Abstract
Background
Cerebral sinus venous thrombosis (CSVT) is an uncommon condition in children with potentially serious outcomes. Large epidemiological studies in children with CSVT are few. The objective of this study is to evaluate the epidemiology and in-hospital outcomes of hospitalized children with CSVT in the United States.
Methods
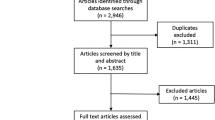
We performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Kids’ Inpatient Database for the combined years 2016 and 2019. The database was queried using the diagnoses for intracranial and intraspinal phlebitis and thrombophlebitis, nonpyogenic thrombosis of the intracranial venous system, and cerebral infarction due to cerebral venous thrombosis. Sample weighting was employed to produce national estimates.
Results
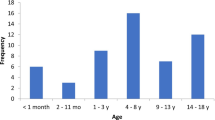
Of 12,165,621 discharges, 3202 had CSVT (in-hospital prevalence 26.3 per 100,000 discharges). Male patients accounted for 57% of CSVT discharges. The median age was 8 years (interquartile range 1–16), with a U-shaped distribution with peaks in patients younger than 4 years and patients aged between 18 and 20 years. A total of 19.3% of children with CSVT had either hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke. Patients with stroke were more likely to require mechanical ventilation (odds ratio [OR] 2.7; 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.1–3.3; p < 0.001) and have higher mortality (OR 2.3; 95% CI 1.6–3.4; p < 0.001). Mechanical ventilation was necessary for 25.2% of patients with CSVT, of whom the majority were neonates and young children. The need for mechanical ventilation was associated with increased mortality (OR 16.6; 95% CI 9.9–27.9; p < 0.001). The overall mortality rate for CSVT was 4.1%, and 16.5% of patients with CSVT were discharged with home health care or to a skilled nursing facility.
Conclusions
CSVT, which has a U-shaped age distribution, is an uncommon condition in children. Stroke is common in children with CSVT, and it is associated with an increased need for mechanical ventilation and increased mortality. The need for mechanical ventilation is more common in infants, and it is associated with increased mortality across all age groups.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ichord RN, Benedict SL, Chan AK, Kirkham FJ, Nowak-Gottl U, International Paediatric Stroke Study G. Paediatric cerebral sinovenous thrombosis: findings of the International Paediatric Stroke Study. Arch Dis Child. 2015;100(2):174–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2014-306382.
Deveber G, Andrew M, Adams C, et al. Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(6):417–23. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200108093450604.
Grunt S, Wingeier K, Wehrli E, et al. Cerebral sinus venous thrombosis in Swiss children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010;52(12):1145–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2010.03722.x.
Heller C, Heinecke A, Junker R, et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis in children: a multifactorial origin. Circulation. 2003;108(11):1362–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000087598.05977.45.
Teksam M, Moharir M, Deveber G, Shroff M. Frequency and topographic distribution of brain lesions in pediatric cerebral venous thrombosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(10):1961–5. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1246.
Mallick AA, Sharples PM, Calvert SE, et al. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: a case series including thrombolysis. Arch Dis Child. 2009;94(10):790–4. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2008.154708.
Vieira JP, Luis C, Monteiro JP, et al. Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children: clinical presentation and extension, localization and recanalization of thrombosis. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2010;14(1):80–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2008.12.004.
Wasay M, Dai AI, Ansari M, Shaikh Z, Roach ES. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in children: a multicenter cohort from the United States. J Child Neurol. 2008;23(1):26–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073807307976.
(HCUP) AfHRaQHCaUP. Introduction to the HCUP KIDS’ inpatient database. www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov (2019).
Sabapathy CA, Djouonang TN, Kahn SR, Platt RW, Tagalakis V. Incidence trends and mortality from childhood venous thromboembolism: a population-based cohort study. J Pediatr. 2016;172:175-180 e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.017.
Sebire G, Tabarki B, Saunders DE, et al. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in children: risk factors, presentation, diagnosis and outcome. Brain. 2005;128(Pt 3):477–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh412.
Deveber G, Monagle P, Chan A, et al. Prothrombotic disorders in infants and children with cerebral thromboembolism. Arch Neurol. 1998;55(12):1539. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.55.12.1539.
Dlamini N, Billinghurst L, Kirkham FJ. Cerebral venous sinus (sinovenous) thrombosis in children. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2010;21(3):511–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2010.03.006.
Sorg AL, Von Kries R, Klemme M, et al. Incidence and risk factors of cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2021;63(6):697–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.14816.
Carvalho KS, Bodensteiner JB, Connolly PJ, Garg BP. Cerebral venous thrombosis in children. J Child Neurol. 2001;16(8):574–80. https://doi.org/10.1177/088307380101600807.
Abend NS, Gutierrez-Colina AM, Topjian AA, et al. Nonconvulsive seizures are common in critically ill children. Neurology. 2011;76(12):1071–7. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0b013e318211c19e.
Herman ST, et al. Consensus statement on continuous EEG in critically ill adults and children, part I: indications. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;32(2):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNP.0000000000000166.
Lindgren E, Silvis SM, Hiltunen S, et al. Acute symptomatic seizures in cerebral venous thrombosis. Neurology. 2020;95(12):e1706–15. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000010577.
Ferro JM, Bousser MG, Canhao P, et al. European Stroke Organization guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis - endorsed by the European Academy of Neurology. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24(10):1203–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13381.
Ferriero DM, et al. Management of stroke in neonates and children: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(3):e51–96. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000183.
Monagle P, et al. American society of hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of pediatric venous thromboembolism. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3292–316. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2018024786.
Lebas A, et al. EPNS/SFNP guideline on the anticoagulant treatment of cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children and neonates. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2012;16(3):219–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2012.02.005.
Moharir MD, Shroff M, Stephens D, et al. Anticoagulants in pediatric cerebral sinovenous thrombosis: a safety and outcome study. Ann Neurol. 2010;67(5):590–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21936.
Jordan LC, et al. Antithrombotic treatment in neonatal cerebral sinovenous thrombosis: results of the International Pediatric Stroke Study. J Pediatr. 2010;156(5):704–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.11.061.
Faustino EVS, Lawson KA, Northrup V, Higgerson RA. Mortality-adjusted duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill children with symptomatic central venous line-related deep venous thrombosis*. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(5):1151–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31820eb8a1.
Sellers A, Meoded A, Quintana J, et al. Risk factors for pediatric cerebral sinovenous thrombosis: a case-control study with case validation. Thromb Res. 2020;194:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2020.06.013.
Fox CK, Johnston SC, Sidney S, Fullerton HJ. High critical care usage due to pediatric stroke: results of a population-based study. Neurology. 2012;79(5):420–7. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0b013e3182616fd7.
Williams CN, Piantino J, Mcevoy C, Fino N, Eriksson CO. The burden of pediatric neurocritical care in the United States. Pediatr Neurol. 2018;89:31–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2018.07.013.
Hammer J. Acute respiratory failure in children. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2013;14(2):64–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prrv.2013.02.001.
Trachsel D, et al. Developmental respiratory physiology. Paediatr Anaesth. 2022;32(2):108–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/pan.14362.
Bushnell CD, Phillips-Bute BG, Laskowitz DT, Lynch JR, Chilukuri V, Borel CO. Survival and outcome after endotracheal intubation for acute stroke. Neurology. 1999;52(7):1374–81. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.52.7.1374.
Funding
The authors have received no additional grants or other financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception or design of the work: JSP and BRT. Data collection: JSP and PS. Data analysis and interpretation: JSP, PAM, and BRT. Drafting the article: JSP. Critical revision of the article: PAM and BRT. Final approval of the version to be published: JSP, PS, PAM, and BRT.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval/Informed Consent
This study was exempt from institutional review board approval.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abstract was presented at the Society of Critical Care Medicine Annual Congress in 2021.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Proaño, J.S., Martinez, P.A., Sendi, P. et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Children with Cerebral Sinus Venous Thrombosis. Neurocrit Care 39, 331–338 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-023-01765-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-023-01765-7