Abstract
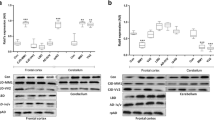
Small GTPases of the Arf family mainly activate the formation of coated carrier vesicles. We showed that class-I Arf1 interacts specifically with full length GPI-anchored cellular prion protein (PrPC). Several recent reports have also demonstrated a missing link between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi-complex role for proper folding, but the exact molecular mechanism is not yet fully understood. In the present study, we identified and characterized the interactive role of Arf1 during PrPC intracellular distribution under pathophysiological conditions. PrPC interaction with Arf1 was investigated in cortical primary neuronal cultures of PrPC wild type and knockout mice (PrP−/−). Arf1 and PrPC co-binding affinity was confirmed using reverse co-immunoprecipitation, co-localization affinity using confocal laser-scanning microscopy. Treatment with brefeldin-A modulated Arf1 expression and resulted in down-regulation and redistribution of PrPC into cytosolic region. In the pre-symptomatic stage of the disease, Arf1 expression was significantly downregulated in the frontal cortex in tg340 mice expressing about fourfold of human PrP-M129 with PrP null background that had been inoculated with human sCJD MM1 brain tissue homogenates (sCJD MM1 mice). In addition, the frontal cortex of CJD human brain demonstrated significant binding capacity of Arf1 protein using co-immunoprecipitation analysis. We also examined Arf1 expression in the brain of CJD patients with the subtypes MM1 and VV2 and found that it was regulated in a region-specific manner. In the frontal cortex, Arf1 expression was not significantly changed in either MM1 or VV2 subtype. Interestingly, Arf1 expression was significantly reduced in the cerebellum in both subtypes as compared to controls. Furthermore, we observed altered RhoA activity, which in turn affects myosin light-chain (MLC) phosphorylation and Arf1-dependent PI3K pathway. Together, our findings underscore a key early symptomatic role of Arf1 in neurodegeneration. Targeting the Arf/Rho/MLC signaling axis might be a promising strategy to uncover the missing link which probably influences disease progression and internal homeostasis of misfolded proteins.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshordel S, Wood WG, Igbavboa U, Muller WE, Eckert GP (2014) Impaired geranylgeranyltransferase-I regulation reduces membrane-associated Rho protein levels in aged mouse brain. J Neurochem 129:732–742. doi:10.1111/jnc.12654
Aguzzi A (2000) Molecular pathology of prion diseases. Vox Sang 78(Suppl 2):25
Aguzzi A, O’Connor T (2010) Protein aggregation diseases: pathogenicity and therapeutic perspectives. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:237–248. doi:10.1038/nrd3050
Alexander NR, Branch KM, Parekh A, Clark ES, Iwueke IC, Guelcher SA, Weaver AM (2008) Extracellular matrix rigidity promotes invadopodia activity. Curr Biol 18:1295–1299. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.07.090
Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K (1996) Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). J Biol Chem 271:20246–20249
Anantharam V, Kanthasamy A, Choi CJ, Martin DP, Latchoumycandane C, Richt JA, Kanthasamy AG (2008) Opposing roles of prion protein in oxidative stress- and ER stress-induced apoptotic signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 45:1530–1541. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.08.028
Boulay PL, Claing A (2009) [ARF proteins: molecular switches controlling tumour proliferation and metastasis]. Med Sci (Paris) 25:783–785. doi:10.1051/medsci/20092510783
Boulay PL, Cotton M, Melancon P, Claing A (2008) ADP-ribosylation factor 1 controls the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway to regulate epidermal growth factor-dependent growth and migration of breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283:36425–36434. doi:10.1074/jbc.M803603200
Bucci C, Thomsen P, Nicoziani P, McCarthy J, van Deurs B (2000) Rab7: a key to lysosome biogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 11:467–480
Bueler H, Fischer M, Lang Y, Bluethmann H, Lipp HP, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB, Aguet M, Weissmann C (1992) Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature 356:577–582. doi:10.1038/356577a0
Burgess TL, Kelly RB (1984) Sorting and secretion of adrenocorticotropin in a pituitary tumor cell line after perturbation of the level of a secretory granule-specific proteoglycan. J Cell Biol 99:2223–2230
Burgess TL, Skoufias DA, Wilson L (1991) Disruption of the Golgi apparatus with brefeldin A does not destabilize the associated detyrosinated microtubule network. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 20:289–300. doi:10.1002/cm.970200405
Campa F, Randazzo PA (2008) Arf GTPase-activating proteins and their potential role in cell migration and invasion. Cell Adh Migr 2:258–262
Carimalo J, Cronier S, Petit G, Peyrin JM, Boukhtouche F, Arbez N, Lemaigre-Dubreuil Y, Brugg B, Miquel MC (2005) Activation of the JNK-c-Jun pathway during the early phase of neuronal apoptosis induced by PrP106-126 and prion infection. Eur J Neurosci 21:2311–2319. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04080.x
Chen LQ, Xiao SJ, Hu PP, Peng L, Ma J, Luo LF, Li YF, Huang CZ (2012) Aptamer-mediated nanoparticle-based protein labeling platform for intracellular imaging and tracking endocytosis dynamics. Anal Chem 84:3099–3110. doi:10.1021/ac202810b
Clark EA, Golub TR, Lander ES, Hynes RO (2000) Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC. Nature 406:532–535. doi:10.1038/35020106
Cockcroft S, Thomas GM, Fensome A, Geny B, Cunningham E, Gout I, Hiles I, Totty NF, Truong O, Hsuan JJ (1994) Phospholipase D: a downstream effector of ARF in granulocytes. Science 263:523–526
Cohen LA, Honda A, Varnai P, Brown FD, Balla T, Donaldson JG (2007) Active Arf6 recruits ARNO/cytohesin GEFs to the PM by binding their PH domains. Mol Biol Cell 18:2244–2253. doi:10.1091/mbc.E06-11-0998
Cory AH, Owen TC, Barltrop JA, Cory JG (1991) Use of an aqueous soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth assays in culture. Cancer Commun 3:207–212
Dagdanova A, Ilchenko S, Notari S, Yang Q, Obrenovich ME, Hatcher K, McAnulty P, Huang L, Zou W, Kong Q, Gambetti P, Chen SG (2010) Characterization of the prion protein in human urine. J Biol Chem 285:30489–30495. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.161794
Daniel B, DeCoster MA (2004) Quantification of sPLA2-induced early and late apoptosis changes in neuronal cell cultures using combined TUNEL and DAPI staining. Brain Res Brain Res Protol 13:144–150. doi:10.1016/j.brainresprot.2004.04.001
DeGeer J, Lamarche-Vane N (2013) Rho GTPases in neurodegeneration diseases. Exp Cell Res 319:2384–2394. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.06.016
Fletcher DA, Mullins RD (2010) Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton. Nature 463:485–492. doi:10.1038/nature08908
Fritz JL, VanBerkum MF (2002) Regulation of rho family GTPases is required to prevent axons from crossing the midline. Dev Biol 252:46–58
Gambetti P, Kong Q, Zou W, Parchi P, Chen SG (2003) Sporadic and familial CJD: classification and characterisation. Br Med Bull 66:213–239
Goldmann W (1993) PrP gene and its association with spongiform encephalopathies. Br Med Bull 49:839–859
Gorodinsky A, Harris DA (1995) Glycolipid-anchored proteins in neuroblastoma cells form detergent-resistant complexes without caveolin. J Cell Biol 129:619–627
Harris DA (2003) Trafficking, turnover and membrane topology of PrP. Br Med Bull 66:71–85
Ho WT, Exton JH, Williger BT (2003) Arfaptin 1 inhibits ADP-ribosylation factor-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion induced by phorbol ester in HT 1080 fibrosarcoma cells. FEBS Lett 537:91–95
Kakinuma N, Roy BC, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Kiyama R (2008) Kank regulates RhoA-dependent formation of actin stress fibers and cell migration via 14-3-3 in PI3K-Akt signaling. J Cell Biol 181:537–549. doi:10.1083/jcb.200707022
Katsube M, Shiota Y, Harada T, Shibata H, Nagai A (2013) A case of MM1 + 2 Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with a longitudinal study of EEG and MRI. Rinsho Byori 61:995–1000
Kawamoto JC, Barrett JN (1986) Cryopreservation of primary neurons for tissue culture. Brain Res 384:84–93
Kimura K, Ito M, Amano M, Chihara K, Fukata Y, Nakafuku M, Yamamori B, Feng J, Nakano T, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Kaibuchi K (1996) Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). Science 273:245–248
Knight RS, Will RG (2004) Prion diseases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(Suppl 1):i36–i42
Knusel B, Michel PP, Schwaber JS, Hefti F (1990) Selective and nonselective stimulation of central cholinergic and dopaminergic development in vitro by nerve growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, epidermal growth factor, insulin and the insulin-like growth factors I and II. J Neurosci 10:558–570
Lewis-Saravalli S, Campbell S, Claing A (2013) ARF1 controls Rac1 signaling to regulate migration of MDA-MB-231 invasive breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 25:1813–1819. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.05.011
Linden R, Martins VR, Prado MA, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Brentani RR (2008) Physiology of the prion protein. Physiol Rev 88:673–728. doi:10.1152/physrev.00007.2007
Llorens F, Ansoleaga B, Garcia-Esparcia P, Zafar S, Grau-Rivera O, Lopez-Gonzalez I, Blanco R, Carmona M, Yague J, Nos C, Del Rio JA, Gelpi E, Zerr I, Ferrer I (2013) PrP mRNA and protein expression in brain and PrP(c) in CSF in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease MM1 and VV2. Prion 7:383–393. doi:10.4161/pri.26416
Llorens F, Zafar S, Ansoleaga B, Shafiq M, Blanco R, Carmona M, Grau-Rivera O, Nos C, Gelpi E, Del Rio JA, Zerr I, Ferrer I (2014) Subtype and regional regulation of prion biomarkers in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. doi:10.1111/nan.12175
Ma J, Wollmann R, Lindquist S (2002) Neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration when PrP accumulates in the cytosol. Science 298:1781–1785. doi:10.1126/science.1073725
Magalhaes AC, Silva JA, Lee KS, Martins VR, Prado VF, Ferguson SS, Gomez MV, Brentani RR, Prado MA (2002) Endocytic intermediates involved with the intracellular trafficking of a fluorescent cellular prion protein. J Biol Chem 277:33311–33318. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203661200
Muralidharan-Chari V, Clancy J, Plou C, Romao M, Chavrier P, Raposo G, D’Souza-Schorey C (2009) ARF6-regulated shedding of tumor cell-derived plasma membrane microvesicles. Curr Biol 19:1875–1885. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.09.059
Nakagomi S, Barsoum MJ, Bossy-Wetzel E, Sutterlin C, Malhotra V, Lipton SA (2008) A Golgi fragmentation pathway in neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 29:221–231. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.08.015
Naslavsky N, Stein R, Yanai A, Friedlander G, Taraboulos A (1997) Characterization of detergent-insoluble complexes containing the cellular prion protein and its scrapie isoform. J Biol Chem 272:6324–6331
Ordonez-Gutierrez L, Torres JM, Gavin R, Anton M, Arroba-Espinosa AI, Espinosa JC, Vergara C, Del Rio JA, Wandosell F (2013) Cellular prion protein modulates beta-amyloid deposition in aged APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.05.019
Padilla D, Beringue V, Espinosa JC, Andreoletti O, Jaumain E, Reine F, Herzog L, Gutierrez-Adan A, Pintado B, Laude H, Torres JM (2011) Sheep and goat BSE propagate more efficiently than cattle BSE in human PrP transgenic mice. PLoS Pathog 7:e1001319. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001319
Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S, Brown P, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Windl O, Zerr I, Budka H, Kopp N, Piccardo P, Poser S, Rojiani A, Streichemberger N, Julien J, Vital C, Ghetti B, Gambetti P, Kretzschmar H (1999) Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol 46:224–233
Pille JY, Denoyelle C, Varet J, Bertrand JR, Soria J, Opolon P, Lu H, Pritchard LL, Vannier JP, Malvy C, Soria C, Li H (2005) Anti-RhoA and anti-RhoC siRNAs inhibit the proliferation and invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther 11:267–274. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.08.029
Popoff V, Langer JD, Reckmann I, Hellwig A, Kahn RA, Brugger B, Wieland FT (2011) Several ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) isoforms support COPI vesicle formation. J Biol Chem 286:35634–35642. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.261800
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:13363–13383
Puxeddu E, Uhart M, Li CC, Ahmad F, Pacheco-Rodriguez G, Manganiello VC, Moss J, Vaughan M (2009) Interaction of phosphodiesterase 3A with brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins BIG1 and BIG2 and effect on ARF1 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:6158–6163. doi:10.1073/pnas.0901558106
Qiang YW, Yao L, Tosato G, Rudikoff S (2004) Insulin-like growth factor I induces migration and invasion of human multiple myeloma cells. Blood 103:301–308. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-06-2066
Rogalski AA, Singer SJ (1984) Associations of elements of the Golgi apparatus with microtubules. J Cell Biol 99:1092–1100
Sabe H, Onodera Y, Mazaki Y, Hashimoto S (2006) ArfGAP family proteins in cell adhesion, migration and tumor invasion. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18:558–564. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2006.08.002
Sahai E, Marshall CJ (2002) RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:133–142. doi:10.1038/nrc725
Schlienger S, Campbell S, Claing A (2014) ARF1 regulates the Rho/MLC pathway to control EGF-dependent breast cancer cell invasion. Mol Biol Cell 25:17–29. doi:10.1091/mbc.E13-06-0335
Schneider B, Pietri M, Pradines E, Loubet D, Launay JM, Kellermann O, Mouillet-Richard S (2011) Understanding the neurospecificity of Prion protein signaling. Front Biosci 16:169–186
Schurmann A, Breiner M, Becker W, Huppertz C, Kainulainen H, Kentrup H, Joost HG (1994) Cloning of two novel ADP-ribosylation factor-like proteins and characterization of their differential expression in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem 269:15683–15688
Shyng SL, Huber MT, Harris DA (1993) A prion protein cycles between the cell surface and an endocytic compartment in cultured neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 268:15922–15928
Shyng SL, Moulder KL, Lesko A, Harris DA (1995a) The N-terminal domain of a glycolipid-anchored prion protein is essential for its endocytosis via clathrin-coated pits. J Biol Chem 270:14793–14800
Shyng SL, Lehmann S, Moulder KL, Harris DA (1995b) Sulfated glycans stimulate endocytosis of the cellular isoform of the prion protein, PrPC, in cultured cells. J Biol Chem 270:30221–30229
Simon D, Herva ME, Benitez MJ, Garrido JJ, Rojo AI, Cuadrado A, Torres JM, Wandosell F (2014) Dysfunction of the PI3K-Akt-GSK-3 pathway is a common feature in cell culture and in vivo models of prion disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 40:311–326. doi:10.1111/nan.12066
Totsukawa G, Yamakita Y, Yamashiro S, Hartshorne DJ, Sasaki Y, Matsumura F (2000) Distinct roles of ROCK (Rho-kinase) and MLCK in spatial regulation of MLC phosphorylation for assembly of stress fibers and focal adhesions in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 150:797–806
Tsai YR, Huang LJ, Lin HY, Hung YJ, Lee MR, Kuo SC, Hsu MF, Wang JP (2013) Inhibition of formyl peptide-stimulated phospholipase D activation by Fal-002-2 via blockade of the Arf6, RhoA and protein kinase C signaling pathways in rat neutrophils. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 386:507–519. doi:10.1007/s00210-013-0851-6
Ulmer JB, Palade GE (1991) Effects of Brefeldin A on the Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum and viral envelope glycoproteins in murine erythroleukemia cells. Eur J Cell Biol 54:38–54
Vey M, Pilkuhn S, Wille H, Nixon R, DeArmond SJ, Smart EJ, Anderson RG, Taraboulos A, Prusiner SB (1996) Subcellular colocalization of the cellular and scrapie prion proteins in caveolae-like membranous domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:14945–14949
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Li Y, Zhang CJ, Kahn RA (2005) Isoform-selective effects of the depletion of ADP-ribosylation factors 1-5 on membrane traffic. Mol Biol Cell 16:4495–4508. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-12-1042
Wang GR, Shi S, Gao C, Zhang BY, Tian C, Dong CF, Zhou RM, Li XL, Chen C, Han J, Dong XP (2010) Changes of tau profiles in brains of the hamsters infected with scrapie strains 263 K or 139 A possibly associated with the alteration of phosphate kinases. BMC Infect Dis 10:86. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-10-86
Weis WI, Scheller RH (1998) Membrane fusion. SNARE the rod, coil the complex. Nature 395:328–329. doi:10.1038/26354
Weise J, Doeppner TR, Muller T, Wrede A, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Zerr I, Witte OW, Bahr M (2008) Overexpression of cellular prion protein alters postischemic Erk1/2 phosphorylation but not Akt phosphorylation and protects against focal cerebral ischemia. Restor Neurol Neurosci 26:57–64
Welch HC, Coadwell WJ, Stephens LR, Hawkins PT (2003) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent activation of Rac. FEBS Lett 546:93–97
Wheeler AP, Ridley AJ (2004) Why three Rho proteins? RhoA, RhoB, RhoC, and cell motility. Exp Cell Res 301:43–49. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.012
Wu G, Nakajima K, Takeyama N, Yukawa M, Taniuchi Y, Sakudo A, Onodera T (2008) Species-specific anti-apoptotic activity of cellular prion protein in a mouse PrP-deficient neuronal cell line transfected with mouse, hamster, and bovine Prnp. Neurosci Lett 446:11–15. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.09.020
Zafar S, von Ahsen N, Oellerich M, Zerr I, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Armstrong VW, Asif AR (2011) Proteomics approach to identify the interacting partners of cellular prion protein and characterization of Rab7a interaction in neuronal cells. J Proteome Res. doi:10.1021/pr2001989
Zafar S, Asif AR, Ramljak S, Tahir W, Schmitz M, Zerr I (2014) Anchorless 23-230 PrP(C) interactomics for elucidation of PrP(C) protective role. Mol Neurobiol 49:1385–1399. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8616-2
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Dr Torres at CISA INIA who produced the tg340 mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author Summary
Prion diseases are fatal neurodegenerative diseases that affect a number of different species, including humans. A long pre-clinical phase of the disease lasting months to years is a basic characteristic of the prion diseases. During the disease replication stage, the affected individual does not show any signs of the disease. The clinical or symptomatic stage of the disease is much shorter than the pre-clinical stage. Variant CJD appears to not only be transmitted by eating contaminated beef but also by blood transfusions. In the latter cases, the blood donors had prion diseases in a pre-clinical stage and the prion disease was diagnosed at a later date. Given the potential for large numbers of people to have a clinically inapparent prion infection, it is critical for public health concerns that diagnostic tools be developed to detect the disease as early as possible. To address this need, we have developed a mouse model of prion disease to study the molecular pathways involved during disease progression. Targeting Arf/Rho/MLC signaling pathways might be a promising strategy to study the most likely cause of variant rate of disease progression and internal homeostasis of misfolded proteins.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zafar, S., Schmitz, M., Younus, N. et al. Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Subtype-Specific Regional and Temporal Regulation of ADP Ribosylation Factor-1-Dependent Rho/MLC Pathway at Pre-Clinical Stage. J Mol Neurosci 56, 329–348 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0544-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0544-3