Abstract
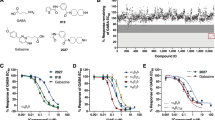
Experimental evidence suggests that GABA ρ1 receptors are potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of a range of neurological conditions, including anxiety and sleep disorders. Homology modelling of the GABA ρ1 extracellular N-terminal domain has revealed a novel hydrophobic area that extends beyond, but not including the GABA-binding site. Phenylalanine 124 (F124) is predicted to be involved in maintaining the structural integrity of the orthosteric-binding site. We have assessed the activity of a series of GABA ρ1 receptors that incorporate a mutation at F124. Wild-type and mutant human GABA ρ1 subunits were expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes and AD293 cells, and the pharmacology and kinetic properties of the receptors were measured using electrophysiological analysis. Mutation of F124 had minimal effect on receptor pharmacology. However, the rate of deactivation was significantly increased compared to wild type. This study provides further information about the role of residues within a novel hydrophobic area of the GABA ρ1 receptor. This knowledge can help future studies into the design of potent and subtype-selective ligands with therapeutic value.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- TPMPA:
-
(1,2,5,6-Tetrahydropyridine-4-yl)methylphosphinic acid
References
Abdel-Halim H, Hanrahan JR, Hibbs DE, Johnston GA, Chebib M (2008) A molecular basis for agonist and antagonist actions at GABA(C) receptors. Chem Biol Drug 71:306–327
Adamian L et al (2009) Structural model of rho1 GABAC receptor based on evolutionary analysis: testing of predicted protein-protein interactions involved in receptor assembly and function. Protein Sci 18:2371–2383
Alakuijala A et al (2005) GABA receptor rho subunit expression in the developing rat brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 154:15–23
Amin J, Weiss DS (1994) Homomeric rho 1 GABA channels: activation properties and domains. Receptor Channel 2:227–236
Arnaud C, Gauthier P, Gottesmann C (2001) Study of a GABAC receptor antagonist on sleep-waking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 154:415–419
Barry PH (1994) JPCalc, a software package for calculating liquid junction potential corrections in patch-clamp, intracellular, epithelial and bilayer measurements and for correcting junction potential measurements. J Neurosci Methods 51:107–116
Blednov YA et al (2014) GABAA receptors containing rho1 subunits contribute to in vivo effects of ethanol in mice. PLoS One 9:e85525
Bormann J (2000) The ‘ABC’ of GABA receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21:16–19
Boue-Grabot E, Roudbaraki M, Bascles L, Tramu G, Bloch B, Garret M (1998) Expression of GABA receptor rho subunits in rat brain. J Neurochem 70:899–907
Brejc K et al (2001) Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature 411:269–276
Carland JE et al (2009) Characterization of the effects of charged residues in the intracellular loop on ion permeation in alpha1 glycine receptor channels. J Biol Chem 284:2023–2030
Cederholm JM, Schofield PR, Lewis TM (2009) Gating mechanisms in Cys-loop receptors. Eur Biophys J 39:37–49
Chang Y, Weiss DS (1999) Channel opening locks agonist onto the GABAC receptor. Nat Neurosci 2:219–225
Chebib M, Mewett KN, Johnston GA (1998) GABA(C) receptor antagonists differentiate between human rho1 and rho2 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 357:227–234
Chebib M et al (2009) Novel, potent, and selective GABAC antagonists inhibit myopia development and facilitate learning and memory. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:448–457
Cheng ZY, Chebib M, Schmid KL (2011) rho1 GABAC receptors are expressed in fibrous and cartilaginous layers of chick sclera and located on sclera fibroblasts and chondrocytes. J Neurochem 118:281–287
Cheng ZY, Chebib M, Schmid KL (2012) Identification of GABA receptors in chick cornea. Mol Vis 18:1107–1114
Colquhoun D (1998) Binding, gating, affinity and efficacy: the interpretation of structure-activity relationships for agonists and of the effects of mutating receptors. Br J Pharmacol 125:924–947
Cunha C, Monfils MH, Ledoux JE (2010) GABA(C) Receptors in the lateral amygdala: a possible novel target for the treatment of fear and anxiety disorders? Front Behav Neurosci 4:6
Enz R, Cutting GR (1998) Molecular composition of GABAC receptors. Vision Res 38:1431–1441
Gavande N et al (2011) Novel cyclic phosphinic acids as GABA(C) rho receptor antagonists: design, synthesis, and pharmacology. ACS Med Chem Lett 2:11–16
Hanrahan JR, Mewett KN, Chebib M, Burden PM, Johnston GAR (2001) An improved, versatile synthesis of the GABA(C) antagonists (1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl)methylphosphinic acid (TPMPA) and (piperidin-4-yl)methylphosphinic acid (P4MPA). J Chem Soc Perk T 1:2389–2392
Harrison NJ, Lummis SC (2006a) Locating the carboxylate group of GABA in the homomeric rho GABA(A) receptor ligand-binding pocket. J Biol Chem 281:24455–24461
Harrison NJ, Lummis SC (2006b) Molecular modeling of the GABA(C) receptor ligand-binding domain. J Mol Model 12:317–324
Hibbs RE, Gouaux E (2011) Principles of activation and permeation in an anion-selective Cys-loop receptor. Nature 474:54–60
Hilf RJ, Dutzler R (2008) X-ray structure of a prokaryotic pentameric ligand-gated ion channel. Nature 452:375–379
Johnston GA (2002) Medicinal chemistry and molecular pharmacology of GABA(C) receptors. Curr Top Med Chem 2:903–913
Laha KT, Tran PN (2013) Multiple tyrosine residues at the GABA binding pocket influence surface expression and mediate kinetics of the GABAA receptor. J Neurochem 124:200–209
Lummis SC, Harrison NJ, Lester HA, Dougherty DA (2005) A cation-pi binding interaction with a tyrosine in the binding site of the GABAC receptor. Chem Biol 12:993–997
Lummis SC et al (2012) Multiple tyrosine residues contribute to GABA binding in the GABA(C) receptor binding pocket. ACS Chem Neurosci 3:186–192
Osolodkin DI, Chupakhin VI, Palyulin VA, Zefirov NS (2007) Modeling and analysis of ligand-receptor interactions in the GABA(c) receptor. Dokl Biochem Biophys 412:25–28
Puskar NL, Lester HA, Dougherty DA (2012) Probing the effects of residues located outside the agonist binding site on drug-receptor selectivity in the nicotinic receptor. ACS Chem Biol 7:841–846
Rozzo A, Armellin M, Franzot J, Chiaruttini C, Nistri A, Tongiorgi E (2002) Expression and dendritic mRNA localization of GABAC receptor rho1 and rho2 subunits in developing rat brain and spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci 15:1747–1758
Sedelnikova A, Smith CD, Zakharkin SO, Davis D, Weiss DS, Chang Y (2005) Mapping the rho1 GABA(C) receptor agonist binding pocket. Constructing a complete model. J Biol Chem 280:1535–1542
Shimada S, Cutting G, Uhl GR (1992) gamma-Aminobutyric acid A or C receptor? gamma-Aminobutyric acid rho 1 receptor RNA induces bicuculline-, barbiturate-, and benzodiazepine-insensitive gamma-aminobutyric acid responses in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol 41:683–687
Stone RA, Liu J, Sugimoto R, Capehart C, Zhu X, Pendrak K (2003) GABA, experimental myopia, and ocular growth in chick. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:3933–3946
Torres VI, Weiss DS (2002) Identification of a tyrosine in the agonist binding site of the homomeric rho1 gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor that, when mutated, produces spontaneous opening. J Biol Chem 277:43741–43748
Yang J, Cheng Q, Takahashi A, Goubaeva F (2006) Kinetic properties of GABA rho1 homomeric receptors expressed in HEK293 cells. Biophys J 91:2155–2162
Acknowledgments
We thank the Xenopus Facility staff for care of frogs. IY acknowledges the support of a John Lamberton Scholarship. JEC acknowledges the support of a UNSW Vice Chancellor’s Research Fellowship.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jane E. Carland and Izumi Yamamoto made equal contributions to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carland, J.E., Yamamoto, I., Hanrahan, J.R. et al. A Hydrophobic Area of the GABA ρ1 Receptor Containing Phenylalanine 124 Influences Both Receptor Activation and Deactivation. J Mol Neurosci 55, 305–313 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0322-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0322-7