Abstract
Purpose
To develop a nomogram for predicting 5-year incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in Chinese adults.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort study from a prospectively collected database. We included a total 32,766 adults free of T2D at baseline with a median follow-up of 3 years. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were applied to identify independent predictors. A nomogram was constructed to predict 5-year incident rate of T2D based on the multivariate analysis results. Harrell's C-indexes and calibration plots were used to evaluate the accuracy of the nomogram in both internal and external validations.
Results
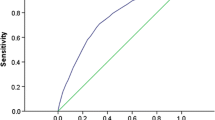
The overall prevalence of T2D was 2.1%. Participants were randomly divided into a training set (n = 21,844) and a validation set (n = 10,922). After multivariate analysis in the training set, age, sex, BMI, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking status, and family history were found as risk predictors and integrated into the nomogram. Harrell's C-indexes were 0.815 (95% CI: 0.797–0.834) and 0.779 (95% CI: 0.747–0.811) in the training and validation sets, respectively. The calibration plots demonstrated good agreement between the estimated probability and the actual observation.
Conclusion
Our nomogram could be a simple and reliable tool for predicting 5-year risk of developing T2D in high-risk Chinese. Through the model, early identifying high-risk individuals is helpful for timely intervention to reduce the incidence of T2D.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.H. Cho, J.E. Shaw, S. Karuranga, Y. Huang, J.D. da Rocha Fernandes, A.W. Ohlrogge, B. Malanda, IDF diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 138, 271–281 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023
H. F. Wolde, A. Atsedeweyen, A. Jember, T. Awoke, M. Mequanent, A. T. Tsegaye, S. Alemu, Predictors of vascular complications among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients at University of Gondar Referral Hospital: a retrospective follow-up study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 18, 52 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-018-0280-0
S. Eid, K.M. Sas, S.F. Abcouwer, E.L. Feldman, T.W. Gardner, S. Pennathur, P.E. Fort, New insights into the mechanisms of diabetic complications: role of lipids and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia 62, 1539–1549 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-4959-1
L. Fuso, D. Pitocco, R. Antonelli-Incalzi, Diabetic lung, an underrated complication from restrictive functional pattern to pulmonary hypertension. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. e3159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3159
American Diabetes Association, Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 37(Suppl 1), S81–S90 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-S081
G. T. Dong, L. L. Qu, X. F. Gong, B. Pang, W. T. Yan, J. P. Wei, Effect of social factors and the natural environment on the etiology and pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Endocrinol. 8749291 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8749291
M.S. Udler, Type 2 diabetes: multiple genes, multiple diseases. Curr. Diab. Rep. 19, 55 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-019-1169-7
J. S. Gold, J. Kong, T. Wang, S. Shen, Z. Zhang, W. Wang, A nomogram predicting the prognosis of young adult patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma: a population-based analysis. PLoS ONE 14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219654
L. Mao, X. H. Zhang, Y. H. Hu, X. P. Wang, Y. P. Song, J. He, W. W. Yang, J. L. Ma, Y. Z. Yan, L. T. Mu, J. Y. Zhang, K. Wang, H. Guo, R. L. Ma, S. X. Guo, Nomogram based on cytokines for cardiovascular diseases in Xinjiang Kazakhs. Mediat. Inflamm. 4756295, (2019). https://doi.ord/10.1155/2019/4756295
Y. Chen, X. Zhang, J. Yuan, B. Cai, X. Wang, X. Wu, Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, T. Yin, X. Zhu, Y. Gu, S. Cui, Z. Lu, X. Li, Association of body mass index and age with incident diabetes in Chinese adults: a population-based cohort study. Dryad Digital Repository, (2018)
Y. Chen, X.P. Zhang, J. Yuan, B. Cai, X.L. Wang, X.L. Wu, Y.H. Zhang, X.Y. Zhang, T. Yin, X.H. Zhu, Y.J. Gu, S.W. Cui, Z.Q. Lu, X.Y. Li, Association of body mass index and age with incident diabetes in Chinese adults: a population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 8, e021768 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021768
R.L. Camp, M. Dolled-Filhart, D.L. Rimm, X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 7252–7259 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0713
WHO Expert Consultation, Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 363, 157–163 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15268-3
F.E. Harrell Jr., K.L. Lee, D.B. Mark, Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat. Med 15, 361–387 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19960229)15:43.0.CO;2-4
M.J. Pencina, R.B. D’Agostino, Overall C as a measure of discrimination in survival analysis: model specific population value and confidence interval estimation. Stat. Med. 23, 2109–2123 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1802
M.B. Schulze, K. Hoffmann, H. Boeing, J. Linseisen, S. Rohrmann, M. Mohlig, A.F. Pfeiffer, J. Spranger, C. Thamer, H.U. Haring, A. Fritsche, H.G. Joost, An accurate risk score based on anthropometric, dietary, and lifestyle factors to predict the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30, 510–515 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc06-2089
H.S. Kahn, Y.J. Cheng, T.J. Thompson, G. Imperatore, E.W. Gregg, Two risk-scoring systems for predicting incident diabetes mellitus in U.S. adults age 45 to 64 years. Ann. Intern. Med. 150, 741–751 (2009). https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-150-11-200906020-00002
H. Bang, A.M. Edwards, A.S. Bomback, C.M. Ballantyne, D. Brillon, M.A. Callahan, S.M. Teutsch, A.I. Mushlin, L.M. Kern, Development and validation of a patient self-assessment score for diabetes risk. Ann. Intern. Med. 151, 775–783 (2009). https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-11-200912010-00005
W.G. Gao, Y.H. Dong, Z.C. Pang, H.R. Nan, S.J. Wang, J. Ren, L. Zhang, J. Tuomilehto, Q. Qiao, A simple Chinese risk score for undiagnosed diabetes. Diabet. Med. 27, 274–281 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.02943.x
C. Pongchaiyakul, P. Kotruchin, E. Wanothayaroj, T.V. Nguyen, An innovative prognostic model for predicting diabetes risk in the Thai population. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 94, 193–198 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2011.07.019
S.M. Chung, J.C. Park, J.S. Moon, J.Y. Lee, Novel nomogram for screening the risk of developing diabetes in a Korean population. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 142, 286–293 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.05.036
C. Glumer, D. Vistisen, K. Borch-Johnsen, S. Colagiuri, DETECT-2 Collaboration, Risk scores for type 2 diabetes can be applied in some populations but not all. Diabetes Care 29, 410–414 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-0945
M.C. Coordt, R.C. Ruhe, R.B. McDonald, Aging and insulin secretion. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 209, 213–222 (1995). https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-209-43879b
T. Dayeh, P. Volkov, S. Salo, E. Hall, E. Nilsson, A.H. Olsson, C.L. Kirkpatrick, C.B. Wollheim, L. Eliasson, T. Ronn, K. Bacos, C. Ling, Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of human pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic donors identifies candidate genes that influence insulin secretion. PLoS Genet. 10, e1004160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004160
K. Bacos, L. Gillberg, P. Volkov, A.H. Olsson, T. Hansen, O. Pedersen, A.P. Gjesing, H. Eiberg, T. Tuomi, P. Almgren, L. Groop, L. Eliasson, A. Vaag, T. Dayeh, C. Ling, Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes. Nat. Commun. 7, 11089 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11089
L.L. Lipscombe, J.E. Hux, Trends in diabetes prevalence, incidence, and mortality in Ontario, Canada 1995–2005: a population-based study. Lancet 369, 750–756 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60361-4
Y.J. Choi, H.C. Kim, H.M. Kim, S.W. Park, J. Kim, D.J. Kim, Prevalence and management of diabetes in Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998–2005. Diabetes Care 32, 2016–2020 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-2228
E. Hall, P. Volkov, T. Dayeh, J. L. S. Esguerra, S. Salo, L. Eliasson, T. Ronn, K. Bacos, C. Ling, Sex differences in the genome-wide DNA methylation pattern and impact on gene expression, microRNA levels and insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets. Genome Biol. 15, 522 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0522-z
E.B. Geer, W. Shen, Gender differences in insulin resistance, body composition, and energy balance. Gend. Med. 6(Suppl 1), 60–75 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genm.2009.02.002
B.M. Popkin, L.S. Adair, S.W. Ng, Global nutrition transition and the pandemic of obesity in developing countries. Nutr. Rev. 70, 3–21 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00456.x
R. Barazzoni, G. Gortan Cappellari, M. Ragni, E. Nisoli, Insulin resistance in obesity: an overview of fundamental alterations. Eat. Weight Disord. 23, 149–157 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0481-6
J. Ye, Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front Med. 7, 14–24 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-013-0262-6
J.R. Sowers, Insulin resistance and hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 286, H1597–H1602 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00026.2004
E.J. Rhee, K. Han, S.H. Ko, K.S. Ko, W.Y. Lee, Increased risk for diabetes development in subjects with large variation in total cholesterol levels in 2,827,950 Koreans: a nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 12, e0176615 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176615
A. Tirosh, I. Shai, R. Bitzur, I. Kochba, D. Tekes-Manova, E. Israeli, T. Shochat, A. Rudich, Changes in triglyceride levels over time and risk of type 2 diabetes in young men. Diabetes Care 31, 2032–2037 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-0825
S. H. Lee, H. S. Kim, Y. M. Park, H. S. Kwon, K. H. Yoon, K. Han, M. K. Kim, HDL-cholesterol, its variability and the risk of diabetes: a nationwide population-based study. J Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2019-01080
M. Janghorbani, N. Soltanian, M. Amini, A. Aminorroaya, Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of type 2 diabetes: the Isfahan diabetes prevention study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 12, 715–719 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2018.04.019
M. Seghieri, D. Trico, A. Natali, The impact of triglycerides on glucose tolerance: lipotoxicity revisited. Diabetes Metab. 43, 314–322 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2017.04.010
J.K. Kruit, L.R. Brunham, C.B. Verchere, M.R. Hayden, HDL and LDL cholesterol significantly influence beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Lipido. 21, 178–185 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1097/MOL.0b013e328339387b
B.G. Drew, K.A. Rye, S.J. Duffy, P. Barter, B.A. Kingwell, The emerging role of HDL in glucose metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 8, 237–245 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.235
H.C. Yeh, B.B. Duncan, M.I. Schmidt, N.Y. Wang, F.L. Brancati, Smoking, smoking cessation, and risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 152, 10–17 (2010). https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-152-1-201001050-00005
C. Chen, Y.Q. Tu, P. Yang, Q.L. Yu, S. Zhang, F. Xiong, C.Y. Wang, Assessing the impact of cigarette smoking on beta-cell function and risk for type 2 diabetes in a non-diabetic Chinese cohort. Am. J. Transl. Res. 10, 2164–2174 (2018)
J. Maddatu, E. Anderson-Baucum, C. Evans-Molina, Smoking and the risk of type 2 diabetes. Transl. Res 184, 101–107 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2017.02.004
S. Akter, A. Goto, T. Mizoue, Smoking and the risk of type 2 diabetes in Japan: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. 27, 553–561 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.je.2016.12.017
K. Hemminki, X. Li, K. Sundquist, J. Sundquist, Familial risks for type 2 diabetes in Sweden. Diabetes Care 33, 293–297 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-0947
M. Sakurai, K. Nakamura, K. Miura, T. Takamura, K. Yoshita, S. Sasaki, S.Y. Nagasawa, Y. Morikawa, M. Ishizaki, T. Kido, Y. Naruse, Y. Suwazono, H. Nakagawa, Family history of diabetes, lifestyle factors, and the 7-year incident risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Japanese men and women. J. Diabetes Investig. 4, 261–268 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12033
M.C. Cornelis, N. Zaitlen, F.B. Hu, P. Kraft, A.L. Price, Genetic and environmental components of family history in type 2 diabetes. Hum. Genet. 134, 259–267 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-014-1519-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, China.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Z., Guo, D., Chen, J. et al. A nomogram for predicting 5-year incidence of type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population. Endocrine 67, 561–568 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-02154-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-02154-x