurosci 58, 162–169 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0650-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0650-2