Abstract
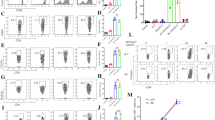
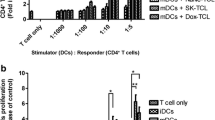
Hsp70, a highly conserved protein, has gained plenty of attention by virtue of its adjuvant capability to induce peptide-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. In this study, we have investigated the effect of autologous Hsp70–peptide complex (or simply autologous Hsp70) on the expression of CD28 on T cells and its effector functions through macrophage activation. Further, we investigated the effect of Hsp70 on the expression of CD80 and CD86 on macrophages isolated from normal and tumor-bearing host to provide costimulatory signal for T cell activation and secretion of IL-2 and IFN-γ during interaction. We found that treatment of autologous Hsp70 effectively activated TAMs to induce higher expression of CD28 on T cells through T cells–macrophage interaction. Treatment of autologous Hsp70 induces higher expression of CD80 and CD86 on TAMs, as a result, increases B7/CD28 interaction, which in turns activates T cells and induces higher production of IL-2 and IFN-γ, thereby increasing antigen-specific T cell proliferation. With our novel study, we have provided the strong insights into the role of extracellular Hsp70 on the expression of CD28 costimulatory molecule on T cells, which helps in the activation and generation of antigen-specific T cell effector functions in a tumor-bearing host to curb malignancy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bukau B, Horwich AL. The Hsp70 and Hsp60 chaperone machines. Cell. 1995;92:351–66.
Rothman JE. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1998;59:591–601.
Srivastava PK. Interaction of heat shock proteins with peptides and antigen presenting cells: chaperoning of the innate and adaptive immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:395–425.
Tamura Y, Peng P, Liu K, Daou M, Srivastava PK. Immunotherapy of tumors with autologous tumor derived heat shock protein preparations. Science. 1997;278:117–20.
Wang XY, Kazim L, Repasky EA, Subjeck JR. Characterization of heat shock protein 110 and glucose-regulated protein 170 as cancer vaccines and the effect of fever-range hyperthermia on vaccine activity. J Immunol. 2001;166:490–7.
Ishii T, Udono H, Yamano T, Ohta H, Uenaka A, Ono T, et al. Isolation of MHC class I-restricted tumor antigen peptide and its precursors associated with heat shock proteins hsp70, hsp90, and gp96. J Immunol. 1999;162:1303–9.
Basu S, Binder RJ, Ramalingam T, Srivastava PK. CD91 is a common receptor for heat shock proteins gp96, hsp90, hsp70, and calreticulin. Immunity. 2001;14:303–13.
Delneste Y, Magistrelli G, Gauchat J, Haeuw J, Aubry J, Nakamura K, et al. Involvement of LOX-1 in dendritic cell-mediated antigen cross-presentation. Immunity. 2002;17:353–62.
Berwin B, Rosser MF, Brinker KG, Nicchitta CV. Transfer of GRP94 (Gp96)-associated peptides onto endosomal MHC class I molecules. Traffic. 2002;3:358–66.
Castellino F, Boucher PE, Eichelberg K, Mayhew M, Rothman JE, Houghton AN, et al. Receptor-mediated uptake of antigen/heat shock protein complexes results in major histocompatibility complex class I antigen presentation via two distinct processing pathways. J Exp Med. 2000;191:1957–64.
Srivastava PK. Roles of heat-shock proteins in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:185–94.
Royer HD, Campen TJ, Ramarli D, Chang HC, Acuto O, Reinherz EL. Molecular aspects of human T lymphocyte antigen recognition. Transplantation. 1985;39:571–9.
Marrack P, Kappler J. The T cell receptor. Science. 1987;238:1073–83.
Oettgen HC, Terhorst T. The T-cell receptor-T3 complex and T-lymphocyte activation. Hum Immunol. 1987;18:187–98.
Nicola LH, Ronchese F. The role of B7 costimulation in T-cell immunity. Immunol Cell Biol. 1999;77:304–11.
Butler JJ, Cochran J, Ward N, Hoskin DW. Activation-induced expression of cell surface CD28 on mouse T lymphocytes is inhibited by cyclosporine. Am J Transplant. 2002;2:215–22.
Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:233–58.
Thompson CB, Lindsten T, Ledbetter JA, Kunkel SL, Young HA, Emerson SG, Leiden JM, June CH. CD28 activation pathway regulates the production of multiple T cell-derived lymphokines/cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:1333–41.
Bryl E, Vallejo AN, Matteson EL, Witkowski JM, Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Modulation of CD28 expression with anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(10):2996–3003.
Turka LA, Ledbetter JA, Lee K, June CH, Thompson CB. CD28 is an inducible T cell surface antigen that transduces a proliferative signal in CD31 mature thymocytes. J Immunol. 1990;144:1646–53.
Freeman GJ, Gribben JG, Boussiotis VA, Ng JW, Restivo VA Jr, Lombard LA, et al. Cloning of B7-2: a CTLA-4 counter-receptor that costimulates human T cell proliferation. Science. 1993;262:909–17.
Linsley PS, Ledbetter JA. The role of CD28 receptor during T cell responses to antigen. Annu Rev Immuno. 1993;11:191–203.
Freeman GJ, Borriello F, Hodes RJ, Reiser H, Gribben JG, Ng JW, et al. Murine B7-2, an alternative CTLA4 counter-receptor that costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med. 1993;178:2185–97.
Levine BL, Ueda Y, Craighead N, Huang ML, June CH. CD28 ligands CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) induce long-term autocrine growth of CD41 T cells and induce similar patterns of cytokine secretion in vivo. Int Immunol. 1995;7:891–9.
Mathur M, Herrmann K, Qin Y, Gulmen F, Li X, Krimins R, Weinstock J, Elliott D, Bluestone JA, Padrid P. CD28 interactions with either CD80 or CD86 are sufficient to induce allergic airway inflammation in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999;21:498–509.
Larsen CP, Ritchie SC, Hendrix R, Linsley PS, Hathcock KS, Hodes RJ, et al. Regulation of immunostimulatory function and costimulatory molecule (B7-1 and B7-2) expression on murine dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1994;152:5208–19.
Liu MF, Li JS, Weng TH, Lei HY. Differential expression and modulation of costimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 on monocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol. 1999;49(1):82–7.
Kumar S, Deepak P, Acharya A. Hsp70 modulates the enhanced production of reactive intermediate metabolites and a pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α expression in a T-cell lymphoma. Eur J Inflamm. 2006;4(3):157–69.
Kumar S, Deepak P, Acharya A. Hsp70 induces Th1 polarization through tumor-associated macrophages in a T-cell lymphoma. Neoplasma. 2007;54(2):113–22.
Peng P, Menoret A, Srivastava PK. Purification of immunogenic heat shock protein 70-peptide complexes by ADP-affinity chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1997;204:13–21.
Mossman T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival. J Immunol Methods. 1998;65:53–64.
Galdiero M, Pisciotta MG, Gorga F, Petrillo G, Marinelli A, Galdiero E. Modulation of costimulatory molecules CD80/CD86 on B cells and macrophages by stress proteins GroEL, GroES and DnaK. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2005;18(4):637–44.
Acuto O, Michel F. CD28-mediated co-stimulation: a quantitative support for TCR signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:939–51.
Figueiredo C, Wittmann M, Wang D, Dressel R, Seltsam A, Blasczyk R, et al. Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) induces cytotoxicity of T-helper cells. Blood. 2009;113(13):3008–16.
Vabulas RM, Ahmad-Nejad P, Ghose S, Kirschning CJ, Issels RD, Wagner H. HSP70 as endogenous stimulus of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor signal pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:15107–12.
Retzlaff C, Yamamoto Y, Hoffman PS, Friedman H, Klein TW. Legionella pneumophila heat shock protein-induced increase of interleukin-1β mRNA involves protein kinase C signaling in macrophages. Immunology. 1996;89:281–8.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to UGC, New Delhi, for the financial support to SK as a postdoctoral research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Gautam, P.K., Tomar, M.S. et al. CD28-mediated T cell response is upregulated by exogenous application of autologous Hsp70–peptide complex in a tumor-bearing host. Immunol Res 64, 313–323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8752-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8752-z