Abstract
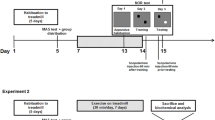
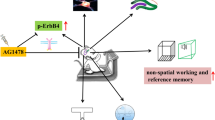
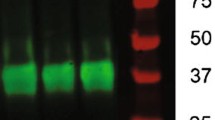
This study aimed to determine the effect of exercise training on cognitive functioning, and hippocampal PGC-1α, FNDC5, BDNF, and other cognition-related gene and protein expression in rats. Rats were divided into 4 groups based on age [3 months (young) vs. 20 months (aged)] and training status (control vs. exercise training). The rats that exercised voluntarily performed exercise training for 90 days, and then all the rats underwent several methods of behavioral assessment. Locomotor activity and spatial memory were lower but anxiety scores were higher in the aged control rats, than in the young control, young exercised, and aged exercised rats (P < 0.05). Hippocampal BDNF, FNDC5, PGC-1α, mTOR, ARC, cF-OS, ERK, SIRT, and FOXO expressions were lower, but NF-κB expressions were higher in the aged control rats than in the young control, young exercised, and aged exercised rats (P < 0.05). Similarly, hippocampal BDNF and FNDC5 protein expression were lower in the aged control rats than in the young control, young exercised, and aged exercised rats (P < 0.05). These findings show that aging-induced cognitive dysfunction is associated with a decrease in hippocampal expression of PGC-1α, FNDC5, and BDNF, and that exercise training might improve cognitive functioning via activation of these genes and proteins.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar, A. S. Jr., Castro, A. A., Moreira, E. L., Glaser, V., Santos, A. R., Tasca, C. I., et al. (2011). Short bouts of mild-intensity physical exercise improve spatial learning and memory in aging rats: Involvement of hippocampal plasticity via AKT, CREB and BDNF signaling. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, 132(11–12), 560–567.
Aid, T., Kazantseva, A., Piirsoo, M., Palm, K., & Timmusk, T. (2007). Mouse and rat BDNF gene structure and expression revisited. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 85(3), 525–535.
Belviranli, M., Atalik, K. E., Okudan, N., & Gökbel, H. (2012). Age and sex affect spatial and emotional behaviors in rats: The role of repeated elevated plus maze test. Neuroscience, 227, 1–9.
Belviranli, M., Okudan, N., Kabak, B., Erdoğan, M., & Karanfilci, M. (2016). The relationship between brain-derived neurotrophic factor, irisin and cognitive skills of endurance athletes. The Physician and Sportsmedicine, 44(3), 290–296.
Belviranlı, M., & Okudan, N. (2015). The effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on cognitive functions in aged female rats: The role of oxidative stress and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Behavioural Brain Research, 278, 453–461.
Belviranlı, M., Okudan, N., Atalık, K. E., & Öz, M. (2013). Curcumin improves spatial memory and decreases oxidative damage in aged female rats. Biogerontology, 14(2), 187–196.
Bergado, J. A., Almaguer, W., Rojas, Y., Capdevila, V., & Frey, J. U. (2011). Spatial and emotional memory in aged rats: A behavioral-statistical analysis. Neuroscience, 172, 256–269.
Bonni, A., Brunet, A., West, A. E., Datta, S. R., Takasu, M. A., & Greenberg, M. E. (1999). Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science, 286(5443), 1358–1362.
Boström, P., Wu, J., Jedrychowski, M. P., Korde, A., Ye, L., Lo, J. C., et al. (2012). A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature, 481(7382), 463–468.
Boulle, F., van den Hove, D. L., Jakob, S. B., Rutten, B. P., Hamon, M., van Os, J., et al. (2012). Epigenetic regulation of the BDNF gene: Implications for psychiatric disorders. Molecular Psychiatry, 17(6), 584–596.
Braidy, N., Poljak, A., Grant, R., Jayasena, T., Mansour, H., Chan-Ling, T., et al. (2015). Differential expression of sirtuins in the aging rat brain. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 9, 167.
Bruel-Jungerman, E., Veyrac, A., Dufour, F., Horwood, J., Laroche, S., & Davis, S. (2009). Inhibition of PI3K-Akt signaling blocks exercise-mediated enhancement of adult neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. PLoS ONE, 4(11), e7901.
Burghardt, P. R., Fulk, L. J., Hand, G. A., & Wilson, M. A. (2004). The effects of chronic treadmill and wheel running on behavior in rats. Brain Research, 1019(1–2), 84–96.
Chen, M. J., & Russo-Neustadt, A. A. (2005). Exercise activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Molecular Brain Research, 135(1–2), 181–193.
Cooper, C., Moon, H. Y., & van Praag, H. (2017). On the run for hippocampal plasticity. In Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine.
Cotman, C. W., Berchtold, N. C., & Christie, L. A. (2007). Exercise builds brain health: Key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends in Neurosciences, 30(9), 464–472.
D’Hooge, R., & De Deyn, P. P. (2001). Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Research Reviews, 36(1), 60–90.
Duzel, E., van Praag, H., & Sendtner, M. (2016). Can physical exercise in old age improve memory and hippocampal function? Brain, 139(Pt 3), 662–673.
Eldomiaty, M. A., Almasry, S. M., Desouky, M. K., & Algaidi, S. A. (2017). Voluntary running improves depressive behaviours and the structure of the hippocampus in rats: A possible impact of myokines. Brain Research, 1657, 29–42.
Erickson, K. I., Prakash, R. S., Voss, M. W., Chaddock, L., Heo, S., McLaren, M., et al. (2010). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with age-related decline in hippocampal volume. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(15), 5368–5375.
Erickson, K. I., Prakash, R. S., Voss, M. W., Chaddock, L., Hu, L., Morris, K. S., et al. (2009). Aerobic fitness is associated with hippocampal volume in elderly humans. Hippocampus, 19(10), 1030–1039.
Fan, X., Wheatley, E. G., & Villeda, S. A. (2017). Mechanisms of hippocampal aging and the potential for rejuvenation. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 40, 251–272.
Farmer, J., Zhao, X., van Praag, H., Wodtke, K., Gage, F. H., & Christie, B. R. (2004). Effects of voluntary exercise on synaptic plasticity and gene expression in the dentate gyrus of adult male Sprague-Dawley rats in vivo. Neuroscience, 124(1), 71–79.
Gürtler, A., Kunz, N., Gomolka, M., Hornhardt, S., Friedl, A. A., McDonald, K., et al. (2013). Stain-Free technology as a normalization tool in Western blot analysis. Analytical Biochemistry, 433(2), 105–111.
Haider, S., Saleem, S., Perveen, T., Tabassum, S., Batool, Z., Sadir, S., et al. (2014). Age-related learning and memory deficits in rats: Role of altered brain neurotransmitters, acetylcholinesterase activity and changes in antioxidant defense system. Age, 36(3), 9653.
Hashemi, M. S., Ghaedi, K., Salamian, A., Karbalaie, K., Emadi-Baygi, M., Tanhaei, S., et al. (2013). Fndc5 knockdown significantly decreased neural differentiation rate of mouse embryonic stem cells. Neuroscience, 231, 296–304.
Hovens, I. B., Schoemaker, R. G., van der Zee, E. A., Heineman, E., Nyakas, C., & van Leeuwen, B. L. (2013). Surgery-induced behavioral changes in aged rats. Experimental Gerontology, 48(11), 1204–1211.
Jenwitheesuk, A., Boontem, P., Wongchitrat, P., Tocharus, J., Mukda, S., & Govitrapong, P. (2017). Melatonin regulates the aging mouse hippocampal homeostasis via the sirtuin1-FOXO1 pathway. EXCLI Journal, 16, 340–353.
Jodeiri Farshbaf, M., Ghaedi, K., Megraw, T. L., Curtiss, J., Shirani Faradonbeh, M., Vaziri, P., et al. (2016). Does PGC1α/FNDC5/BDNF elicit the beneficial effects of exercise on neurodegenerative disorders? Neuromolecular Medicine, 18(1), 1–15.
Kohman, R. A., Rodriguez-Zas, S. L., Southey, B. R., Kelley, K. W., Dantzer, R., & Rhodes, J. S. (2011). Voluntary wheel running reverses age-induced changes in hippocampal gene expression. PLoS ONE, 6(8), e22654.
Koscak Tivadar, B. (2017). Physical activity improves cognition: Possible explanations. Biogerontology, 18(4), 477–483.
Küçük, A., Gölgeli, A., Saraymen, R., & Koç, N. (2008). Effects of age and anxiety on learning and memory. Behavioural Brain Research, 195(1), 147–152.
Leal, G., Bramham, C. R., & Duarte, C. B. (2017). BDNF and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Vitamins and Hormones, 104, 153–195.
Li, D. J., Li, Y. H., Yuan, H. B., Qu, L. F., & Wang, P. (2017). The novel exercise-induced hormone irisin protects against neuronal injury via activation of the Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways and contributes to the neuroprotection of physical exercise in cerebral ischemia. Metabolism, 68, 31–42.
Liu, P., Zou, D., Yi, L., Chen, M., Gao, Y., Zhou, R., et al. (2015). Quercetin ameliorates hypobaric hypoxia-induced memory impairment through mitochondrial and neuron function adaptation via the PGC-1α pathway. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 33(2), 143–157.
Lloyd, B. A., Hake, H. S., Ishiwata, T., Farmer, C. E., Loetz, E. C., Fleshner, M., et al. (2017). Exercise increases mTOR signaling in brain regions involved in cognition and emotional behavior. Behavioural Brain Research, 323, 56–67.
Lovatel, G. A., Elsner, V. R., Bertoldi, K., Vanzella, C., Moysés Fdos, S., Vizuete, A., et al. (2013). Treadmill exercise induces age-related changes in aversive memory, neuroinflammatory and epigenetic processes in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 101, 94–102.
Luellen, B. A., Bianco, L. E., Schneider, L. M., & Andrews, A. M. (2007). Reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with a loss of serotonergic innervation in the hippocampus of aging mice. Genes, Brain and Behavior, 6(5), 482–490.
Marosi, K., Bori, Z., Hart, N., Sárga, L., Koltai, E., Radák, Z., et al. (2012). Long-term exercise treatment reduces oxidative stress in the hippocampus of aging rats. Neuroscience, 226, 21–28.
Marosi, K., & Mattson, M. P. (2014). BDNF mediates adaptive brain and body responses to energetic challenges. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, 25(2), 89–98.
Mattson, M. P. (2012). Evolutionary aspects of human exercise—Born to run purposefully. Ageing Research Reviews, 11(3), 347–352.
Miyawaki, C. E., Bouldin, E. D., Kumar, G. S., & McGuire, L. C. (2017). Associations between physical activity and cognitive functioning among middle-aged and older adults. The Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging, 21(6), 637–647.
Okudan, N., & Belviranlı, M. (2017). Long-term voluntary exercise prevents post-weaning social isolation-induced cognitive impairment in rats. Neuroscience, 360, 1–8.
Pardon, M. C., Pérez-Diaz, F., Joubert, C., & Cohen-Salmon, C. (2000). Age-dependent effects of a chronic ultramild stress procedure on open-field behaviour in B6D2F1 female mice. Physiology & Behavior, 70(1–2), 7–13.
Peters, M., Bletsch, M., Stanley, J., Wheeler, D., Scott, R., & Tully, T. (2014). The PDE4 inhibitor HT-0712 improves hippocampus-dependent memory in aged mice. Neuropsychopharmacology, 39(13), 2938–2948.
Pietrelli, A., Lopez-Costa, J., Goñi, R., Brusco, A., & Basso, N. (2012). Aerobic exercise prevents age-dependent cognitive decline and reduces anxiety-related behaviors in middle-aged and old rats. Neuroscience, 202, 252–266.
Qiu, J., Dunbar, D. R., Noble, J., Cairns, C., Carter, R., Kelly, V., et al. (2016). Decreased Npas4 and Arc mRNA Levels in the hippocampus of aged memory-impaired wild-type but not memory preserved 11β-HSD1 deficient mice. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 28(1).
Rattan, S. I. (2012). Biogerontology: From here to where? The Lord Cohen Medal Lecture-2011. Biogerontology, 13, 83–91.
Rodgers, R. J., & Dalvi, A. (1997). Anxiety, defence and the elevated plus-maze. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 21(6), 801–810.
Salehpour, M., Khodagholi, F., Zeinaddini Meymand, A., Nourshahi, M., & Ashabi, G. (2017). Exercise training with concomitant nitric oxide synthase inhibition improved anxiogenic behavior, spatial cognition, and BDNF/P70S6 kinase activation in 20-month-old rats. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 30, 1–9.
Schmittgen, T. D., & Livak, K. J. (2008). Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nature Protocols, 3(6), 1101–1108.
Steiner, J. L., Murphy, E. A., McClellan, J. L., Carmichael, M. D., & Davis, J. M. (2011). Exercise training increases mitochondrial biogenesis in the brain. Journal of Applied Physiology, 111(4), 1066–1071.
Stranahan, A. M., & Mattson, M. P. (2012). Metabolic reserve as a determinant of cognitive aging. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 30(Suppl 2), S5–S13.
Teufel, A., Malik, N., Mukhopadhyay, M., & Westphal, H. (2002). Frcp1 and Frcp2, two novel fibronectin type III repeat containing genes. Gene, 297(1–2), 79–83.
Torma, F., Bori, Z., Koltai, E., Felszeghy, K., Vacz, G., Koch, L., et al. (2014). Eating habits modulate short term memory and epigenetical regulation of brain derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampus of low- and high running capacity rats. Brain Research Bulletin, 107, 54–60.
Torras-Garcia, M., Costa-Miserachs, D., Coll-Andreu, M., & Portell-Cortés, I. (2005). Decreased anxiety levels related to aging. Experimental Brain Research, 164(2), 177–184.
van Praag, H., Shubert, T., Zhao, C., & Gage, F. H. (2005). Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(38), 8680–8685.
Vanzella, C., Neves, J. D., Vizuete, A. F., Aristimunha, D., Kolling, J., Longoni, A., et al. (2017). Treadmill running prevents age-related memory deficit and alters neurotrophic factors and oxidative damage in the hippocampus of Wistar rats. Behavioural Brain Research, 334, 78–85.
Vivar, C., Potter, M. C., & van Praag, H. (2013). All about running: Synaptic plasticity, growth factors and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences, 15, 189–210.
Wang, S. J., Zhao, X. H., Chen, W., Bo, N., Wang, X. J., Chi, Z. F., et al. (2015). Sirtuin 1 activation enhances the PGC-1α/mitochondrial antioxidant system pathway in status epilepticus. Molecular Medicine Reports, 11(1), 521–526.
Wrann, C. D. (2015). FNDC5/irisin—Their role in the nervous system and as a mediator for beneficial effects of exercise on the brain. Brain Plasticity, 1(1), 55–61.
Wrann, C. D., White, J. P., Salogiannnis, J., Laznik-Bogoslavski, D., Wu, J., Ma, D., et al. (2013). Exercise induces hippocampal BDNF through a PGC-1α/FNDC5 pathway. Cell Metabolism, 18(5), 649–659.
Wu, H., Zhao, J., Chen, M., Wang, H., Yao, Q., Fan, J., et al. (2017). The anti-aging effect of erythropoietin via the ERK/Nrf2-ARE pathway in aging rats. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 61(3), 449–458.
Xu, B. (2013). BDNF (I)rising from exercise. Cell Metabolism, 18(5), 612–614.
Yan, B. C., Jiang, D., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhu, X., Xu, P., et al. (2018…). Both decreased Akt expression and mTOR phosphorylation are related to decreased neuronal differentiation in the hippocampal alveus of aged mice. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research, 30(7), 737–743.
Zhao, H., Alam, A., San, C. Y., Eguchi, S., Chen, Q., Lian, Q., et al. (2017). Molecular mechanisms of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuro-protection: Recent developments. Brain Research, 1665, 1–21.
Zigmond, M. J., & Smeyne, R. J. (2014). Exercise: Is it a neuroprotective and if so, how does it work? Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 20(Suppl 1), S123–S127.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Selçuk University Scientific Research and Project Committee (project number: 15401171). The authors would like to thank Scott Evans for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest—financial or otherwise—related to the material presented herein.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belviranlı, M., Okudan, N. Exercise Training Protects Against Aging-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction via Activation of the Hippocampal PGC-1α/FNDC5/BDNF Pathway. Neuromol Med 20, 386–400 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-018-8500-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-018-8500-3