Abstract
Purpose
Osteoporosis (OP) is a common disease among adults aged >50 years. At present, the main approach to screen or to diagnosis OP is mainly via bone mineral density (BMD) testing, which might not be optimal for OP screening. This study aimed to develop and validate a convenient and effective prediction model for screening OP based on the demographic information, medical history, and lifestyle habits in the elderly in the United States.
Methods
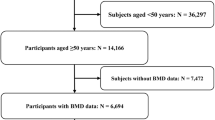
All data were collected from the National Health and Nutrition Survey database. Participants aged ≥50 years with complete BMD data were included in this study. Twelve candidate predictors were initially selected to develop the prediction model. Final predictors screening and model development were based on multivariate logistic regression. Model discrimination (C statistic) and calibration (Brier scores) were calculated to evaluate the performance of the model. Internal validation was performed using the bootstrap resampling technique, and external validation was based on the validation cohort.
Results
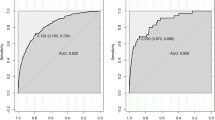
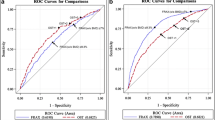
The screening tool was developed with individual patient data from 1941 patients and validated with data from 1947 patients after the development of the model. Seven predictors (patient age, sex, race, body mass index, physical activity, sleep duration, and history of fracture) were included in the final prediction model, and the final model had a C statistic of 0.849 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.820–0.878] and Brier scores of 0.062 [95% CI: 0.054–0.070] on the development cohort. For the validation of the developed model, the results showed a C statistic >0.800 and Brier scores <0.070, irrespective of internal validation or external validation.
Conclusions
A novel screening tool for OP in the elderly, which has excellent discrimination and useful calibration, has been developed and externally validated. Considering its simplicity, generalizability, and accuracy, this tool has the potential to become a practical mean for the elderly to screen OP.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets obtained and analysed during the current study are available on the NHANES database [https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm].
References
J.E. Compston, M.R. McClung, W.D. Leslie, Osteoporosis. Lancet 393, 364–376 (2019)
IOF. About Osteoporosis. https://www.osteoporosis.foundation/patients/about-osteoporosis (2021) Accessed July 1 2021
J.J. Chamberlain, A.S. Rhinehart, C.F. Shaefer Jr, A. Neuman, Diagnosis and management of diabetes: synopsis of the 2016 American diabetes association standards of medical care in diabetes. Ann. Intern Med 164, 542–552 (2016)
P.K. Whelton, R.M. Carey, W.S. Aronow, D.E. Casey Jr, K.J. Collins, C. Dennison Himmelfarb, S.M. DePalma, S. Gidding, K.A. Jamerson, D.W. Jones et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension 71, e13–e115 (2018)
B.N.R. Jaja, G. Saposnik, H.F. Lingsma, E. Macdonald, K.E. Thorpe, M. Mamdani, E.W. Steyerberg, A. Molyneux, A.L.O. Manoel, B. Schatlo et al. Development and validation of outcome prediction models for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: the SAHIT multinational cohort study. Bmj 360, j5745 (2018)
D. Vistisen, G.S. Andersen, C.S. Hansen, A. Hulman, J.E. Henriksen, H. Bech-Nielsen, M.E. Jørgensen, Prediction of first cardiovascular disease event in Type 1 diabetes mellitus: the steno Type 1 risk engine. Circulation 133, 1058–1066 (2016)
J. Hippisley-Cox, C. Coupland, Predicting risk of osteoporotic fracture in men and women in England and Wales: prospective derivation and validation of QFractureScores. Bmj 339, b4229 (2009)
J.A. Kanis, A. Oden, O. Johnell, H. Johansson, C. De Laet, J. Brown, P. Burckhardt, C. Cooper, C. Christiansen, S. Cummings et al. The use of clinical risk factors enhances the performance of BMD in the prediction of hip and osteoporotic fractures in men and women. Osteoporos. Int 18, 1033–1046 (2007)
K.H. Rubin, S. Möller, T. Holmberg, M. Bliddal, J. Søndergaard, B. Abrahamsen, A. New, Fracture risk assessment tool (FREM) based on public health registries. J. Bone Min. Res 33, 1967–1979 (2018)
Y. Wang, L. Wang, Y. Sun, M. Wu, Y. Ma, L. Yang, C. Meng, L. Zhong, M.A. Hossain, B. Peng, Prediction model for the risk of osteoporosis incorporating factors of disease history and living habits in physical examination of population in Chongqing, Southwest China: based on artificial neural network. BMC Public Health 21, 991 (2021)
L.T. Ho-Pham, M.C. Doan, L.H. Van, T.V. Nguyen, Development of a model for identification of individuals with high risk of osteoporosis. Arch. Osteoporos. 15, 111 (2020)
L.K. Koh, W.B. Sedrine, T.P. Torralba, A. Kung, S. Fujiwara, S.P. Chan, Q.R. Huang, R. Rajatanavin, K.S. Tsai, H.M. Park, J.Y. Reginster, A simple tool to identify asian women at increased risk of osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int 12, 699–705 (2001)
Z. Ma, Y. Yang, J. Lin, X. Zhang, Q. Meng, B. Wang, Q. Fei, BFH-OST, a new predictive screening tool for identifying osteoporosis in postmenopausal Han Chinese women. Clin. Inter. Aging 11, 1051–1059 (2016)
S. Moradi, S. Shab-Bidar, S. Alizadeh, K. Djafarian, Association between sleep duration and osteoporosis risk in middle-aged and elderly women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Metabolism 69, 199–206 (2017)
J. Xu, G. Lombardi, W. Jiao, G. Banfi, Effects of exercise on bone status in female subjects, from young girls to postmenopausal women: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Sports Med 46, 1165–1182 (2016)
R.S. Hardy, H. Zhou, M.J. Seibel, M.S. Cooper, Glucocorticoids and bone: consequences of endogenous and exogenous excess and replacement therapy. Endocr. Rev. 39, 519–548 (2018)
CDC. National Health and Nutrition Survey. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about_nhanes.htm (2021) Accessed July 1 2021
CDC. NCHS Research Ethics Review Board (ERB) Approval. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/irba98.htm (2021) Accessed July 1 2021
CDC. NHANES 2013–2014. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/ContinuousNhanes/Default.aspx?BeginYear=2013 (2021) Accessed July 1 2021
CDC. NHANES 2017–2018. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/continuousnhanes/default.aspx?BeginYear=2017 (2021) Accessed July 1 2021
D. Moher, A. Liberati, J. Tetzlaff, D.G. Altman, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Bmj 339, b2535 (2009)
P. Peduzzi, J. Concato, E. Kemper, T.R. Holford, A.R. Feinstein, A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 49, 1373–1379 (1996)
B.H. Huang, M.J. Duncan, P.A. Cistulli, N. Nassar, M. Hamer, E. Stamatakis, Sleep and physical activity in relation to all-cause, cardiovascular disease and cancer mortality risk. Br J Sports Med. (2021). Online ahead of print
WHO. Physical activity. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity (2021) Accessed July 1 2021
CDC. Appendix 1. Suggested MET Scores. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/PAQ_H.htm#Appendix_1.__Suggested_MET_Scores (2021) Accessed July 1 2021
M. Hirshkowitz, K. Whiton, S.M. Albert, C. Alessi, O. Bruni, L. DonCarlos, N. Hazen, J. Herman, E.S. Katz, L. Kheirandish-Gozal et al. National Sleep Foundation’s sleep time duration recommendations: methodology and results summary. Sleep. Health 1, 40–43 (2015)
CDC. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) Scan. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2013-2014/manuals/2013_Body_Composition_DXA.pdf (2021) Accessed July 1 2021
A.C. Looker, E.S. Orwoll, C.C. Johnston Jr, R.L. Lindsay, H.W. Wahner, W.L. Dunn, M.S. Calvo, T.B. Harris, S.P. Heyse, Prevalence of low femoral bone density in older U.S. adults from NHANES III. J. Bone Min. Res 12, 1761–1768 (1997)
R.R. Seethala, P.C. Hou, I.P. Aisiku, G. Frendl, P.K. Park, M.E. Mikkelsen, S.Y. Chang, O. Gajic, J. Sevransky, Early risk factors and the role of fluid administration in developing acute respiratory distress syndrome in septic patients. Ann. Intensive Care 7, 11–11 (2017)
U.A. Tahir, G. Doros, J.S. Kim, L.H. Connors, D.C. Seldin, F. Sam, Predictors of mortality in light chain cardiac amyloidosis with heart failure. Sci. Rep. 9, 8552–8552 (2019)
A. Chiu, M. Ayub, C. Dive, G. Brady, C.J. Miller, twoddpcr: an R/Bioconductor package and Shiny app for Droplet Digital PCR analysis. Bioinformatics 33, 2743–2745 (2017)
Z. Cheraghi, A. Doosti-Irani, A. Almasi-Hashiani, V. Baigi, N. Mansournia, M. Etminan, M.A. Mansournia, The effect of alcohol on osteoporosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 197, 197–202 (2019)
K. Zhu, R.L. Prince, Lifestyle and osteoporosis. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 13, 52–59 (2015)
K.T. Borer, Physical activity in the prevention and amelioration of osteoporosis in women: interaction of mechanical, hormonal and dietary factors. Sports Med. 35, 779–830 (2005)
M.B. Pinheiro, J. Oliveira, A. Bauman, N. Fairhall, W. Kwok, C. Sherrington, Evidence on physical activity and osteoporosis prevention for people aged 65+ years: a systematic review to inform the WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Int J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 17, 150 (2020)
P. Chotiyarnwong, E.V. McCloskey, Pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and options for treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 16, 437–447 (2020)
L. Buckley, M.B. Humphrey, Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med 379, 2547–2556 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81874017, 81960403 and 82060405); Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China (20JR5RA320); Cuiying Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Lanzhou University Second Hospital (CY2017-ZD02); “Innovation Star” project for Excellent Graduate Students of the Education Department of Gansu Province (2021CXZX-143). At the same time, we would like to express our gratitude to Editage (https://www.editage.cn/) for the language editing services provided.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81874017, 81960403 and 82060405); Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China (20JR5RA320); Cuiying Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Lanzhou University Second Hospital (CY2017-ZD02); Innovation Star Project for Excellent Graduate Students of the Education Department of Gansu Province (2021CXZX-143).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.T. and Z.L. contributed equally to this work. Y.T.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing. Z.L.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, formal analysis, writing—review & editing. S.W.: methodology, investigation, writing—review & editing. Q.Y.: methodology, investigation, resources. Y.X.: writing—review & editing, funding acquisition. B.G.: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review & editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All analyses were based on data of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The study was approved by the ethics review board of the National Center for Health Statistics. The National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board protocol numbers are Continuation of Protocol #2011-17 (NHANES 2013–2014 and 2017–2018), Protocol #2018-01 (NHANES 2017–2018), respectively. The detailed information located on the NHANES website.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from each participant before their inclusion on the NHANES database. Detailed information on the ethics application and written informed consent are provided on the NHANES website.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Yuchen Tang, Zhongcheng Liu
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, S. et al. Development and validation of a novel screening tool for osteoporosis in older US adults: The NHANES cross-sectional study. Endocrine 76, 446–456 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-022-03001-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-022-03001-2