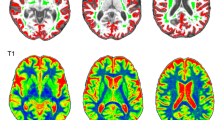
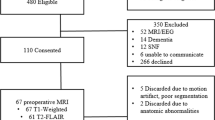
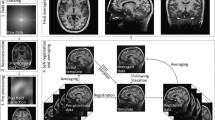
Abstract
During aging the brain undergoes a series of structural changes, in size, shape as well as tissue composition. In particular, cortical atrophy and ventricular enlargement are often present in the brain of elderly individuals. This poses serious challenges in the spatial registration of structural MR images. In this study, we addressed this open issue by proposing an enhanced framework for MR registration and segmentation. Our solution was compared with other approaches based on the tools available in SPM12, a widely used software package. Performance of the different methods was assessed on 229 T1-weighted images collected in healthy individuals, with age ranging between 55 and 90 years old. Our method showed a consistent improvement as compared to other solutions, especially for subjects with enlarged lateral ventricles. It also provided a superior inter-subject alignment in cortical regions, with the most marked improvement in the frontal lobe. We conclude that our method is a valid alternative to standard approaches based on SPM12, and is particularly suitable for the processing of structural MR images of brains with cortical atrophy and ventricular enlargement. The method is integrated in our software toolbox MRTool, which is freely available to the scientific community.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Cabronero, J., Williams, G. B., Pereira, J. M. S., Pengas, G., & Nestor, P. J. (2008). The impact of skull-stripping and radio-frequency bins correction on grey-matter segmentation for voxel-based morphometry. NeuroImage, 39, 1654–1665.
Allen, J. S., Bruss, J., Mehta, S., Grabowski, T., Brown, C. K., & Damasio, H. (2008). Effects of spatial transformation on regional brain volume estimates. NeuroImage, 42, 535–547.
Apostolova, L. G., Green, A. E., Babakchanian, S., Hwang, K. S., Chou, Y. Y., Toga, A. W., & Thompson, P. M. (2012). Hippocampal atrophy and ventricular enlargement in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 26, 17–27.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (1999). Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Human Brain Mapping, 7, 254–266.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2005). Unified segmentation. NeuroImage, 26, 839–851.
Brett, M., Johnsrude, I. S., & Owen, A. M. (2002). The problem of functional localization in the human brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3, 243–249.
Collignon, A., Maes, F., Delaere, D., Vandermeulen, D., Suetens, P., & Marchal, G. (1995). Automated multi-modality image registration based on information theory. Information Processing in Medical Imaging, 3, 263–274.
Colloby, S. J., Firbank, M. J., Vasudev, A., Parry, S. W., Thomas, A. J., & O'brien, J. T. (2011). Cortical thickness and VBM-DARTEL in late-life depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 133, 158–164.
Crivello, F., Schormann, T., Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Roland, P. E., Zilles, K., & Mazoyer, B. M. (2002). Comparison of spatial normalization procedures and their impact on functional maps. Human Brain Mapping, 16, 228–250.
Dade, L. A., Gao, F. Q., Kovacevic, N., Roy, P., Rockel, C., O'toole, C. M., Lobaugh, N. J., Feinstein, A., Levine, B., & Black, S. E. (2004). Semiautomatic brain region extraction: A method of parcellating brain regions from structural magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage, 22, 1492–1502.
Dewey, J., Hana, G., Russell, T., Price, J., Mccaffrey, D., Harezlak, J., Sem, E., Anyanwu, J. C., Guttmann, C. R., Navia, B., Cohen, R., Tate, D. F., & Consortium, H. N. (2010). Reliability and validity of MRI-based automated volumetry software relative to auto-assisted manual measurement of subcortical structures in HIV-infected patients from a multisite study. NeuroImage, 51, 1334–1344.
Dong, L., & Boyer, A. L. (1995). An image correlation procedure for digitally reconstructed radiographs and electronic portal images. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, 33, 1053–1060.
Eloyan, A., Shou, H. C., Shinohara, R. T., Sweeney, E. M., Nebel, M. B., Cuzzocreo, J. L., Calabresi, P. A., Reich, D. S., Lindquist, M. A., & Crainiceanu, C. M. (2014). Health effects of lesion localization in multiple sclerosis: Spatial registration and confounding adjustment. PLoS One, 9, e107263.
Fein, G., Landman, B., Tran, H., Barakos, J., Moon, K., Di Sclafani, V., & Shumway, R. (2006). Statistical parametric mapping of brain morphology: Sensitivity is dramatically increased by using brain-extracted images as inputs. NeuroImage, 30, 1187–1195.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., Van Der Kouwe, A., Killiany, R., Kennedy, D., Klaveness, S., Montillo, A., Makris, N., Rosen, B., & Dale, A. M. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: Automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33, 341–355.
Fischmeister, F. P. S., Hollinger, I., Klinger, N., Geissler, A., Wurnig, M. C., Matt, E., Rath, J., Robinson, S. D., Trattnig, S., & Beisteiner, R. (2013). The benefits of skull stripping in the normalization of clinical fMRI data. Neuroimage Clinical, 3, 369–380.
Ganzetti, M., Wenderoth, N., & Mantini, D. (2015). Quantitative evaluation of intensity inhomogeneity correction methods for structural MR brain images. Neuroinformatics, 14, 5–21.
Ganzetti, M., Wenderoth, N., & Mantini, D. (2016). Intensity inhomogeneity correction of structural MR images: A data-driven approach to define input algorithm parameters. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 10, 10.
Han, Z., Thornton-Wells, T. A., Dykens, E. M., Gore, J. C., & Dawant, B. M. (2012). Effect of nonrigid registration algorithms on deformation-based morphometry: A comparative study with control and Williams syndrome subjects. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 30, 774–788.
Hoeksma, M. R., Kenemans, J. L., Kemner, C., & Van Engeland, H. (2005). Variability in spatial normalization of pediatric and adult brain images. Clinical Neurophysiology, 116, 1188–1194.
Izquierdo-Garcia, D., Hansen, A. E., Forster, S., Benoit, D., Schachoff, S., Furst, S., Chen, K. T., Chonde, D. B., & Catana, C. (2014). An SPM8-based approach for attenuation correction combining segmentation and nonrigid template formation: Application to simultaneous PET/MR brain imaging. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 55, 1825–1830.
Kennedy, K. M., Erickson, K. I., Rodrigue, K. M., Voss, M. W., Colcombe, S. J., Kramer, A. F., Acker, J. D., & Raz, N. (2009). Age-related differences in regional brain volumes: A comparison of optimized voxel-based morphometry to manual volumetry. Neurobiology of Aging, 30, 1657–1676.
Klein, A., Andersson, J., Ardekani, B. A., Ashburner, J., Avants, B., Chiang, M. C., Christensen, G. E., Collins, D. L., Gee, J., Hellier, P., Song, J. H., Jenkinson, M., Lepage, C., Rueckert, D., Thompson, P., Vercauteren, T., Woods, R. P., Mann, J. J., & Parsey, R. V. (2009). Evaluation of 14 nonlinear deformation algorithms applied to human brain MRI registration. NeuroImage, 46, 786–802.
Kleinbaum, D. G., Kupper, L. L., Nizam, A., & Muller, K. E. (2007). Applied regression analysis and other multivariable methods. Belmont: Duxbury Press.
Lemieux, L., Jagoe, R., Fish, D. R., Kitchen, N. D., & Thomas, D. G. T. (1994). A patient-to-computed-tomography image registration method based on digitally reconstructed radiographs. Medical Physics, 21, 1749–1760.
Maes, F., Collignon, A., Vandermeulen, D., Marchal, G., & Suetens, P. (1997). Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 16, 187–198.
Martino, M. E., De Villoria, J. G., Lacalle-Aurioles, M., Olazaran, J., Cruz, I., Navarro, E., Garcia-Vazquez, V., Carreras, J. L., & Desco, M. (2013). Comparison of different methods of spatial normalization of FDG-PET brain images in the voxel-wise analysis of MCI patients and controls. Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 27, 600–609.
Mcdonald, C. R., Mcevoy, L. K., Gharapetian, L., Fennema-Notestine, C., Hagler, D. J., Holland, D., Koyama, A., Brewer, J. B., Dale, A. M., & Initi, A. S. D. N. (2009). Regional rates of neocortical atrophy from normal aging to early Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 73, 457–465.
Pallant, J. (2013). SPSS survival manual: A step by step guide to data analysis using IBM Spss. Allen & Unwin.
Peelle, J. E., Cusack, R., & Henson, R. N. A. (2012). Adjusting for global effects in voxel-based morphometry: Gray matter decline in normal aging. NeuroImage, 60, 1503–1516.
Petersen, R. C., Aisen, P. S., Beckett, L. A., Donohue, M. C., Gamst, A. C., Harvey, D. J., Jack Jr., C. R., Jagust, W. J., Shaw, L. M., Toga, A. W., Trojanowski, J. Q., & Weiner, M. W. (2010). Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI): Clinical characterization. Neurology, 74, 201–209.
Pohl, K. M., Fisher, J., Levitt, J. J., Shenton, M. E., Kikinis, R., Grimson, W. E. L., & Wells, W. M. (2005). A unifying approach to registration, segmentation, and intensity correction. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 8(Pt 1), 310–318.
Pu, F., Xu, L. Q., Li, D. Y., Fan, Y. B., Niu, H. J., & Li, S. Y. (2013). Comparison of two nonlinear registration techniques to investigate brain atrophy patterns in normal aging. Journal of Neuroradiology, 40, 326–334.
Salonen, O., Autti, T., Raininko, R., Ylikoski, A., & Erkinjuntti, T. (1997). MRI of the brain in neurologically healthy middle-aged and elderly individuals. Neuroradiology, 39, 537–545.
Shattuck, D. W., Sandor-Leahy, S. R., Schaper, K. A., Rottenberg, D. A., & Leahy, R. M. (2001). Magnetic resonance image tissue classification using a partial volume model. NeuroImage, 13, 856–876.
Van Leemput, K., Maes, F., Vandermeulen, D., & Suetens, P. (1999a). Automated model-based bias field correction of MR images of the brain. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18, 885–896.
Van Leemput, K., Maes, F., Vandermeulen, D., & Suetens, P. (1999b). Automated model-based tissue classification of MR images of the brain. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18, 897–908.
Weiner, M. W., Veitch, D. P., Aisen, P. S., Beckett, L. A., Cairns, N. J., Green, R. C., Harvey, D., Jack, C. R., Jagust, W., Liu, E., Morris, J. C., Petersen, R. C., Saykin, A. J., Schmidt, M. E., Shaw, L., Siuciak, J. A., Soares, H., Toga, A. W., Trojanowski, J. Q., & Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging, I. (2012). The Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative: A review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement, 8, S1–68.
Wells 3rd, W. M., Viola, P., Atsumi, H., Nakajima, S., & Kikinis, R. (1996). Multi-modal volume registration by maximization of mutual information. Medical Image Analysis, 1, 35–51.
Whitwell, J. L., Shiung, M. M., Przybelski, S. A., Weigand, S. D., Knopman, D. S., Boeve, B. F., Petersen, R. C., & Jack, C. R. (2008). MRI patterns of atrophy associated with progression to AD in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neurology, 70, 512–520.
Wilke, M., Schmithorst, V. J., & Holland, S. K. (2002). Assessment of spatial normalization of whole-brain magnetic resonance images in children. Human Brain Mapping, 17, 48–60.
Acknowledgements
Data collection and sharing for this project was funded by the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (National Institutes of Health Grant U01 AG024904) and DOD ADNI (Department of Defense award number W81XWH-12-2-0012). ADNI is funded by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, and through generous contributions from the following: AbbVie, Alzheimer’s Association; Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation; Araclon Biotech; BioClinica, Inc.; Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; CereSpir, Inc.; Cogstate; Eisai Inc.; Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Eli Lilly and Company; EuroImmun; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. and its affiliated company Genentech, Inc.; Fujirebio; GE Healthcare; IXICO Ltd.; Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research & Development, LLC.; Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development LLC.; Lumosity; Lundbeck; Merck & Co., Inc.; Meso Scale Diagnostics, LLC.; NeuroRx Research; Neurotrack Technologies; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; Pfizer Inc.; Piramal Imaging; Servier; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; and Transition Therapeutics. The Canadian Institutes of Health Research is providing funds to support ADNI clinical sites in Canada. Private sector contributions are facilitated by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (www.fnih.org). The grantee organization is the Northern California Institute for Research and Education, and the study is coordinated by the Alzheimer’s Therapeutic Research Institute at the University of Southern California. ADNI data are disseminated by the Laboratory for Neuro Imaging at the University of Southern California. Author MG received funding from the FWO and European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No: 665,501.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) is a Group/Institutional Author
Data used in preparation of this article were obtained from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database (adni.loni.usc.edu). As such, the investigators within the ADNI contributed to the design and implementation of ADNI and/or provided data but did not participate in analysis or writing of this report. A complete listing of ADNI investigators can be found at: http://adni.loni.usc.edu/wpcontent/uploads/how_to_apply/ADNI_Acknowledgement_List.pdf
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 831 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganzetti, M., Liu, Q., Mantini, D. et al. A Spatial Registration Toolbox for Structural MR Imaging of the Aging Brain. Neuroinform 16, 167–179 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9355-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9355-3