Abstract
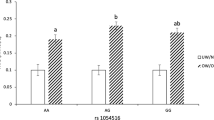
Polymorphisms near the MC4R gene may be related to an increased risk for obesity, but studies of variations in this gene and its relation to cardiometabolic profiles and food intake are scarce and controversial. The aim of this study is to evaluate the influence of the variants rs12970134 and rs17782313 near the MC4R gene in food intake, binge eating (BE) behavior, anthropometric parameters, body composition, metabolic profile, and cardiometabolic risk factors in obese children and adolescents. This is a cross-sectional study that included obese children and adolescents. We evaluated anthropometric, metabolic parameters and cardiometabolic risk factors, including hypertension, impaired fasting glucose, hypertriglyceridemia, and low HDL-cholesterol. BE was assessed through the BE scale, and a 24-h recall was used to evaluate total caloric intake and percentage of macronutrients and types of dietary fat. The MC4R variants rs12970134 and rs17782313 were genotyped using TaqMan assay. To assess the magnitude of risk, a logistic regression adjusted for Z-BMI, age, and gender was performed, adopting the significance level of 0.05. The study included 518 subjects (52.1 % girls, 12.7 ± 2.7 years old, Z-BMI = 3.24 ± 0.57). Carriers of the variant rs17782313 exhibit increased triglyceride levels (108 ± 48 vs. 119 ± 54, p = 0.034) and an increased risk of hypertriglyceridemia (OR 1.985, 95 % CI 1.288–3.057, p = 0.002). There was no association of the SNP rs12970134 with clinical, metabolic, or nutritional parameters. The variant rs12970134 and rs17782313 did not influence food intake or the presence of BE. The variant rs17782313 is associated with an increased risk of hypertriglyceridemia in obese children and adolescents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Schonfeld-Warden, C.H. Warden, Pediatric obesity. An overview of etiology and treatment. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 44(2), 339–361 (1997)
J. Rossi, N. Balthasar, D. Olson, M. Scott, E. Berglund, C.E. Lee et al., Melanocortin-4 receptors expressed by cholinergic neurons regulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.01.010
R.A. Adan, B. Tiesjema, J.J. Hillebrand, S.E. la Fleur, M.J. Kas, M. de Krom, The MC4 receptor and control of appetite. Br. J. Pharmacol. (2006). doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706929
M.M. Hagan, P.A. Rushing, S.C. Benoit, S.C. Woods, R.J. Seeley, Opioid receptor involvement in the effect of AgRP- (83–132) on food intake and food selection. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 280(3), R814–R821 (2001)
I.S. Farooqi, J.M. Keogh, G.S. Yeo, E.J. Lank, T. Cheetham, S. O’Rahilly, Clinical spectrum of obesity and mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor gene. N. Engl. J. Med. (2003). doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022050
R.J. Loos, C.M. Lindgren, S. Li, E. Wheeler, J.H. Zhao, I. Prokopenko et al., Common variants near MC4R are associated with fat mass, weight and risk of obesity. Nat. Genet. (2008). doi:10.1038/ng.140
J.C. Chambers, P. Elliott, D. Zabaneh, W. Zhang, Y. Li, P. Froguel et al., Common genetic variation near MC4R is associated with waist circumference and insulin resistance. Nat. Genet. (2008). doi:10.1038/ng.156
L. Qi, P. Kraft, D.J. Hunter, F.B. Hu, The common obesity variant near MC4R gene is associated with higher intakes of total energy and dietary fat, weight change and diabetes risk in women. Hum. Mol. Genet. (2008). doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn242
D.P. Zobel, C.H. Andreasen, N. Grarup, H. Eiberg, T.I. Sørensen, A. Sandbaek et al., Variants near MC4R are associated with obesity and influence obesity-related quantitative traits in a population of middle-aged people: studies of 14,940 Danes. Diabetes (2009). doi:10.2337/db08-0620
A. Acosta, M. Camilleri, A. Shin, P. Carlson, D. Burton, J. O’Neill et al., Association of melanocortin 4 receptor gene variation with satiation and gastric emptying in overweight and obese adults. Genes Nutr. (2014). doi:10.1007/s12263-014-0384-8
F. Stutzmann, S. Cauchi, E. Durand, C. Calvacanti-Proença, M. Pigeyre, A.L. Hartikainen et al., Common genetic variation near MC4R is associated with eating behaviour patterns in European populations. Int. J. Obes. (2009). doi:10.1038/ijo.2008.279
A.L. Hasselbalch, L. Angquist, L. Christiansen, B.L. Heitmann, K.O. Kyvik, T.I. Sørensen, A variant in the fat mass and obesity-associated gene (FTO) and variants near the melanocortin-4 receptor gene (MC4R) do not influence dietary intake. J. Nutr. (2010). doi:10.3945/jn.109.114439
S.R. Freitas, C.S. Lopes, J.C. Appolinario, W. Coutinho, The assessment of binge eating disorder in obese women: a comparison of the binge eating scale with the structured clinical interview for the DSM-IV. Eat. Behav. 7(3), 282–289 (2006)
D. Pastucha, V. Talafa, J. Malincikova, C. Cihalik, J. Hyjanek, D. Horakova et al., Obesity, hypertension and insulin resistance in childhood–a pilot study. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 154(1), 77–81 (2010)
X. Han, Y. Luo, X. Zhang, C. Lv, X. Sun, X. Zhou et al., Rs4074134 near BDNF gene is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Han population independently of body mass index. PLoS One (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056898
A. Mejía-Benítez, M. Klünder-Klünder, L. Yengo, D. Meyre, C. Aradillas, E. Cruz et al., Analysis of the contribution of FTO, NPC1, ENPP1, NEGR1, GNPDA2 and MC4R genes to obesity in Mexican children. BMC Med. Genet. (2013). doi:10.1186/1471-2350-14-21
J. Wang, H. Mei, W. Chen, Y. Jiang, W. Sun, F. Li et al., Study of eight GWAS-identified common variants for association with obesity-related indices in Chinese children at puberty. Int. J. Obes. (2012). doi:10.1038/ijo.2011.218
S.K. Vasan, T. Fall, V. Job, H.F. Gu, E. Ingelsson, K. Brismar et al., A common variant in the FTO locus is associated with waist-hip ratio in Indian adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. (2013). doi:10.1111/j.2047-6310.2013.00118.x
B. Xi, X. Zhao, Y. Shen, L. Wu, K. Hotta, D. Hou et al., Associations of obesity susceptibility loci with hypertension in Chinese children. Int. J. Obes. (2013). doi:10.1038/ijo.2013.37
F. Bauer, C.C. Elbers, R.A. Adan, R.J. Loos, N.C. Onland-Moret, D.E. Grobbee et al., Obesity genes identified in genome-wide association studies are associated with adiposity measures and potentially with nutrient-specific food preference. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. (2009). doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.27781
R. Branson, N. Potoczna, J.G. Kral, K.U. Lentes, M.R. Hoehe, F.F. Horber, Binge eating as a major phenotype of melanocortin 4 receptor gene mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. (2003). doi:10.1056/NEJMoa021971
F. Stutzmann, K. Tan, V. Vatin, C. Dina, B. Jouret, J. Tichet et al., Prevalence of melanocortin-4 receptor deficiency in Europeans and their age-dependent penetrance in multigenerational pedigrees. Diabetes (2008). doi:10.2337/db08-0153
S. Katsuura-Kamano, H. Uemura, K. Arisawa, M. Yamaguchi, N. Hamajima, K. Wakai et al., A polymorphism near MC4R gene (rs17782313) is associated with serum triglyceride levels in the general Japanese population: the J-MICC Study. Endocrine (2014). doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0306-y
R. Nogueiras, P. Wiedmer, D. Perez-Tilve, C. Veyrat-Durebex, J.M. Keogh, G.M. Sutton et al., The central melanocortin system directly controls peripheral lipid metabolism. J. Clin. Invest. (2007). doi:10.1172/JCI31743
S. Granell, S. Mohammad, R. Ramanagoudr-Bhojappa, G. Baldini, Obesity-linked variants of melanocortin-4 receptor are misfolded in the endoplasmic reticulum and can be rescued to the cell surface by a chemical chaperone. Mol. Endocrinol. (2010). doi:10.1210/me.2010-0071
G.H. Werstuck, S.R. Lentz, S. Dayal, G.S. Hossain, S.K. Sood, Y.Y. Shi et al., Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes dysregulation of the cholesterol and triglyceride biosynthetic pathways. J. Clin. Invest. (2001). doi:10.1172/JCI11596
H.L. Kammoun, H. Chabanon, I. Hainault, S. Luquet, C. Magnan, T. Koike et al., GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress-induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J. Clin. Invest. (2009). doi:10.1172/JCI37007
D.T. Rutkowski, J. Wu, S.H. Back, M.U. Callaghan, S.P. Ferris, J. Iqbal et al., UPR pathways combine to prevent hepatic steatosis caused by ER stress-mediated suppression of transcriptional master regulators. Dev. Cell (2008). doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.10.015
S.I. Kring, C. Holst, S. Toubro, A. Astrup, T. Hansen, O. Pedersen et al., Common variants near MC4R in relation to body fat, body fat distribution, metabolic traits and energy expenditure. Int. J. Obes. (2010). doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.215
L. Tao, Z. Zhang, Z. Chen, D. Zhou, W. Li, M. Kan et al., A Common variant near the melanocortin 4 receptor is associated with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol in the Chinese Han population. Mol. Biol. Rep. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11033-012-1476-4
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) Grants 2011/23340-6 and 2011/05320-8. There are not any competing financial interests in relation to the work.
Disclosure
The authors have nothing to disclose
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, A.E., de Melo, M.E., Fujiwara, C.T.H. et al. Associations between a common variant near the MC4R gene and serum triglyceride levels in an obese pediatric cohort. Endocrine 49, 653–658 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0616-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0616-8