Abstract
Background and Aim
Sodium valproate (SV), a novel class of histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors commonly used as an antiepileptic drug. HDAC inhibitors are known to possess anticancer potentials. In this study, we investigated the cytotoxic potential of SV in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2 cells) cell line.
Methods
MTT assay was used to analyze cytotoxicity. Intracellular ROS and cytochrome c expression were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Morphology-related apoptosis was analyzed by dual staining with acridine orange/ethidium bromide. Caspase 3 protein expression was investigated by Western blotting analysis.
Results
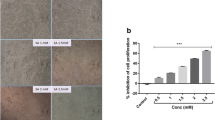
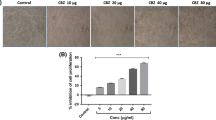
Sodium valproate treatments in HepG2 cells caused significant and dose-dependent cytotoxicity. Intracellular ROS was remarkably increased in the cells which are treated with SV and caused early and late apoptosis as evidenced by dual staining. SV-treated cells expressed cytochrome c and caspase 3 protein expression.
Conclusion
These results suggest the cytotoxic potentials of SV in HepG2 cells. This study may give an important clue for the inclusion of SV as an adjuvant along with standard anticancer agents after necessary in vivo and clinical studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jindal A, Thadi A, Shailubhai K. Hepatocellular carcinoma: etiology and current and future drugs. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019;9:221–32.
Ezhilarasan D. Lead compounds with the potentials for the treatment of chronic liver diseases. In: Egbuna C, Kumar S, Ifemeje J, Ezzat S, Kaliyaperumal S, editors. Phytochemicals as lead compounds for new drug discovery. 1st ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2019. p. 195–210.
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Madduru D, Ijaq J, Dhar S, Sarkar S, Poondla N, Das PS, et al. Systems challenges of hepatic carcinomas: a review. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019;9:233–44.
Rimassa L, Danesi R, Pressiani T, Merle P. Management of adverse events associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: improving outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;77:20–8.
Granito A, Marinelli S, Negrini G, Menetti S, Benevento F, Bolondi L. Prognostic significance of adverse events in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2016;9:240–9.
Gheena S, Ezhilarasan D. Syringic acid triggers reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2019;38:694–702.
Shebi S, Ezhilarasan D, Thomas J, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A. Gracilaria foliifera (Forssk.) Børgesen ethanolic extract triggers apoptosis via activation of p53 expression in HepG2 cells. Phcog Mag. 2019;15:259–63.
Ezhilarasan D. Herbal therapy for cancer. In: Prakash Srinivasan, Timiri Shanmugam., editors. Understanding cancer therapies, CRC Press; 2018. pp. 129–166.
Brookes RL, Crichton S, Wolfe CDA, Yi Q, Li L, Hankey GJ, et al. Sodium valproate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, is associated with reduced stroke risk after previous ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2018;49:54–61.
Göttlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, Krämer OH, Schimpf A, Giavara S, et al. Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J. 2001;20:6969–78.
Li Y, Seto E. HDACs and HDAC inhibitors in cancer development and therapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6:a026831.
Schizas D, Mastoraki A, Naar L, Tsilimigras DI, Katsaros I, Fragkiadaki V, et al. Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) in gastric cancer: an update of their emerging prognostic and therapeutic role. Curr Med Chem. 2019. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867326666190712160842.
Ishikawa D, Takasu C, Kashihara H, Nishi M, Tokunaga T, Higashijima J, et al. The significance of MicroRNA-449a and its potential target HDAC1 in patients with colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019;39:2855–60.
Buckwalter JM, Chan W, Shuman L, Wildermuth T, Ellis-Mohl J, Walter V, et al. Characterization of histone deacetylase expression within in vitro and in vivo bladder cancer model systems. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:E2599.
Linares A, Assou S, Lapierre M, Thouennon E, Duraffourd C, Fromaget C, et al. Increased expression of the HDAC9 gene is associated with antiestrogen resistance of breast cancers. Mol Oncol. 2019;13:1534–47.
Ma S, Liu T, Xu L, Wang Y, Zhou J, Huang T, et al. Histone deacetylases inhibitor MS-275 suppresses human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell growth and progression via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:22400–10.
Wang Z, Wang H, Shen P, Xie R. Expression of HDAC4 in stage B hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on survival. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019;49:189–92.
Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M, Hrabeta J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:E1414.
Suraweera A, O'Byrne KJ, Richard DJ. Combination therapy with histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) for the treatment of cancer: achieving the full therapeutic potential of HDACi. Front Oncol. 2018;8:92.
Gavrilov V, Lavrenkov K, Ariad S, Shany S. Sodium valproate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances the efficacy of vinorelbine-cisplatin-based chemoradiation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:6565–72.
Sohaib M, Ezhilarasan D. Carbamazepine, a histone deacetylase inhibitor induces apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma cell line HT-29. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-019-00286-x.
Gong P, Wang Y, Jing Y. Apoptosis induction by histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer cells: role of Ku70. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:E1601.
Bao L, Diao H, Dong N, Su X, Wang B, Mo Q, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor induces cell apoptosis and cycle arrest in lung cancer cells via mitochondrial injury and p53 up-acetylation. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016;32:469–82.
PonselviInduja M, Ezhilarasan D, Ashok VN. Evolvulusalsinoidesmethanolic extract triggers apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2018;8:504–12.
Lakshmi T, Ezhilarasan D, Vijayaragavan R, Bhullar SK, Rajendran R. Acacia catechu ethanolic bark extract induces apoptosis in human oral squamous carcinoma cells. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2017;8:143–9.
Tsilimigras DI, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Moris D, Spartalis E, Pawlik TM. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma: a therapeutic perspective. Surg Oncol. 2018;27:611–8.
Liu KY, Wang LT, Hsu SH. Modification of epigenetic histone acetylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2018;10:E8.
Han BR, You BR, Park WH. Valproic acid inhibits the growth of HeLa cervical cancer cells via caspase-dependent apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:2999–3005.
Ma XJ, Wang YS, Gu WP, Wang Y, Zhou J, Huang T, et al. The role and possible molecular mechanism of valproic acid in the growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Croat Med J. 2017;58:349–57.
Sargazi S, Kooshkaki O, Zavar Reza J, Saravani R, Zarei Jaliani H, Mirinejad S, et al. Mild antagonistic effect of valproic acid in combination with AZD2461 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2019;33:29.
Ghecham A, Senator A, Pawlowska E, Bouafia W, Błasiak J. Epigenetic modifiers 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine and valproic acid differentially change viability, DNA damage and gene expression in metastatic and non-metastatic colon cancer cell lines. Acta Biochim Pol. 2019;66(3):355–60.
Li H, Zhang Z, Gao C, Wu S, Duan Q, Wu H, et al. Combination chemotherapy of valproic acid (VPA) and gemcitabine regulates STAT3/Bmi1 pathway to differentially potentiate the motility of pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Biosci. 2019;9:50.
Ezhilarasan D, Apoorva VS, Ashok Vardhan N. Syzygium cumini extract induced reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in human oral squamous carcinoma cells. J Oral Pathol Med. 2019;48:115–21.
Rohit Singh T, Ezhilarasan D. Ethanolic extract of Lagerstroemia Speciosa (L.) Pers., induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cells. Nutr Cancer. 2020;72:146–56.
Rivera-Del Valle N, Cheng T, Irwin ME, Donnella H, Singh MM, Chandra J. Combinatorial effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), vorinostat and entinostat, and adaphostin are characterized by distinct redox alterations. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018;81:483–95.
Lee JH, Jeong EG, Choi MC, Kim SH, Park JH, Song SH, et al. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 10 induces thioredoxin-interacting protein and causes accumulation of reactive oxygen species in SNU-620 human gastric cancer cells. Mol Cells. 2010;30:107–12.
Cornago M, Garcia-Alberich C, Blasco-Angulo N, Vall-Llaura N, Nager M, Herreros J, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote glioma cell death by G2 checkpoint abrogation leading to mitotic catastrophe. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1435.
Tseng JH, Chen CY, Chen PC, Hsiao SH, Fan CC, Liang YC, et al. Valproic acid inhibits glioblastoma multiforme cell growth via paraoxonase 2 expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8:14666–79.
Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863;2016:2977–92.
Wang L, Hu T, Shen J, Zhang L, Li LF, Chan RL, et al. Miltirone induced mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS-dependent apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Life Sci. 2016;151:224–34.
Wang Y, Luo Q, He X, Wei H, Wang T, Shao J, et al. Emodin induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells via induction of autophagy in a ROS-dependent manner. Oncol Res. 2018;26:889–99.
Gong D, Zeng Z, Yi F, Wu J. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 11 promotes human liver cancer cell apoptosis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:983–90.
Cavalcante GC, Schaan AP, Cabral GF, Santana-da-Silva MN, Pinto P, Vidal AF, et al. A cell’s fate: an overview of the molecular biology and genetics of apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:E4133.
Jin H, Ko YS, Park SW, Chang KC, Kim HJ. 13-Ethylberberine induces apoptosis through the mitochondria-related apoptotic pathway in radiotherapy-resistant breast cancer cells. Molecules. 2019;24:E2448.
Heimer S, Knoll G, Schulze-Osthoff K, Ehrenschwender M. Raptinal bypasses BAX, BAK, and BOK for mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and intrinsic apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:556.
Kanipandian N, Li D, Kannan S. Induction of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in A549 lung cancer cells using silver nanoparticles from Gossypium hirsutum and evaluation of in vivo toxicity. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2019;23:e00339.
Vairavel M, Devaraj E, Shanmugam R. An eco-friendly synthesis of Enterococcus sp.-mediated gold nanoparticle induces cytotoxicity in human colorectal cancer cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07511-x.
Tong XH, Zheng C, Jiang GJ, Dong SY. Sodium valproate enhances doxorubicin cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells in vitro. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015;35:62–5.
Killick-Cole CL, Singleton WGB, Bienemann AS, Asby DJ, Wyatt MJ, Boulter LJ, et al. Repurposing the anti-epileptic drug sodium valproate as an adjuvant treatment for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0176855.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank M/s. Anjan Drug Private Limited, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India, for providing sodium valproate EP as gratis. Special thanks to Dr. S. Gheena, Department of Oral Pathology, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Chennai, India, for the drug procurement procedures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PR and ED performed the research. PR reviewed the literature and drafted the manuscript, and ED corrected the manuscript, designed the figures, and submitted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rithanya, P., Ezhilarasan, D. Sodium Valproate, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Provokes Reactive Oxygen Species–Mediated Cytotoxicity in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. J Gastrointest Canc 52, 138–144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-020-00370-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-020-00370-7