Abstract
Purpose
C-peptide secretion is deficient or absent in type 1 diabetes mellitus. It is well accepted that insulin replacement therapy cannot prevent the development of long-term diabetes-related complications, which can often be disabling or even life-threatening. Several cross-sectional investigations have suggested that residual C-peptide production in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus would help prevent a number of complications. In animal models of diabetes and in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, C-peptide replacement improves renal function, skin and skeletal muscle blood flow, nerve conduction, glucose utilization, and other diabetes-related complications. Recent investigations suggest a new beneficial effect of C-peptide, which to date has never been studied. It is known that osteoporosis is the most prevalent short-term complication in type 1 diabetes mellitus. This review will highlight new insights into the pathophysiology and future therapeutic modalities for osteoporosis in individuals with diabetes.
Methods
This review provides a concise summary of old and new insights into the role of C-peptide in diabetes-related complications.
Results
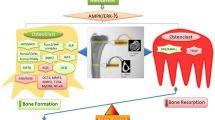
The data suggest that C-peptide is a bioactive peptide, acting independently of insulin, which binds to a G-protein-coupled membrane binding site in different cell types. By triggering Ca2+-dependent intracellular signaling pathways, both Na+, K+-ATPase and endothelial nitric oxide synthase are activated. C-peptide may act on osteoblast cells by ERK 1/2 pathway activation, modulate collagen biosynthesis and RANKL expression. Furthermore, C-peptide-deficient postmenopausal women, not affected by diabetes, have a lower bone mineral density than those with normal C-peptide levels.
Conclusion
Taken together these studies encourage further investigations to elucidate the role of C-peptide in preventing bone loss in type 1 diabetes mellitus and in those individuals with C-peptide deficiency and osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Clark, S. Cho, A.H. Rubenstein, D.F. Steiner, Isolation of a proinsulin connecting peptide fragment (C-peptide) from bovine and human pancreas. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 35, 456–461 (1969)
K.S. Polonsky, J. Licinio-Paixao, B.D. Given, W. Pugh, P. Rue, J. Galloway et al., Use of biosynthetic human C-peptide in the measurement of insulin secretion rates in normal volunteers and type I diabetic patients. J. Clin. Invest. 77, 98–105 (1986)
P.M. Clark, Assays for insulin, proinsulin(s) and C-peptide. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 36, 541–564 (1999)
A.G. Jones, A.T. Hattersley, The clinical utility of C-peptide measurement in the care of patients with diabetes. Diabet. Med. 30, 803–817 (2013)
S. Sjoberg, R. Gunnarsson, M. Gjotterberg, A.K. Lefvert, A. Persson, J. Ostman, Residual insulin production, glycaemic control and prevalence of microvascular lesions and polyneuropathy in long-term type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 30, 208–213 (1987)
K. Suzuki, K. Watanabe, T. Motegi, H. Kajinuma, High prevalence of proliferative retinopathy in diabetic patients with low pancreatic B-cell capacity. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 6, 45–52 (1989)
J.M. Lachin, P. McGee, J.P. Palmer, DCCT/EDIC research group. impact of C-peptide preservation on metabolic and clinical outcomes in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes 63, 739–748 (2014)
P.H. Winocour, J. Jeacock, P. Kalsi, C. Gordon, D.C. Anderson, The relevance of persistent C-peptide secretion in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus to glycaemic control and diabetic complications. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 9, 23–35 (1990)
A.M. Brooks, R. Oram, P. Home, N. Steen, J.A. Shaw, Demonstration of an intrinsic relationship between endogenous C-peptide concentration and determinants of glycemic control in type 1 diabetes following islet transplantation. Diabetes Care 38, 105–112 (2015)
Y. Ido, A. Vindigni, K. Chang, L. Stramm, R. Chance, W.F. Heath, R.O. DiMarchi, E. DiCera, J.R. Williamson, Prevention of vascular and neural dysfunction in diabetic rats by C-peptide. Science 277, 563–566 (1997)
N. Al-Rasheed, F. Meakin, E. Royal et al., Potent activation of multiple signalling pathways by C-peptide in opossum kidney proximal tubular cells. Diabetologia 47, 987–997 (2004)
R. Rigler, A. Pramanik, P. Jonasson, G. Kratz, O. Jansson, P.Å. Nygren, S. Ståhl, K. Ekberg, B.-L. Johansson, S. Uhlén, M. Uhlén, H. Jüornvall, J. Wahren, Specific binding of proinsulin C-peptide to human cell membranes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13318–13323 (1999)
Y. Ohtomo, T. Bergman, B.-L. Johansson, H. Jörnvall, J. Wahren, Diabetologia 41, 287–291 (1998)
L. Nordquist, K. Shimada, T. Ishii, D.T. Furuya, A. Kamikawa, K. Kimura, Proinsulin C-peptide prevents type-1 diabetes-induced decrease of renalNa+-K+-ATPase alpha1-subunit in rats. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 26, 193–199 (2010)
J. Wahren, K. Ekberg, J. Johansson, M. Henriksson, A. Pramavik, B.-L. Johansson, R. Rigler, H. Jüornvall, Role of C-peptide in human physiology. Am. J. Physiol. 278, E759–E768 (2000)
Z. Zhong, O. Kotova, A. Davidescu et al., C-peptide stimulates Na+, K+-ATPase via activation of ERK1/2 MAP kinases in human renal tubular cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61, 2782–2790 (2004)
T. Kitamura, K. Kimura, B.D. Jung, K. Makondo, N. Sakane, T. Yoshida, M. Saito, Proinsulin C-peptide activates cAMP response element binding proteins through the p38 mitogen activated protein kinase pathway in mouse lung capillary endothelial cells. Biochem. J. 366, 377–744 (2002)
T. Kitamura, K. Kimura, B.D. Jung, K. Makondo, S. Okamoto, X. Canas, N. Sakane, T. Yoshida, M. Saito, Proinsulin C-peptide rapidly stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinases in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: requirement of protein kinase C, phosphoinositide3-kinase and pertussis toxin-sensitive Gprotein. Biochem. J. 355, 123–129 (2001)
A. Kamikawa, T. Ishii, K. Shimada et al., Proinsulin C-peptide abrogates type-1 diabetes-induced increase of renal endothelial nitric oxide synthase in rats. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 24, 331–338 (2008)
B.-L. Johansson, S. Sjöberg, J. Wahren, The influence of human C-peptide on renal function and glucose utilization in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 35, 121–128 (1992)
M. Sjöquist, W. Huang, B.-L. Johansson, Effects of C-peptide on renal function at the early stage of experimental diabetes. Kidney Int. 54, 758–764 (1998)
B.-L. Johansson, B. Linde, J. Wahren, Effects of C-peptide on blood flow, capillary diffusion capacity and glucose utilization in the exercising forearm of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 35, 1151–1158 (1992)
B.-L. Johansson, K. Borg, E. Fernqvist-Forbes, T. Odergren, S. Remahl, J. Wahren, C-peptide improves autonomic nerve function in IDDM patients. Diabetologia 39, 687–695 (1996)
B.-L. Johansson, K. Borg, E. Fernqvist-Forbes, A. Kernell, T. Odergren, J. Wahren, Beneficial effects of C-peptide on incipient nephropathy and neuropathy in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 17, 181–189 (2000)
K. Ekberg, T. Brismar, B.L. Johansson, B. Jonsson, P. Lindström, J. Wahren, Amelioration of sensory nerve dysfunction by C-Peptide in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 52, 536 (2003)
J. Wahren, H. Foyt, M. Daniels, J.C. Arezzo, Long-acting C-peptide and neuropathy in type 1 diabetes: a 12-month clinical trial. Diabetes Care 39, 596–602 (2016)
B.-L. Johansson, A. Kernell, S. Sjöberg, J. Wahren, Influence of combined C-peptide and insulin administration on renal function and metabolic control in diabetes type 1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 77, 976–981 (1993)
P. Vestergaard, Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes—a meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 18, 427–444 (2007)
R.S. Clements Jr, D.S. Bell, Complications of diabetes. Prevalence, detection, current treatment, and prognosis. Am. J. Med. 79(5A), 2–7 (1985)
P. Gunczler, R. Lanes, V. Paz-Martinez, R. Martins, S. Esaa, V. Colmenares, J.R. Weisinger, Decreased lumbar spine bone mass and low bone turnover in children and adolescents with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus followed longitudinally. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 11, 413–419 (1998)
J.D. Ringe, F. Kuhlencordt, H.P. Kruse, Proceedings: bone mineral determinations on long-term diabetics. Am. J. Roentgenol. 126, 1300–1301 (1976)
M.E. Levin, V.C. Boisseau, L.V. Avioli, Effects of diabetes mellitus on bone mass in juvenile and adult-onset diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 294, 241–245 (1976)
P. McNair, S. Madsbad, M.S. Christensen, C. Christiansen, O.K. Faber, C. Binder, I. Transbol, Bone mineral loss in insulin-treated diabetes mellitus: studies on pathogenesis. Acta Endocrinol. 90, 463–472 (1979)
J.V. Santiago, W.H. McAlister, S.K. Ratzan, Y. Bussman, M.W. Haymond, G. Shackelford, V.V. Weldon, Decreased cortical thickness and osteopenia in children with diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 45, 845–848 (1977)
F.S. Hough, Alterations of bone and mineral metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Part I. An overview. S. Afr. Med. J. 72, 116–119 (1987)
V.A. Koivisto, L.K. Stevens, M. Mattock, P. Ebeling, M. Muggeo, J. Stephenson, B. Idzior-Walus, Cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in IDDM in Europe. EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study Group. Diabetes Care 19, 689–697 (1996)
T. Montalcini, S. Romeo, Y. Ferro, V. Migliaccio, C. Gazzaruso, A. Pujia, Osteoporosis in chronic inflammatory disease: the role of malnutrition. Endocrine 43, 59–64 (2013)
P.J. López-Ibarra, M.M. Pastor, F. Escobar-Jiménez, M.D. Pardo, A.G. González, J.D. Luna, M.E. Requena, M.A. Diosdado, Bone mineral density at time of clinical diagnosis of adult-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Pract. 7, 346–351 (2001)
Y. Li, H. Liu, Y. Sato, The association between the serum C-peptide level and bone mineral density. PLoS One 8, e83107 (2013)
T. Montalcini, P. Gallotti, A. Coppola, V. Zambianchi, M. Fodaro, E. Galliera, M.G. Marazzi, S. Romeo, S. Giannini, M.M. Corsi Romanelli, A. Pujia, C. Gazzaruso, Association between low C-peptide and low lumbar bone mineral density in postmenopausal women without diabetes. Osteoporos. Int. 26, 1639–1646 (2015)
A.S. Kujath, L. Quinn, M.E. Elliott, T.J. LeCaire, N. Binkley, A.R. Molino, K.K. Danielson, Different health behaviours and clinical factors associated with bone mineral density and bone turnover in premenopausal women with and without type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 31, 421–432 (2015)
T. Yamaguchi, I. Kanazawa, M. Yamamoto, S. Kurioka, M. Yamauchi, S. Yano, T. Sugimoto, Associations between components of the metabolic syndrome versus bone mineral density and vertebral fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes. Bone 45, 174–179 (2009)
E. Barrett-Connor, T.L. Holbrook, Sex differences in osteoporosis in older adults with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. JAMA 268, 3333–3337 (1992)
P. van Daele, R. Stolk, H. Burger, D. Algra, D. Grobbee, A. Hofman, J. Birkenhager, H. Pols, Bone density in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the Rotterdam study. Ann. Intern. Med. 122, 409–414 (1995)
M. Lunt, P. Masaryk, C. Scheidt-Nave, J. Nijs, G. Poor, H. Pols, G. Falch Jam Hammermeister, D.M. Reid, L. Benevolenskaya, K. Weber, J. Cannata, T.W. O’Neill, D. Felsenberg, A.J. Silman, J. Reeve, The effects of lifestyle, dietary dairy intake, and diabetes on bone density and vertebral deformity prevalence: the EVOS study. Osteoporos. Int. 12, 688–698 (2001)
A. Schwartz, D. Sellmeyer, K. Ensrud, J. Cauley, H. Tabor, P. Schreiner, S. Jamal, D. Black, Cummings S for the osteoporotic fractures research group older women with diabetes have an increased risk of fracture: a prospective study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 32–38 (2001)
M. Saito, K. Marumo, Collagen cross-links as a determinant of bone quality: a possible explanation for bone fragility in aging, osteoporosis, and diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos. Int. 21, 195–214 (2010)
C. Russo, V. Lazzaro, C. Gazzaruso, S. Maurotti, Y. Ferro, P. Pingitore, F. Fumo, A. Coppola, G. Gallotti, V. Zambianchi, M. Fodaro, E. Galliera, M.G. Marazzi, M.M. Corsi Romanelli, S. Giannini, S. Romeo, A. Pujia, T. Montalcini, Proinsulin C-peptide modulates the expression of ERK1/2, type I collagen and RANKL in human Osteoblast-like cells (Saos-2). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 442, 134–141 (2017). doi:10.1016/j.mce.2016.12.012
W. Zhang, H. Kamiya, K. Ekberg, J. Wahren, A.A. Sima, C-peptide improves neuropathy in type 1 diabetic BB/Wor-rats. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 23, 63–70 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pujia, A., Gazzaruso, C. & Montalcini, T. An update on the potential role of C-peptide in diabetes and osteoporosis. Endocrine 58, 408–412 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1286-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1286-5