Abstract
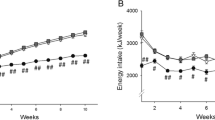
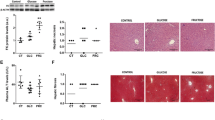
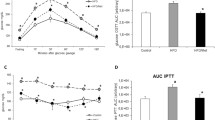
Several studies have demonstrated that a high-fructose (FRUC) diet induces metabolic and haemodynamic abnormalities, known as the metabolic syndrome, which are characterised by obesity, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, dyslipidaemia and hypertension. In this study, the effect of a FRUC diet (60 % fructose) for 8 weeks on the metabolism of lipids in liver and epididymal adipose tissue from Wistar rats was compared with the AIN-93M diet and the effects of the AIN-93M diet were compared with a chow diet. The FRUC diet induced marked increases in both hepatocyte lipid droplet volume and postprandial serum levels of triacylglycerol (TAG), but reduced the postprandial serum levels of insulin. The AIN-93M diet induced marked increases in the hepatocyte lipid droplet volume and the serum levels of insulin, without affecting the serum levels of TAG. We found that isocaloric substitution of cornstarch, dextrinised cornstarch and sucrose (AIN-93M diet) for fructose did not affect the hepatic VLDL-TAG secretion and adipose tissue glucose uptake, lipolysis and cytosolic lipases activities in rats. However, the high-fructose diet induced a severe steatosis in liver accompanied by a decrease in cytosolic lipases activities. In adipose tissue, the FRUC diet induced a decrease in the lipoprotein lipase activity, and an increase in lipogenesis. FRUC and AIN-93M diets induced changes in lipid homeostasis in liver and adipose tissue by distinct biochemical mechanisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Livesey, R. Taylor, Fructose consumption and consequences for glycation, plasma triacylglycerol, and body weight: meta-analyses and meta-regression models of intervention studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 88, 1419–1437 (2008)
V. Ha, J.L. Sievenpiper, R.J. de Souza, L. Chiavaroli, D.D. Wang, A.I. Cozma, A. Mirrahimi, M.E. Yu, A.J. Carleton, M. Dibuono, A.L. Jenkins, L.A. Leiter, T.M. Wolever, J. Beyene, C.W. Kendall, D.J. Jenkins, Effect of fructose on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled feeding trials. Hypertension 59, 787–795 (2012)
J.L. Sievenpiper, R.J. de Souza, A. Mirrahimi, M.E. Yu, A.J. Carleton, J. Beyene, L. Chiavaroli, M. Di Buono, A.L. Jenkins, L.A. Leiter, T.M. Wolever, C.W. Kendall, D.J. Jenkins, Effect of fructose on body weight in controlled feeding trials: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 156, 291–304 (2012)
S. Chiu, J.L. Sievenpiper, R.J. de Souza, A.I. Cozma, A. Mirrahimi, A.J. Carleton, V. Ha, M. Di Buono, A.L. Jenkins, L.A. Leiter, T.M. Wolever, A.C. Don-Wauchope, J. Beyene, C.W. Kendall, D.J. Jenkins, Effect of fructose on markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled feeding trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 68, 416–423 (2014)
D.D. Wang, J.L. Sievenpiper, R.J. de Souza, L. Chiavaroli, V. Ha, A.I. Cozma, A. Mirrahimi, M.E. Yu, A.J. Carleton, M. Di Buono, A.L. Jenkins, L.A. Leiter, T.M. Wolever, J. Beyene, C.W. Kendall, D.J. Jenkins, The effects of fructose intake on serum uric acid vary among controlled dietary trials. J. Nutr. 142, 916–923 (2012)
D.D. Wang, J.L. Sievenpiper, R.J. de Souza, A.I. Cozma, L. Chiavaroli, V. Ha, A. Mirrahimi, A.J. Carleton, M. Di Buono, A.L. Jenkins, L.A. Leiter, T.M. Wolever, J. Beyene, C.W. Kendall, D.J. Jenkins, Effect of fructose on postprandial triacylglycerols: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled feeding trials. Atherosclerosis 232, 125–133 (2014)
A.I. Cozma, J.L. Sievenpiper, R.J. de Souza, L. Chiavaroli, V. Ha, D.D. Wang, A. Mirrahimi, M.E. Yu, A.J. Carleton, M. Di Buono, A.L. Jenkins, L.A. Leiter, T.M. Wolever, J. Beyene, C.W. Kendall, D.J. Jenkins, Effect of fructose on glycemic control in diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled feeding trial. Diabetes Care 35, 1611–1620 (2012)
J.L. Sievenpiper, A.J. Carleton, S. Chatha, H.Y. Jiang, R.J. de Souza, J. Beyene, C.W. Kendall, D.J. Jenkins, Heterogeneous effects of fructose on blood lipids in individuals with type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental trials in humans. Diabetes Care 32, 1930–1937 (2009)
F. Ameer, L. Scandiuzzi, S. Hasnain, H. Kalbacher, N.De Zaidi, novo lipogenesis in health and disease. Metabolism 63, 895–902 (2014)
V.E. Chaves, D. Frasson, N.H. Kawashita, Several agents and pathways regulate lipolysis in adipocytes. Biochimie 93, 1631–1640 (2011)
Y. Kawano, D.E. Cohen, Mechanisms of hepatic triglyceride accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 48, 434–441 (2013)
A. Lass, R. Zimmermann, G. Haemmerle, M. Riederer, G. Schoiswohl, M. Schweiger, P. Kienesberger, J.G. Strauss, G. Gorkiewicz, R. Zechner, Adipose triglyceride lipase-mediated lipolysis of cellular fat stores is activated by CGI-58 and defective in Chanarin-Dorfman Syndrome. Cell Metab. 3, 309–319 (2006)
X. Yang, X. Lu, M. Lombès, G.B. Rha, Y.I. Chi, T.M. Guerin, E.J. Smart, J. Liu, The G0/G1 switch Gene 2 regulates adipose lipolysis through association with adipose triglyceride lipase. Cell Metab. 11, 194–205 (2010)
J.W. Wu, S.P. Wang, F. Alvarez, S. Casavant, N. Gauthier, L. Abed, K.G. Soni, G. Yang, G.A. Mitchell, Deficiency of liver adipose triglyceride lipase in mice causes progressive hepatic steatosis. Hepatology 54, 122–132 (2011)
K.T. Ong, M.T. Mashek, S.Y. Bu, A.S. Greenberg, D.G. Mashek, Adipose triglyceride lipase is a major hepatic lipase that regulates triacylglycerol turnover and fatty acid signaling and partitioning. Hepatology 53, 116–126 (2011)
B.N. Reid, G.P. Ables, O.A. Otlivanchik, G. Schoiswohl, R. Zechner, W.S. Blaner, I.J. Goldberg, R.F. Schwabe, S.C. Chua Jr, L.S. Huang, Hepatic overexpression of hormone-sensitive lipase and adipose triglyceride lipase promotes fatty acid oxidation, stimulates direct release of free fatty acids, and ameliorates steatosis. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 13087–13099 (2008)
L. Rui, Energy metabolism in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 4, 177–197 (2014)
L. Tappy, K.A. Lê, Metabolic effects of fructose and the worldwide increase in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 90, 23–46 (2010)
J.B. Moore, P.J. Gunn, B.A. Fielding, The role of dietary sugars and de novo lipogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients 6, 5679–5703 (2014)
J. Folch, M. Lees, G.A. Stanley, A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1957)
H.G. Windmueller, A.E. Spaeth, Perfusion in situ with tritium oxide to measure hepatic lipogenesis and lipid secretion. Normal and orotic acid-fed rats. J. Biol. Chem. 241, 2891–2899 (1966)
M. Rodbell, Metabolism of isolated fat cells. I. Effects of hormones on glucose metabolism and lipolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 239, 375–380 (1964)
L.M. Botion, A. Green, Long-term regulation of lipolysis and hormone-sensitive lipase by insulin and glucose. Diabetes 48, 1691–1697 (1999)
S. Gasic, A. Green, Gi down-regulation and heterologous desensitization in adipocytes after treatment with α agonist UK 14304. Biochem. Pharmacol. 49, 785–790 (1995)
P.H. Iverius, A.M. Ostlund-Lindqvist, Preparation, characterization, and measurement of lipoprotein lipase. Methods Enzymol. 129, 691–704 (1986)
P. Nilsson-Ehle, M.C. Schotz, A stable, radioactive substrate emulsion for assay of lipoprotein lipase. J. Lipid Res. 17, 536–541 (1976)
P. Belfrage, M. Vaughan, Simple liquid-liquid partition system for isolation of labeled oleic acid from mixtures with glycerides. J. Lipid Res. 10, 341–344 (1969)
E. Wei, W. Gao, R. Lehner, Attenuation of adipocyte triacylglycerol hydrolase activity decreases basal fatty acid efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 8027–8035 (2007)
V.W. Dolinsky, D.N. Douglas, R. Lehner, D.E. Vance, Regulation of the enzymes of microsomal triacylglycerol lipolysis and re-esterification by the glucocorticoid dexamethasone. Biochem. J. 378, 967–974 (2004)
M.M. Bradford, A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976)
T. Mita, M. Furuhashi, S. Hiramitsu, J. Ishii, K. Hoshina, S. Ishimura, T. Fuseya, Y. Watanabe, M. Tanaka, K. Ohno, H. Akasaka, H. Ohnishi, H. Yoshida, S. Saitoh, K. Shimamoto, T. Miura, FABP4 is secreted from adipocytes by adenyl cyclase-PKA and guanylyl cyclase-PKG-dependent lipolytic mechanisms. Obesity 23, 359–367 (2015)
P.R. Manna, J. Cohen-Tannoudji, R. Counis, C.W. Garner, I. Huhtaniemi, F.B. Kraemer, D.M. Stocco, Mechanisms of action of hormone-sensitive lipase in mouse Leydig cells: its role in the regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 8505–8518 (2013)
Z. Wan, S. Matravadia, G.P. Holloway, D.C. Wright, FAT/CD36 regulates PEPCK expression in adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 304, C478–C484 (2013)
J. Grisouard, E. Bouillet, K. Timper, T. Radimerski, K. Dembinski, D.M. Frey, R. Peterli, H. Zulewski, U. Keller, B. Müller, M. Christ-Crain, Both inflammatory and classical lipolytic pathways are involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced lipolysis in human adipocytes. Innate Immun. 18, 25–34 (2012)
J. Iglesias, J. Lamontagne, H. Erb, S. Gezzar, S. Zhao, E. Joly, V.L. Truong, K. Skorey, S. Crane, Murthy Madiraju SR, Prentki M. Simplified assays of lipolysis enzymes for drug discovery and specificity assessment of known inhibitors. J. Lipid Res. 57(1), 131–141 (2016)
G.G. Muccioli, G. Labar, D.M. Lambert, CAY10499, novel monoglyceride lipase inhibitor evidenced by an expeditious MGL assay. ChenBioChem 9(16), 2704–2710 (2008)
W.Z. Hassid, S. Abraham, Determination of glycogen with anthrone reagent, in Methods of enzymology III, ed. by S.P. Colowick, N.O. Kaplan (Academic Press, New York, 1957), pp. 35–36
C. Taghibiglou, A. Carpentier, S.C. Van Iderstine, B. Chen, D. Rudy, A. Aiton, G.F. Lewis, K. Adeli, Mechanisms of hepatic very low density lipoprotein overproduction in insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 8416–8425 (2000)
J. Busserolles, E. Gueux, E. Rock, C. Demigné, A. Mazur, Y. Rayssiguier, Oligofructose protects against the hypertriglyceridemic and pro-oxidative effects of a high fructose diet in rats. J. Nutr. 133, 1903–1908 (2003)
R. Ragheb, A.M. Medhat, G.M. Shanab, D.M. Seoudi, I.G. Fantus, Links between enhanced fatty acid flux, protein kinase C and NFkappaB activation, and apoB-lipoprotein production in the fructose-fed hamster model of insulin resistance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 370, 134–139 (2008)
I. Hininger-Favier, R. Benaraba, S. Coves, R.A. Anderson, A.M. Roussel, Green tea extract decreases oxidative stress and improves insulin sensitivity in an animal model of insulin resistance, the fructose-fed rat. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 28, 355–361 (2009)
I. Cornaciu, A. Boeszoermenyi, H. Lindermuth, H.M. Nagy, I.K. Cerk, C. Ebner, B. Salzburger, A. Gruber, M. Schweiger, R. Zechner, A. Lass, R. Zimmermann, M. Oberer, The minimal domain of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) ranges until leucine 254 and can be activated and inhibited by CGI-58 and G0S2, respectively. PLoS One 6(10), e26349 (2011)
M. Schweiger, R. Schreiber, G. Haemmerle, A. Lass, C. Fledelius, P. Jacobsen, H. Tornqvist, R. Zechner, R. Zimmermann, Adipose triglyceride lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase are the major enzymes in adipose tissue triacylglycerol catabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 40236–40241 (2006)
J.B. Young, L. Landsberg, Stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system during sucrose feeding. Nature 269, 615–617 (1977)
J.B. Young, J. Weiss, N. Boufath, Effects of dietary monosaccharides on sympathetic nervous system activity in adipose tissues of male rats. Diabetes 53, 1271–1278 (2004)
V.E. Chaves, D. Frasson, M.E. Martins-Santos, R.P. Boschini, M.A. Garófalo, W.T. Festuccia, I.C. Kettelhut, R.H. Migliorini, Glyceroneogenesis is reduced and glucose uptake is increased in adipose tissue from cafeteria diet-fed rats independently of tissue sympathetic innervation. J. Nutr. 136, 2475–2480 (2006)
M. Van Epps-Fung, J. Williford, A. Wells, R.W. Hardy, Fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in adipocytes. Endocrinology 138, 4338–4345 (1997)
C. Yu, Y. Chen, G.W. Cline, D. Zhang, H. Zong, Y. Wang, R. Bergeron, J.K. Kim, S.W. Cushman, G.J. Cooney, B. Atcheson, M.F. White, E.W. Kraegen, G.I. Shulman, Mechanism by which fatty acids inhibit insulin activation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1)-associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 50230–50236 (2002)
B. Maiztegui, M.I. Borelli, M.A. Raschia, H. Del Zotto, J.J. Gagliardino, Islet adaptive changes to fructose-induced insulin resistance: beta-cell mass, glucokinase, glucose metabolism, and insulin secretion. J. Endocrinol. 200, 139–149 (2009)
H.Y. Koo, M. Miyashita, B.H. Cho, M.T. Nakamura, Replacing dietary glucose with fructose increases ChREBP activity and SREBP-1 protein in rat liver nucleus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 390, 285–289 (2009)
L.M. Botion, M.N. Brito, N.A. Brito, S.R. Brito, I.C. Kettelhut, R.H. Migliorini, Glucose contribution to in vivo synthesis of glyceride-glycerol and fatty acids in rats adapted to a high-protein, carbohydrate-free diet. Metabolism 47, 1217–1221 (1998)
V.E. Chaves, D. Frasson, M.A. Garófalo, L.C. Navegantes, R.H. Migliorini, I.C. Kettelhut, Increased glyceride-glycerol synthesis in liver and brown adipose tissue of rat: in vivo contribution of glycolysis and glyceroneogenesis. Lipids 47, 773–780 (2012)
B.W. Huang, M.T. Chiang, H.T. Yao, W. Chiang, The effect of high-fat and high-fructose diets on glucose tolerance and plasma lipid and leptin levels in rats. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 6, 120–126 (2004)
A.H. Stark, B. Timar, Z. Madar, Adaptation of Sprague Dawley rats to long-term feeding of high fat or high fructose diets. Eur. J. Nutr. 39, 229–234 (2000)
Acknowledgments
We thank to the fellowship students of Undergraduate Research Program from Federal University of São João del-Rei, M.T.M. Lacerda and A.B. Bilheiro, for their help in determining the rate of the VLDL-TAG secretion and the liver glycogen concentration, respectively. This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (APQ-00299-12) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (471544/2012-4). A.H.R. received a fellowship from the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). C.C.L.M., E.G.M. and L.M.S.C. received a fellowship from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the development, analysis and drafting of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, A.H., Moreira, C.C.L., Mario, É.G. et al. Differential modulation of cytosolic lipases activities in liver and adipose tissue by high-carbohydrate diets. Endocrine 53, 423–432 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0886-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0886-9