Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the safety and efficacy of once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide as monotherapy or add-on to other antihyperglycaemic agents (AHAs) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
PubMed, Embase, Cochrane library and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched from the inception to January 18, 2018. Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing semaglutide with placebo or other AHAs in T2DM patients were included in our meta-analysis. Risk ratio (RR) and mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were used to evaluate the outcomes.
Results
A total of 11 studies with 9519 patients were included in our meta-analysis. The results revealed that compared with placebo or other AHAs, semaglutide had further reduced the level of haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) [MD 1.03%, 95% CI (0.85%, 1.22%), p < 0.00001], self-measured plasma glucose (SMPG) [MD 1.19 mmol/L, 95% CI (0.84 mmol/L, 1.53 mmol/L), p < 0.00001], fasting plasma glucose (FPG) [MD 1.33 mmol/L, 95% CI (0.97 mmol/L, 1.69 mmol/L), p < 0.00001] and weight [MD 3.61 kg, 95% CI (3.05 kg, 4.17 kg), p < 0.00001] and significantly increased participants who achieved HbA1c < 7.0% [RR 2.26, 95% CI (1.89, 2.70), p < 0.00001] in T2DM patients. Semaglutide had a significant increase in the incidence of adverse events (AEs) [RR 1.06, 95% CI (1.02, 1.11), p < 0.0001] and an analogous incidence in serious adverse events (SAEs) [RR 0.94, 95% CI (0.86, 1.02), p = 0.11] and hypoglycaemic events (severe or blood glucose (BG)-confirmed symptomatic) [RR 0.93, 95% CI (0.74, 1.16), p = 0.50] compared with the control group.
Conclusions
This article revealed that semaglutide had a favourable efficacy and safety in treating T2DM patients. It maybe a superior choice for T2DM patients who have obesity or a poor adherence to daily AHAs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
IDF, IDF diabetes atlas, 8th edn (2017). http://www.diabetesatlas.org/. Accessed 15 July 2018
WHO, World Health Organization Global Report on Diabetes (2016). http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/204871/1/9789241565257_eng.pdf?ua=1. Accessed 15 July 2018
S.E. Inzucchi, R.M. Bergenstal, J.B. Buse, M. Diamant, E. Ferrannini, M. Nauck, A.L. Peters, A. Tsapas, R. Wender, D.R. Matthews, Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 38(1), 140–149 (2015)
K.J. Lipska, X. Yao, J. Herrin, R.G. McCoy, J.S. Ross, M.A. Steinman, S.E. Inzucchi, T.M. Gill, H.M. Krumholz, N.D. Shah, Trends in drug utilization, glycemic control, and rates of severe hypoglycemia, 2006–2013. Diabetes Care 40(4), 468–475 (2017)
The ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 358(24), 2560–2572 (2008)
R.R. Holman, S.K. Paul, M.A. Bethel, D.R. Matthews, H.A. Neil, 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 359(15), 1577–1589 (2008)
O. Hamdy, S. Ashrafzadeh, A. Mottalib, Weight management in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multidisciplinary real-world approach. Curr. Diab. Rep. 18(9), 66 (2018)
H.W. Rodbard, L. Blonde, S.S. Braithwaite, E.M. Brett, R.H. Cobin, Y. Handelsman, R. Hellman, P.S. Jellinger, L.G. Jovanovic, P. Levy, J.I. Mechanick, F. Zangeneh, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for the management of diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Pract. 13(Suppl 1), 1–68 (2007)
S. Madsbad, Review of head-to-head comparisons of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 18(4), 317–332 (2016)
A.R. Meloni, M.B. DeYoung, C. Lowe, D.G. Parkes, GLP-1 receptor activated insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells: mechanism and glucose dependence. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 15(1), 15–27 (2013)
J.E. Potts, L.J. Gray, E.M. Brady, K. Khunti, M.J. Davies, D.H. Bodicoat, The effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists on weight loss in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10(6), e0126769 (2015)
J. van Can, B. Sloth, C.B. Jensen, A. Flint, E.E. Blaak, W.H. Saris, Effects of the once-daily GLP-1 analog liraglutide on gastric emptying, glycemic parameters, appetite and energy metabolism in obese, non-diabetic adults. Int. J. Obes. 38(6), 784–793 (2014)
A. McGovern, W. Hinton, S. Calderara, N. Munro, M. Whyte, S. de Lusignan, A class comparison of medication persistence in people with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective observational study. Diabetes Ther. 9(1), 229–242 (2018)
K. Iglay, S.E. Cartier, V.M. Rosen, V. Zarotsky, S.N. Rajpathak, L. Radican, K. Tunceli, Meta-analysis of studies examining medication adherence, persistence, and discontinuation of oral antihyperglycemic agents in type 2 diabetes. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 31(7), 1283–1296 (2015)
F. Zaccardi, Z.Z. Htike, D.R. Webb, K. Khunti, M.J. Davies, Benefits and harms of once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatments: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 164(2), 102–113 (2016)
J. Lau, P. Bloch, L. Schaffer, I. Pettersson, J. Spetzler, J. Kofoed, K. Madsen, L.B. Knudsen, J. McGuire, D.B. Steensgaard, H.M. Strauss, D.X. Gram, S.M. Knudsen, F.S. Nielsen, P. Thygesen, S. Reedtz-Runge, T. Kruse, Discovery of the once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue semaglutide. J. Med. Chem. 58(18), 7370–7380 (2015)
C. Sorli, S.I. Harashima, G.M. Tsoukas, J. Unger, J.D. Karsbøl, T. Hansen, S.C. Bain, Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide monotherapy versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 1): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multinational, multicentre phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5(4), 251–260 (2017)
B. Ahrén, L. Masmiquel, H. Kumar, M. Sargin, J.D. Karsbøl, S.H. Jacobsen, F. Chow, Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily sitagliptin as an add-on to metformin, thiazolidinediones, or both, in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 2): a 56-week, double-blind, phase 3a, randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5(5), 341–354 (2017)
R.E. Pratley, V.R. Aroda, I. Lingvay, J. Lüdemann, C. Andreassen, A. Navarria, A. Viljoen, SUSTAIN 7 investigators, Semaglutide versus dulaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): a randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial. Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. 6(4), 275–286 (2018)
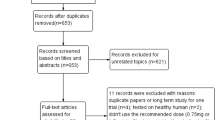
D. Moher, A. Liberati, J. Tetzlaff, D.G. Altman, PRISMA Group, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339, b2535 (2009)
A. Liberati, D.G. Altman, J. Tetzlaff, C. Mulrow, P.C. Gøtzsche, J.P. Ioannidis, M. Clarke, P.J. Devereaux, J. Kleijnen, D. Moher, The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339, b2700 (2009)
J. P. T. Higgins, S. Green (eds.), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. http://handbook.cochrane.org (2011). Accessed 27 July 2018
C. Kapitza, K. Dahl, J.B. Jacobsen, M.B. Axelsen, A. Flint, Effects of semaglutide on beta cell function and glycaemic control in participants with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetologia 60(8), 1390–1399 (2017)
K. Kaku, Y. Yamada, H. Watada, A. Abiko, T. Nishida, J. Zacho, A. Kiyosue, Safety and efficacy of once-weekly semaglutide vs additional oral antidiabetic drugs in Japanese people with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 20(5), 1202–1212 (2018)
M. Davies, T.R. Pieber, M.L. Hartoft-Nielsen, O.K.H. Hansen, S. Jabbour, J. Rosenstock, Effect of oral semaglutide compared with placebo and subcutaneous semaglutide on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 318(15), 1460–1470 (2017)
A.J. Ahmann, M. Capehorn, G. Charpentier, F. Dotta, E. Henkel, I. Lingvay, A.G. Holst, M.P. Annett, V.R. Aroda, Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus exenatide ER in subjects with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 3): a 56-week, open-label, randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 41(2), 258–266 (2018)
V.R. Aroda, S.C. Bain, B. Cariou, M. Piletič, L. Rose, M. Axelsen, E. Rowe, J.H. DeVries, Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily insulin glargine as add-on to metformin (with or without sulfonylureas) in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 4): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, multinational, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5(5), 355–366 (2017)
H.W. Rodbard, I. Lingvay, J. Reed, R. de la Rosa, L. Rose, D. Sugimoto, E. Araki, P.L. Chu, N. Wijayasinghe, P. Norwood, Semaglutide added to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 5): a randomized, controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 103(6), 2291–2301 (2018)
S.P. Marso, S.C. Bain, A. Consoli, F.G. Eliaschewitz, E. Jódar, L.A. Leiter, I. Lingvay, J. Rosenstock, J. Seufert, M.L. Warren, V. Woo, O. Hansen, A.G. Holst, J. Pettersson, T. Vilsbøll, SUSTAIN-6 investigators, semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 375(19), 1834–1844 (2016)
Y. Seino, Y. Terauchi, T. Osonoi, D. Yabe, N. Abe, T. Nishida, J. Zacho, S. Kaneko, Safety and efficacy of semaglutide once weekly vs sitagliptin once daily, both as monotherapy in Japanese people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 20(2), 378–388 (2018)
D.M. Nathan, J.B. Buse, M.B. Davidson, E. Ferrannini, R.R. Holman, R. Sherwin, B. Zinman, American Diabetes Association, European Association for Study of Diabetes, Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(1), 193–203 (2009)
American Diabetes Association, Standards of medical care in diabetes–2010. Diabetes Care 33(Suppl 1), S11–S61 (2010)
I.M. Stratton, A.I. Adler, H.A. Neil, D.R. Matthews, S.E. Manley, C.A. Cull, D. Hadden, R.C. Turner, R.R. Holman, Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ 321(7258), 405–412 (2000)
D. Russell-Jones, A. Vaag, O. Schmitz, B.K. Sethi, N. Lalic, S. Antic, M. Zdravkovic, G.M. Ravn, R. Simó, Liraglutide effect and action in diabetes 5 (LEAD-5) met + SU Study Group, liraglutide vs insulin glargine and placebo in combination with metformin and sulfonylurea therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus (LEAD-5 met + SU): a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 52(10), 2046–2055 (2009)
M. Diamant, L. Van Gaal, B. Guerci, S. Stranks, J. Han, J. Malloy, M.K. Boardman, M.E. Trautmann, Exenatide once weekly versus insulin glargine for type 2 diabetes (DURATION-3): 3-year results of an open-label randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(6), 464–473 (2014)
A.S. Matheus, L.R. Tannus, R.A. Cobas, C.C. Palma, C.A. Negrato, M.B. Gomes, Impact of diabetes on cardiovascular disease: an update. Int. J. Hypertens. 2013, 653789 (2013)
B. Zinman, C. Wanner, J.M. Lachin, D. Fitchett, E. Bluhmki, S. Hantel, M. Mattheus, T. Devins, O.E. Johansen, H.J. Woerle, U.C. Broedl, S.E. Inzucchi, EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators, empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 373(22), 2117–2128 (2015)
S.P. Marso, G.H. Daniels, K. Brown-Frandsen, P. Kristensen, J.F. Mann, M.A. Nauck, S.E. Nissen, S. Pocock, N.R. Poulter, L.S. Ravn, W.M. Steinberg, M. Stockner, B. Zinman, R.M. Bergenstal, J.B. Buse, LEADER Steering Committee, LEADER Trial Investigators, Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 375(4), 311–322 (2016)
J.B. Hjerpsted, A. Flint, A. Brooks, M.B. Axelsen, T. Kvist, J. Blundell, Semaglutide improves postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism, and delays first-hour gastric emptying in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 20(3), 610–619 (2018)
J. Blundell, G. Finlayson, M. Axelsen, A. Flint, C. Gibbons, T. Kvist, J.B. Hjerpsted, Effects of once-weekly semaglutide on appetite, energy intake, control of eating, food preference and body weight in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 19(9), 1242–1251 (2017)
P. Poirier, T.D. Giles, G.A. Bray, Y. Hong, J.S. Stern, F.X. Pi-Sunyer, R.H. Eckel, American Heart Association, Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical activity, and metabolism, obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 113(6), 898–918 (2006)
R.T. Jung, Obesity as a disease. Br. Med. Bull. 53(2), 307–321 (1997)
T.S. Han, M.A. Tijhuis, M.E. Lean, J.C. Seidell, Quality of life in relation to overweight and body fat distribution. Am. J. Public Health 88(12), 1814–1820 (1998)
F.X. Pi-Sunyer, The impact of weight gain on motivation, compliance, and metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Postgrad. Med. 121(5), 94–107 (2009)
A. Farmer, A.L. Kinmonth, S. Sutton, Measuring beliefs about taking hypoglycaemic medication among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 23(3), 265–270 (2006)
J.P. Wilding, The importance of weight management in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 68(6), 682–691 (2014)
T. Chalmer, T.P. Almdal, T. Vilsbøll, F.K. Knop, Adverse drug reactions associated with the use of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes-focus on pancreatitis and pancreas cancer. Expert. Opin. Drug. Saf. 14(1), 171–180 (2015)
H. Wang, Y. Liu, Q. Tian, J. Yang, R. Lu, S. Zhan, J. Haukka, T. Hong, Incretin-based therapies and risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 20(4), 910–920 (2018)
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Early worsening of diabetic retinopathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 116(7), 874–886 (1998)
K. Dahl-Jørgensen, O. Brinchmann-Hansen, K.F. Hanssen, L. Sandvik, O. Aagenaes, Rapid tightening of blood glucose control leads to transient deterioration of retinopathy in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: the Oslo study. Br. Med. J. 290(6471), 811–815 (1985)
M. Witkowski, L. Wilkinson, N. Webb, A. Weids, D. Glah, H. Vrazic, A systematic literature review and network meta-analysis comparing once-weekly semaglutide with other GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes previously receiving 1-2 oral anti-diabetic drugs. Diabetes Ther. 9(3), 1149–1167 (2018)
M. Witkowski, L. Wilkinson, N. Webb, A. Weids, D. Glah, H. Vrazic, A systematic literature review and network meta-analysis comparing once-weekly semaglutide with other GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes previously receiving basal insulin. Diabetes Ther. 9(3), 1233–1251 (2018)
R. Sharma, L. Wilkinson, H. Vrazic, E. Popoff, S. Lopes, S. Kanters, E. Druyts, Comparative efficacy of once-weekly semaglutide and SGLT-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy: a systematic literature review and network meta-analysis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 29, 1–9 (2018)
F.H. Shi, H. Li, M. Cui, Z.L. Zhang, Z.C. Gu, X.Y. Liu, Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 576 (2018)
P. Andreadis, T. Karagiannis, K. Malandris, I. Avgerinos, A. Liakos, A. Manolopoulos, E. Bekiari, D. R. Matthews, A. Tsapas, Semaglutide for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13361. [Epub ahead of print]
Author contributions
G.L. and X.L. made contributions to have the idea for this study and design this study. G.L., X.W. and S.Q. contributed towards literature search, data extraction, data analysis, drafting and critical revision of the manuscript. X.L., Y.Z. and Y.L. made contributions to data interpretation, assess the quality of the studies, drafting and critical revision of the manuscript. All authors had reviewed the manuscript, approved the final draft and decided to submit it for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Qie, S., Wang, X. et al. The safety and efficacy of once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine 62, 535–545 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1708-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1708-z