Abstract
Introduction
Children with type 1 diabetes (T1D) are at the same risk of developing metabolic syndrome (MS) as the general population. Several environmental factors such as lifestyle, exogenous insulin therapy (over-insulinization) and genetic/familial factors are thought to underlie the phenotype of 'double diabetes' (co-existence of MS components in patients with T1D).
Objectives
To determine the prevalence of overweight/obesity and MS and to identify its predictors in Indian children, adolescents and young adults with T1D.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 355 children and youth aged 6–23 years with T1D. Demographic data were obtained from patients using questionnaires. Anthropometry, blood pressure, sexual maturity rating, biochemical measurements and body composition measurements were performed using standard protocols. Insulin resistance (IR) was calculated using estimated glucose disposal rate (eGDR) and MS was diagnosed using the international diabetes federation (IDF) consensus definition 2017.
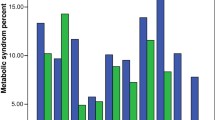
Results
The prevalence of overweight/obesity and MS in our study was 15.5% and 4.5%, respectively. Abnormal HDL-cholesterol was the most common component of MS (55.6%) among children with T1D. Age, gender, body mass index (BMI) and eGDR were identified as significant predictors of the likelihood of MS.
Conclusions
We found a similar prevalence of MS in children with T1D as compared to other healthy children, which emphasises the need for monitoring of eGDR to determine IR in these children.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors agree to deposit data that support the findings of their research in a public repository.
References
L.M. Thorn, C. Forsblom, J. Fagerudd, M.C. Thomas, K. Pettersson-Fernholm, M. Saraheimo, J. Wadén, M. Rönnback, M. Rosengård-Bärlund, C.G. Af Björkesten, M.R. Taskinen,, Metabolic syndrome in type 1 diabetes: association with diabetic nephropathy and glycemic control (the FinnDiane study). Diabetes Care 28(8), 2019–2024 (2005)
Ö.Y. Köken, C. Kara, G.C. Yılmaz, H.M. Aydın, Prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome in children with type 1 diabetes: a comparative assessment based on criteria established by the international diabetes federation, world health organisation and national cholesterol education program. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 12(1), 55 (2020)
I.M. Libman, Μ Pietropaolo, S.A. Arslanian, R.E. LaPorte, D.J. Becker, Changing prevalence of overweight children and adolescents at onset of insulin-treated diabetes. Diabetes Care 26, 2871–2875 (2003)
E.S. Kilpatrick, A.S. Rigby, S.L. Atkin, Insulin resistance, the metabolic syndrome, and complication risk in type 1 diabetes:“double diabetes” in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care 30(3), 707–12 (2007)
E.P. Atance, M.J. Herrera, P.G. Muiña, R.R. Cano, A.L. Martín, J.G. Muiña, Estimated glucose disposal rate in patients under 18 years of age with type 1 diabetes mellitus and overweight or obesity. Endocrinol. Nutr. 60(7), 379–85. (2013)
A. Garg, Regional adiposity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89(9), 4206–10 (2004)
G. Priya, S. Kalra, A review of insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes: is there a place for adjunctive metformin? Diabetes Ther. 9(1), 349–61 (2018)
A.B. Goldfine, C. Bouche, R.A. Parker, C. Kim, A. Kerivan, J.S. Soeldner, B.C. Martin, J.H. Warram, C.R. Kahn, Insulin resistance is a poor predictor of type 2 diabetes in individuals with no family history of disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100(5), 2724–9 (2003)
P. Pozzilli, G. Chiara, C. Sonia, R. Buzzetti et al. Obesity, autoimmunity, and double diabetes in youth. Diab Care 34(Supplement 2), S166–70 (2011)
The IDF consensus definition of the METABOLIC SYNDROME in children and adolescents. (2007) https://www.idf.org/e-library/consensus-statements/61-idf-consensus-definition-of-metabolic-syndrome-in-children-and-adolescents.html
N. Barbosa, C.E. Sanchez, J.A. Vera, W. Perez, J.C. Thalabard, M. Rieu, A physical activity questionnaire: reproducibility and validity. J. Sports Sci. Med. 6(4), 505 (2007)
V.V. Khadilkar, A.V. Khadilkar, Revised Indian academy of pediatrics 2015 growth charts for height, weight and body mass index for 5–18-year-old Indian children. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 19(4), 470–476 (2015)
W.A. Marshall, J.M. Tanner, in Postnatal Growth Neurobiology (Springer, Boston,1986), pp. 171–209
G.R. Warnick, R.H. Knopp, V. Fitzpatrick, L. Branson, Estimating low-density lipoprotein cholesterol by the Friedewald equation is adequate for classifying subjects on the basis of nationally recommended cutpoints. Clin. Chem. 36(1), 15–19 (1990)
U.G. Kyle, I. Bosaeus, A.D. De Lorenzo et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis—Part II: utilization in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 23(6), 1430–1453 (2004)
A.V. Khadilkar, N.J. Sanwalka, S.A. Chiplonkar, V.V. Khadilkar, D. Pandit, Body fat reference percentiles on healthy affluent Indian children and adolescents to screen for adiposity. Int J. Obes. 37, 947–53 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.19
R. Kahn, J. Buse, E. Ferrannini, M. Stern, The metabolic syndrome: time for a critical appraisal: joint statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 28, 2289–2304 (2005)
D.R. Ragland, Dichotomizing continuous outcome variables: dependence of the magnitude of association and statistical power on the cutpoint. Epidemiology. 3, 434–440 (1992)
V.V. Khadilkar, A.V. Khadilkar, A.B. Borade, S.A. Chiplonkar, Body mass index cut-offs for screening for childhood overweight and obesity in Indian children. Indian Pediatr. 49(1), 29–34 (2012)
FOR EP, CHILDREN RR, Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents: summary report. Pediatrics 128(Suppl 5), S213 (2011)
D.B. Petitti, G.J. Klingensmith, R.A. Bell, J.S. Andrews, D. Dabelea, G. Imperatore, S. Marcovina, C. Pihoker, D. Standiford, B. Waitzfelder, E. Mayer-Davis,, Glycemic control in youth with diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in Youth Study. J. Pediatr. 155(5), 668–72 (2009)
K.V. Williams, J.R. Erbey, D. Becker, S. Arslanian, T.J. Orchard, Can clinical factors estimate insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes? Diabetes 49, 626–632 (2000)
T. Reinehr, R.W. Holl, C.L. Roth et al. Insulin resistance in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: relation to obesity. Pediatr. Diabetes 6, 5–12 (2005)
K.C. Donaghue, M.L. Marcovecchio, R.P. Wadwa et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Microvascular and macrovascular complications in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes 19(27), 262–274 (2018)
S.M. Grundy, J.I. Cleeman, S.R. Daniels, K.A. Donato, R.H. Eckel, B.A. Franklin, D.J. Gordon, R.M. Krauss, P.J. Savage, S.C. Smith Jr, J.A. Spertus, F. Costa, American Heart Association; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 112, 2735–2752 (2005)
H. Ranjani, T.S. Mehreen, R. Pradeepa, R.M. Anjana, R. Garg, K. Anand, V. Mohan, Epidemiology of childhood overweight & obesity in India: a systematic review. Indian J. Med. Res. 143(2), 160–174 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-5916.180203
L.L. Liu, J.M. Lawrence, C. Davis, A.D. Liese, D.J. Pettitt, C. Pihoker, D. Dabelea, R. Hamman, B. Waitzfelder, H.S. Kahn; SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group, Prevalence of overweight and obesity in youth with diabetes in USA: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study. Pediatr. Diabetes. 11(1), 4–11 (2010)
A. Billow, R.M. Anjana, M. Ngai, A. Amutha, R. Pradeepa, S. Jebarani, R. Unnikrishnan, E. Michael, V. Mohan, Prevalence and clinical profile of metabolic syndrome among type 1 diabetes mellitus subjects in southern India. J. Diabetes Complications. 29(5), 659–64 (2015)
R. Singh, A. Bhansali, R. Sialy, A. Aggarwal,, Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adolescents from a north Indian population. Diabet. Med. 24(2), 195–9 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02066.x
R. Belete, Z. Ataro, A. Abdu, M. Sheleme, Global prevalence of metabolic syndrome among subjects with type I diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 13(1), 1–3 (2021)
K.O. Schwab, J. Doerfer, W. Hecker, J. Grulich-Henn, D. Wiemann, O. Kordonouri, P. Beyer, R.W. Holl, Spectrum and prevalence of atherogenic risk factors in 27,358 children, adolescents, and young adults with type 1 diabetes: cross-sectional data from the German diabetes documentation and quality management system (DPV). Diabetes Care 29(2), 218–25 (2006)
F. Saki, Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in children with type 1 diabetes in South of Iran. J. Comprehensive Pediatr. 7(3), (2016)
M. van Vliet, J.C. Van der Heyden, M. Diamant, I.A. Von Rosenstiel, R.K. Schindhelm, H.J. Aanstoot, H.J. Veeze, Overweight is highly prevalent in children with type 1 diabetes and associates with cardiometabolic risk. J. Pediatr. 156(6), 923–9 (2010)
T. Bulut, F. Demirel, A. Metin, The prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated factors in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 30(2), 181–7 (2017)
T.K. Homma, C.M. Endo, T. Saruhashi, A.P. Mori, R.M. Noronha, O. Monte, L.E. Calliari, Dyslipidemia in young subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 59, 215–9 (2015)
W. Łuczyński, A. Szypowska, B. Głowińska-Olszewska, A. Bossowski, Overweight, obesity and features of metabolic syndrome in children with diabetes treated with insulin pump therapy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 170(7), 891–8 (2011)
S.H. Beigh, S. Jain, Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and gender differences. Bioinformation 8(13), 613–616 (2012). https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630008613
L. Huo, L. Ji, W. Deng, J.E. Shaw, P. Zhang, F. Zhao, H.C. McGuire, K. Kissimova-Skarbek, D. Whiting, Age distribution and metabolic disorders in people with Type 1 diabetes in Beijing and Shantou, China: a cross-sectional study. Diabet. Med 35(6), 721–728 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.13616
N.G. Boule et al. Effects of exercise on glycaemic control and body mass in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. JAMA. 286, 1218–1227 (2011)
B.K. Mishra, P. Shukla, M. Aslam, A.A. Siddiqui, S.V. Madhu, Prevalence of double diabetes in youth onset diabetes subjects from east Delhi and neighboring NCR region. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 12(6), 839–842 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2017.08.016
N.E. Hassan, S.A. El-Masry, W.A. Fouad, L. Sherif, A. Elwakkad, M. Anwar, S.T. Zaki, Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among obese school students. e-SPEN Eur. e-J. Clin. Nutr. Metab. 6(6), e248–52 (2011)
J.J. Chillaron, A. Goday, J.A. Flores-Le-Roux, D. Benaiges, M.J. Carrera, J. Puig, J.F. Cano-Perez, J. Pedro-Botet, Estimated glucose disposal rate in assessment of the metabolic syndrome and microvascular complications in subjects with type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94(9), 3530–4 (2009)
G. Valerio, D. Iafusco, S. Zucchini, C. Maffeis, Abdominal adiposity and cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 97(1), 99–104 (2012)
P.I. Guidone, P. Di Filippo, S. Tumini,, Insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes: evidence and new insights. Curr. Res. Diabetes Obes. J. 6(3), 36–9 (2018)
H.M. Soliman, Y.O. Mosaad, A. Ibrahim, The prevalence and the clinical profile of metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res Rev. 13, 1723–6 (2019)
M.L. Bîcu, D. Bîcu, S. Gârgavu, M. Sandu, M.I. Vladu, D. Clenciu, E. Moța, M. Moța, Estimated glucose disposal rate (egdr)–a marker for the assessment of insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Rom. J. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. Dis. 23(2), 177–82. (2016)
E.J. Epstein, J.L. Osman, H.W. Cohen, S.N. Rajpathak, O. Lewis, J.P. Crandall,, Use of the estimated glucose disposal rate as a measure of insulin resistance in an urban multiethnic population with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 36(8), 2280e5 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc12-1693
Author contributions
All the listed authors played a role in the clinical management, planning, execution, analysis, writing of the manuscript and that they all agree and accept responsibility for the contents of the manuscript submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The local Institutional Review Board has approved the proposal.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study and Informed consent was obtained from the parents.
Consent for publication
The participants have consented to the submission of the article to the journal.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oza, C., Khadilkar, V., Karguppikar, M. et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and predictors of metabolic risk in Indian children, adolescents and youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 75, 794–803 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02924-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02924-6