Abstract
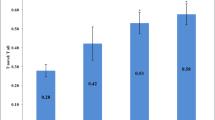
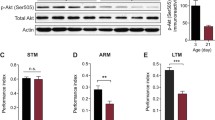
It has been shown that microtubule (MT) activity and dynamics can have huge impacts on synaptic plasticity and memory formation. This is mainly due to various functions of MTs in neurons; MTs are involved in dendritic spine formation, axonal transportation, neuronal polarity, and receptor trafficking. Recent studies from our group and other labs have suggested the possible role of brain MT dynamicity and activity in memory; however, there is a need for more detailed studies regarding this aspect. In this study, we have tried to evaluate the importance of microtubule dynamicity rather than stability in memory formation in vivo. In order to investigate the role of MT stability in memory formation, we treated mice with paclitaxel—a classic microtubule-stabilizing agent. We then studied the behavior of treated animals using Morris water maze (MWM) test. To measure the effect of injected paclitaxel on MT polymerization kinetics, we conducted polymerization assays on brain extracts of the same paclitaxel-treated animals. Our results show that paclitaxel treatment affects animals’ memory in a negative way and treated animals behave poorly in MWM compared to control group. In addition, our kinetics studies show that MT stability is significantly increased in brain extracts from paclitaxel-treated mice, but MT dynamics is reduced. Thus, we suggest that dynamicity is a very important feature of MT protein structures, and regarding memory formation, dynamicity is more important than stability and high activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura N, Kaibuchi K (2007) Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(3):194–205
Arnal I, Wade RH (1995) How does taxol stabilize microtubules? Curr Biol 5(8):900–908
Ballatore C, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(9):663–672
Blagosklonny MV, Fojo T (1999) Molecular effects of paclitaxel: myths and reality (a critical review). Int J Cancer 83(2):151–156
Brandt R, Hundelt M, Shahani N (2005) Tau alteration and neuronal degeneration in tauopathies: mechanisms and models. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Mol Basis Dis 1739(2):331–354
Collingridge GL, Isaac JT, Wang YT (2004) Receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(12):952–962
Collins CA, Vallee RB (1987) Temperature-dependent reversible assembly of taxol-treated microtubules. J Cell Biol 105(6):2847–2854
Cooke S, Bliss T (2006) Plasticity in the human central nervous system. Brain 129(7):1659–1673
Desai A, Mitchison TJ (1997) Microtubule polymerization dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13(1):83–117
Eskandari-Sedighi G, Hossein Riazi G, Reza Vaez Mahdavi M, Cheraghi T, Atarod D, Rafiei S (2014) Chronic, long-term social stress can cause decreased microtubule protein network activity and dynamics in cerebral cortex of male Wistar rats. J Mole Neurosci 55(3):579–586
Falnikar A, Baas PW (2009) Critical roles for microtubules in axonal development and disease. Springer, Cell Biology of the Axon, pp 47–64
Fanara P, Banerjee J, Hueck RV, Harper MR, Awada M, Turner H, Husted KH, Brandt R, Hellerstein MK (2007) Stabilization of hyperdynamic microtubules is neuroprotective in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Biol Chem 282(32):23465–23472
Fanara P, Husted K, Selle K, Wong P-Y, Banerjee J, Brandt R, Hellerstein M (2010) Changes in microtubule turnover accompany synaptic plasticity and memory formation in response to contextual fear conditioning in mice. Neuroscience 168(1):167–178
Fellner S, Bauer B, Miller DS, Schaffrik M, Fankhänel M, Spruß T, Bernhardt G, Graeff C, Färber L, Gschaidmeier H (2002) Transport of paclitaxel (Taxol) across the blood–brain barrier in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest 110(9):1309–1318
Gu J, Firestein BL, Zheng JQ (2008) Microtubules in dendritic spine development. J Neurosci 28(46):12120–12124
Hasegawa M, Smith MJ, Goedert M (1998) Tau proteins with FTDP-17 mutations have a reduced ability to promote microtubule assembly. FEBS Lett 437(3):207–210
Hu X, Viesselmann C, Nam S, Merriam E, Dent EW (2008) Activity-dependent dynamic microtubule invasion of dendritic spines. J Neurosci 28(49):13094–13105
Jaworski J, Kapitein LC, Gouveia SM, Dortland BR, Wulf PS, Grigoriev I, Camera P, Spangler SA, Di Stefano P, Demmers J (2009) Dynamic microtubules regulate dendritic spine morphology and synaptic plasticity. Neuron 61(1):85–100
Kim C-H, Lisman JE (2001) A labile component of AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission is dependent on microtubule motors, actin, and N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor. J Neurosci 21(12):4188–4194
Lau CG, Zukin RS (2007) NMDA receptor trafficking in synaptic plasticity and neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(6):413–426
Long BH, Fairchild CR (1994) Paclitaxel inhibits progression of mitotic cells to G1 phase by interference with spindle formation without affecting other microtubule functions during anaphase and telephase. Cancer Res 54(16):4355–4361
Lynch M (2004) Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84(1):87–136
Malinow R, Malenka RC (2002) AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 25(1):103–126
Martin S, Grimwood P, Morris R (2000) Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis. Annu Rev Neurosci 23(1):649–711
Matsuoka Y, Jouroukhin Y, Gray AJ, Ma L, Hirata-Fukae C, Li H-F, Feng L, Lecanu L, Walker BR, Planel E (2008) A neuronal microtubule-interacting agent, NAPVSIPQ, reduces tau pathology and enhances cognitive function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325(1):146–153
Michaelis M, Ranciat N, Chen Y, Bechtel M, Ragan R, Hepperle M, Liu Y, Georg G (1998) Protection against β-amyloid toxicity in primary neurons by paclitaxel (Taxol). J Neurochem 70(4):1623–1627
Milner B, Squire LR, Kandel ER (1998) Cognitive neuroscience and the study of memory. Neuron 20(3):445–468
Mitsuyama F, Futatsugi Y, Okuya M, Karagiozov K, Kato Y, Kanno T, Sano H, Koide T (2007) Microtubules to form memory. Italian journal of anatomy and embryology=Archivio italiano di anatomia ed embriologia 113(4):227–235
Nakayama T, Sawada T (2002) Involvement of microtubule integrity in memory impairment caused by colchicine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71(1):119–138
Paulson JC, McClure WO (1974) Microtubules and axoplasmic transport. Brain Res 73(2):333–337
Qian A, Burton P, Himes R (1993) A comparison of microtubule assembly in brain extracts from young and old rats. Mol Brain Res 18(1):100–106
Rowinsky M, Eric K (1997) The development and clinical utility of the taxane class of antimicrotubule chemotherapy agents. Annu Rev Med 48(1):353–374
Schiff PB, Fant J and Horwitz SB (1979) Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature 277:665–667
Xiao H, Verdier-Pinard P, Fernandez-Fuentes N, Burd B, Angeletti R, Fiser A, Horwitz SB, Orr GA (2006) Insights into the mechanism of microtubule stabilization by Taxol. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(27):10166–10173
Yvon A-MC, Wadsworth P, Jordan MA (1999) Taxol suppresses dynamics of individual microtubules in living human tumor cells. Mol Biol Cell 10(4):947–959
Zhang B, Maiti A, Shively S, Lakhani F, McDonald-Jones G, Bruce J, Lee EB, Xie SX, Joyce S, Li C (2005) Microtubule-binding drugs offset tau sequestration by stabilizing microtubules and reversing fast axonal transport deficits in a tauopathy model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(1):227–231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atarod, D., Eskandari-Sedighi, G., Pazhoohi, F. et al. Microtubule Dynamicity Is More Important than Stability in Memory Formation: an In Vivo Study. J Mol Neurosci 56, 313–319 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0535-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0535-4