Abstract
Introduction
Angiotensin 2 has been shown to promote angiogenesis through multiple pathways. Reduction of angiotensin 2 production by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) could enhance the antiangiogenic effect of bevacizumab and lead to improved survival.
Methods
Data from metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients treated with bevacizumab in our hospital were retrospectively collected. Patients were divided into groups taking ACEi or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) or neither. We performed survival analysis and COX proportional hazard modelling and calculated the hazard ratio (HR). Multivariate analyses were performed to measure the impact of factors affecting survival, and subgroup analyses were performed for patients younger than 65 years.
Results
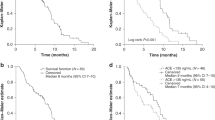
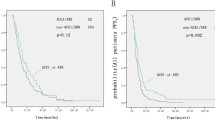
We enrolled 133 patients who received bevacizumab therapy. Eighty patients were male, and 53 were female. Twenty-three patients received ACEi treatment, and 34 patients received ARB. The median age was 58 years. Progression-free survival was higher in the ACEi group than in the ARB group or in the group receiving neither (7.66 vs. 5.98 vs. 5.0 months; p < 0.01), corresponding to a HR of 0.44 for the ACEi group (95% CI 0.26–0.74). Overall survival was not significantly longer in the ACEi group than in the ARB group or in the group receiving neither (22.0 vs. 23.5 vs. 19.7 months; p = 0.30), HR 0.66 (95% CI 0.38–1.2). In a subgroup analysis, overall survival was higher in patients younger than 65 years in the ACEi group (45.0 vs. 16.2 months; p = 0.02).
Conclusion
In the final analysis, ACEi use in patients treated with bevacizumab resulted in prolonged progression-free survival, but this did not affect overall survival. Because our study is the first to look at the enhancement of the effect of bevacizumab by ACEi treatment and ACEi receiving patients are older, it would be useful to confirm our results by randomized trials.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. 2009;350(23):2335–42. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa032691.
Munk VC, De Miguel LS, Petrimpol M, et al. Angiotensin II induces angiogenesis in the hypoxic adult mouse heart in vitro through an AT2-B2 receptor pathway. Hypertension. 2007;[cited 2022 Jan 9];49(5):1178–85. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.106.080242.
Si W, Xie W, Deng W, et al. Angiotensin II increases angiogenesis by NF-κB–mediated transcriptional activation of angiogenic factor AGGF1. The FASEB J 2018 [cited 2022 Jan 9];32(9):5051. Available from: https://www.pmc/articles/PMC6103173/.
Shen Y, Wang X, Lu J, et al. Reduction of liver metastasis stiffness improves response to bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell. 2020;37(6):800-817.e7.
Chen X, Yi CH, Ya KG. Renin–angiotensin system inhibitor use and colorectal cancer risk and mortality: a dose–response meta analysis. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. [Internet] 2020 [cited 2022 Jan 17];21(3). Available from: https://www.pmc/articles/PMC7338647/.
Neo JH, Malcontenti-Wilson C, Muralidharan V, Christophi C. Effect of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists in a mouse model of colorectal cancer liver metastases. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22(4):577–84.
Roth IM, Wickremesekera AC, Wickremesekera SK, Davis PF, Tan ST. Therapeutic targeting of cancer stem cells via modulation of the renin-angiotensin system. Front Oncol. 2019;9(AUG):745.
Tabatabai E, Khazaei M, Asgharzadeh F, et al. Inhibition of angiotensin II type 1 receptor by candesartan reduces tumor growth and ameliorates fibrosis in colorectal cancer. EXCLI J. 2021;20:863.
Stokes WA, Molina E, McDermott JD, et al. Survival impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists in head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 2021;43(11):3255–75.
Xiong L, Wei Y, Zhou X, et al. AGTR1 inhibits the progression of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:8535–50.
Wu C-N, Wu S-C, Chen W-C, et al. Angiotensin II receptor blockers and oral squamous cell carcinoma survival: a propensity-score-matched cohort study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(12): e0260772.
Ren T, Jia H, Wu Q, et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis and extracellular matrix remodeling: synergistic effect of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors and bevacizumab. Front Oncol. 2022;12.
Makar GA, Holmes JH, Yang YX. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy and colorectal cancer risk. JNCI J Nat Canc Inst. 2014;106(2).
Ozawa T, Hashiguchi Y, Yagi T, et al. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers may reduce tumor recurrence in left-sided and early colorectal cancers. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019;34(10):1731–9.
Cui Y, Wen W, Zheng T, et al. Use of antihypertensive medications and survival rates for breast, colorectal, lung, or stomach cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(8):1512–28.
Osumi H, Matsusaka S, Wakatsuki T, Suenaga M, Shinozaki E, Mizunuma N. Angiotensin II type-1 receptor blockers enhance the effects of bevacizumab-based chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Mol Clin Oncol. 2015 [cited 2022 Jan 17];3(6):1295–300. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2015.630.
Zeman M, Skałba W, Wilk AM, Cortez AJ, Maciejewski A, Czarniecka A. Impact of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on the survival of patients with rectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1).
Engineer DR, Burney BO, Hayes TG, Garcia JM. Exposure to ACEI/ARB and β-blockers is associated with improved survival and decreased tumor progression and hospitalizations in patients with advanced colon cancer. Transl Oncol. 2013;6(5):539–45.
Deng Y, Xie Y, Wang M, et al. Effects of antihypertensive drugs use on risk and prognosis of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of 37 observational studies. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally, and all authors have reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Erdat, E.C., Koksoy, E.B. & Utkan, G. Enhancing the Anti-angiogenic Effect of Bevacizumab with ACE Inhibition on mCRC. J Gastrointest Canc 54, 897–902 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-022-00890-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-022-00890-4